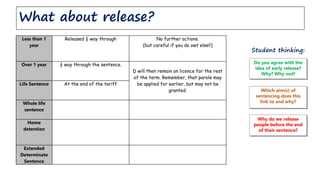
The document discusses factors considered when sentencing offenders. It describes four levels of understanding from limited to well-developed knowledge. The higher levels expect candidates to cite relevant statutes and case law. Candidates are asked to discuss which sentences are most appropriate for deterring offending where deterrence is the aim of sentencing. Victim impact meetings are suggested to deter future harm, but may not work if the offender does not want change.
![What’s left?
Answering the Question of course!
End
20 minutes.
Remember what you want to improve… and
demonstrate your brilliance!
Describe the aims and factors taken into account when
sentencing an offender. [18]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adultsent2013-141231104426-conversion-gate02/75/Adult-Sentencing-1-2048.jpg)

![Discussing the pesky law…
(b)* Discuss which sentences are most appropriate where the aim of sentencing is to deter offending [12]
Point Because However Because
Victim impact
meetings,
especially for
youth offenders
It can bring home the consequences
and get them to see the V as a
human being and appreciate the
harm they have caused, especially in
a property offence, deterring them
from harming others in the future.
D has to want to
meet and make a
change
Otherwise it is just a tick box
exercise, as with young people on
an ISSP, and it will have no
impact as they are not sorry, and
so will not stop offending.
Conclusion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adultsent2013-141231104426-conversion-gate02/85/Adult-Sentencing-3-320.jpg)