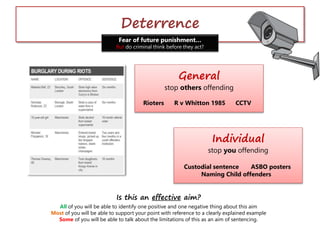
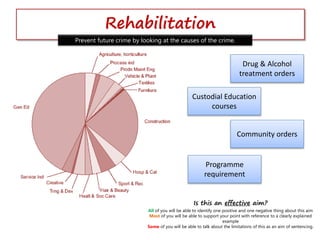
The document discusses the different aims of sentencing contained in the Criminal Justice Act 2003 and additional factors courts must consider when determining a sentence. It provides examples of different types of sentences that could achieve each aim and has students evaluate the effectiveness of each sentencing aim through group activities and case studies. The document is intended to educate students on the complexities of sentencing and how courts determine an appropriate punishment.





![Denunciation
“ Punishment is the is the way in which society expresses its
denunciation of what D is doing.”
Releasing the names of
child offenders
Megan’s Law
[Sarah’s Law]
Vests for community
payback
Is this an effective aim?
All of you will be able to identify one positive and one negative
thing about this aim
Most of you will be able to support your point with reference
to a clearly explained example
Some of you will be able to talk about the limitations of this as
an aim of sentencing.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theories2013-141231104918-conversion-gate01/85/Aims-and-Factors-of-Sentencing-7-320.jpg)






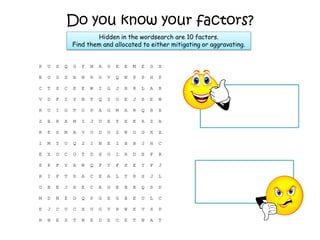





![Describe the aims and factors taken into account when
sentencing an offender. [18]
What can you tell me about how to answer this
question?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theories2013-141231104918-conversion-gate01/85/Aims-and-Factors-of-Sentencing-22-320.jpg)
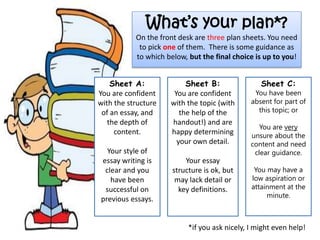
![Describe the aims and factors taken into account when
sentencing an offender. [18]
Task:
Use your notes and
understanding to complete
your essay plan.
Need more of a challenge?
Take a look at the BBC article on new offences. Could you
incorporate any recent developments to develop the detail in your
response?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theories2013-141231104918-conversion-gate01/85/Aims-and-Factors-of-Sentencing-24-320.jpg)




![Creating a problem answer.
Advise your defendant as to the factors and aims which would be
taken into account in sentencing them [12]
We are looking at least
5 applied points being
used.
Aim to include at least
three contradicted
points.
Use the defendant’s
name!
Conclude.
As Mavis is a single mother, this may work as a mitigating factor as if
she were sent to prison the children would be put into care
However, she is also a drug dealer which would act as a aggravating
factor as she is much more likely to reoffend.
In addition, as she is a drug dealer she is unlikely to have another
income and so be more likely to commit a further offence, so the
court would want to consider rehabilitation in her sentence, to try
and provide an alternative. However, Arthur is likely to want some
compensation for the loss, so the court may also consider
reparation as a theory, and she could pay him compensation as part
of the sentence.
As she has stolen his wallet, the harm is not likely to be high and this
may work as mitigating factor, and reduce her sentence accordingly.
Overall, it would seem that the most important aim in sentencing
Mavis is rehabilitation to enable her to keep her family and stop
being a drug dealer.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theories2013-141231104918-conversion-gate01/85/Aims-and-Factors-of-Sentencing-29-320.jpg)