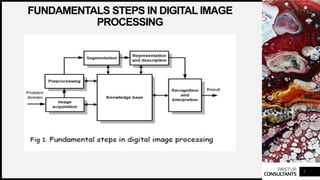
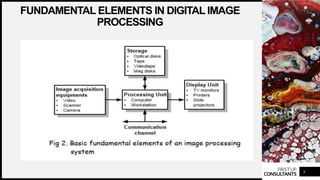
The document discusses the fundamentals of digital image processing. It covers applications of image processing like improving pictorial information and machine perception. An image is defined as a 2D light intensity function where brightness values are assigned to spatial coordinates. For computer processing, an image needs to be digitized by sampling spatial coordinates and quantizing amplitude. The fundamental steps of image processing are acquisition, pre-processing, segmentation, representation, description, recognition, and interpretation. Digital image processing systems have fundamental elements like input, output, memory, processing units and programs.