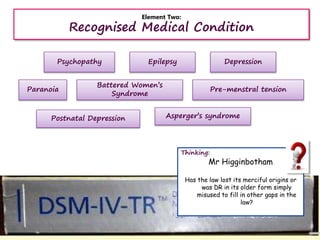
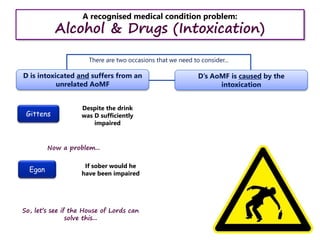
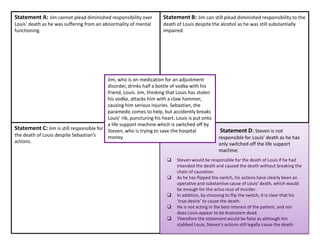
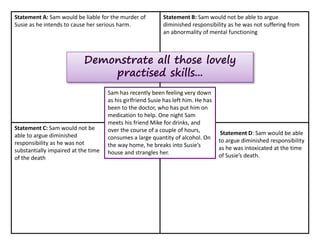
The document provides information and discussion questions about the defense of diminished responsibility in English criminal law. There are four key elements to the defense that must be proven: 1) abnormality of mental functioning, 2) recognized medical condition causing the abnormality, 3) substantial impairment, and 4) the abnormality must provide an explanation for the killing. The document examines cases that have helped define these elements and discusses debates around topics like the burden of proof, the role of intoxication, and proposed reforms to the defense. Students are prompted to consider application of the law to hypothetical scenarios and to critically analyze statements related to diminished responsibility.