A diode is a two-terminal semiconductor device that allows current to flow in only one direction, typically forming a p-n junction. When forward-biased, it requires a small voltage (approx. 0.7V for silicon) to start conducting, while in reverse-bias, it permits a minimal leakage current until breakdown voltage is reached. Diodes are widely used in applications such as rectification, signal modulation, and voltage regulation.






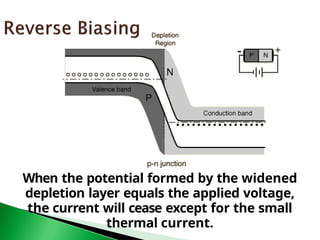







![Workin
g
🞂 A P-N junction diode is one-way device
offering low resistance when forward-biased
[Fig. (a)] and behaving almost as an insulator
when reverse-biased [Fig. (b)].
🞂 Hence, such diodes are mostly used as
rectifiers i.e. for converting alternating current
into direct current.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diodes-250210080309-6acb78db/85/Diodesusesofdiodesandfunctionalityapolication-pptx-15-320.jpg)



































