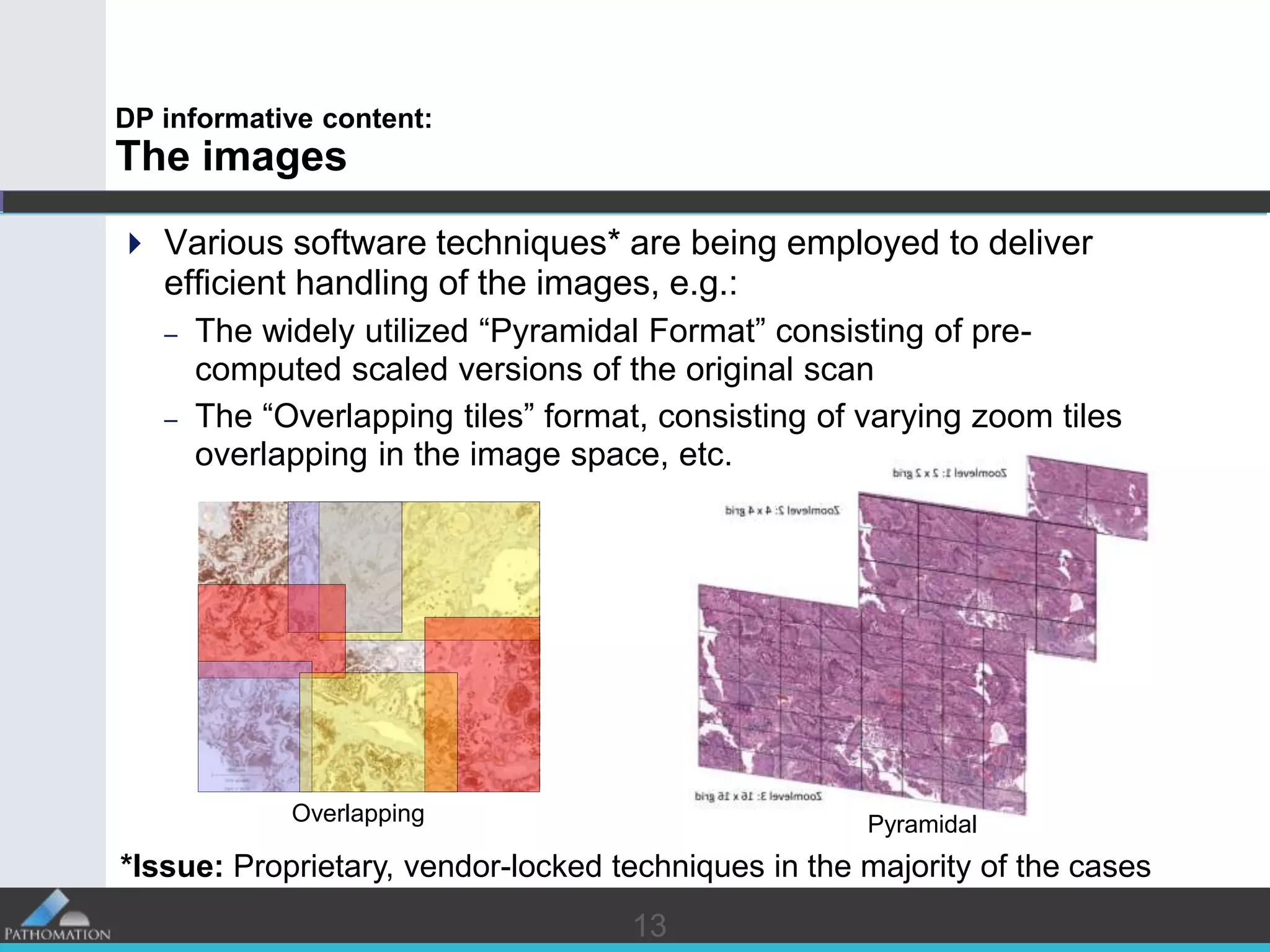
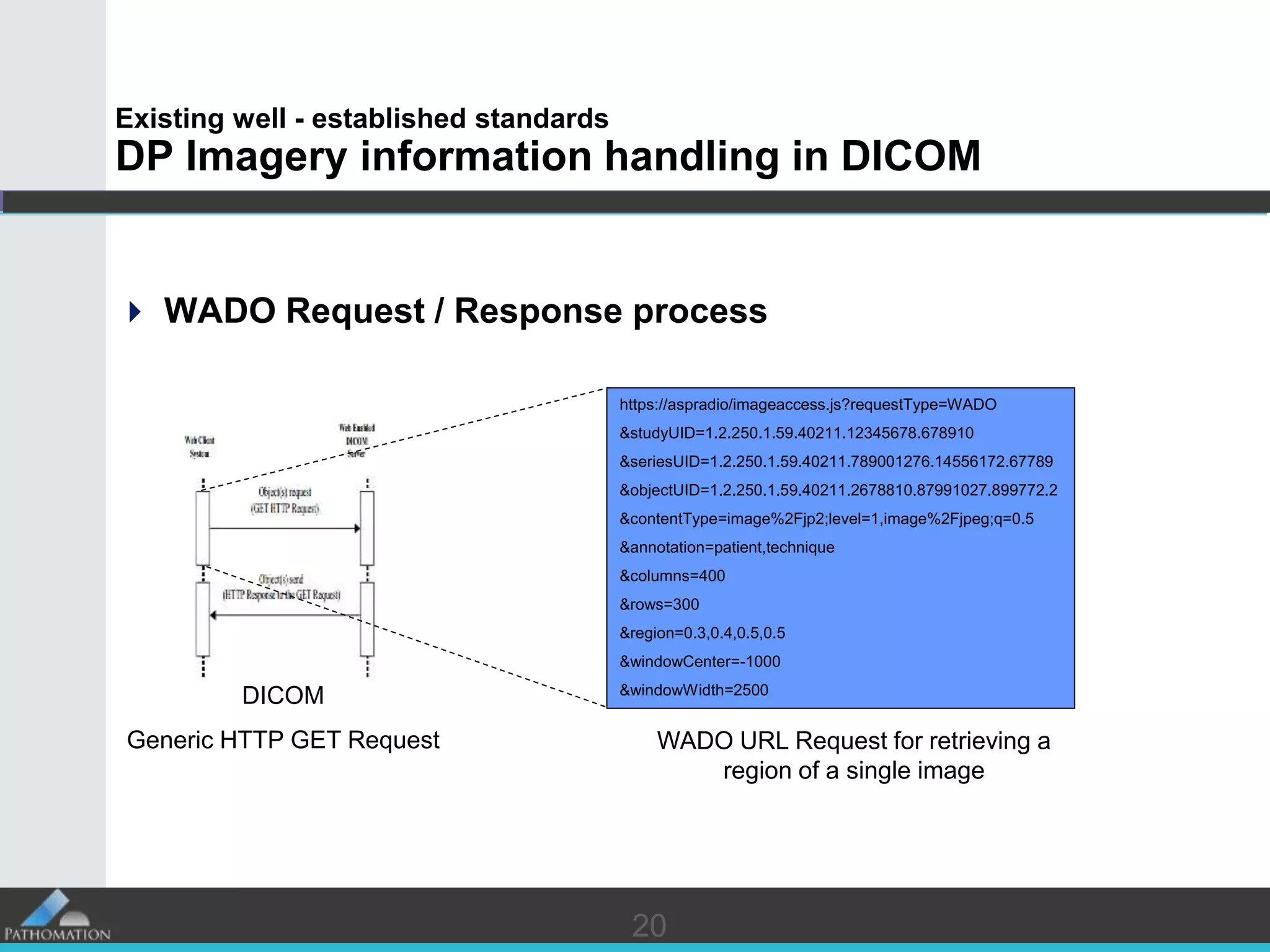
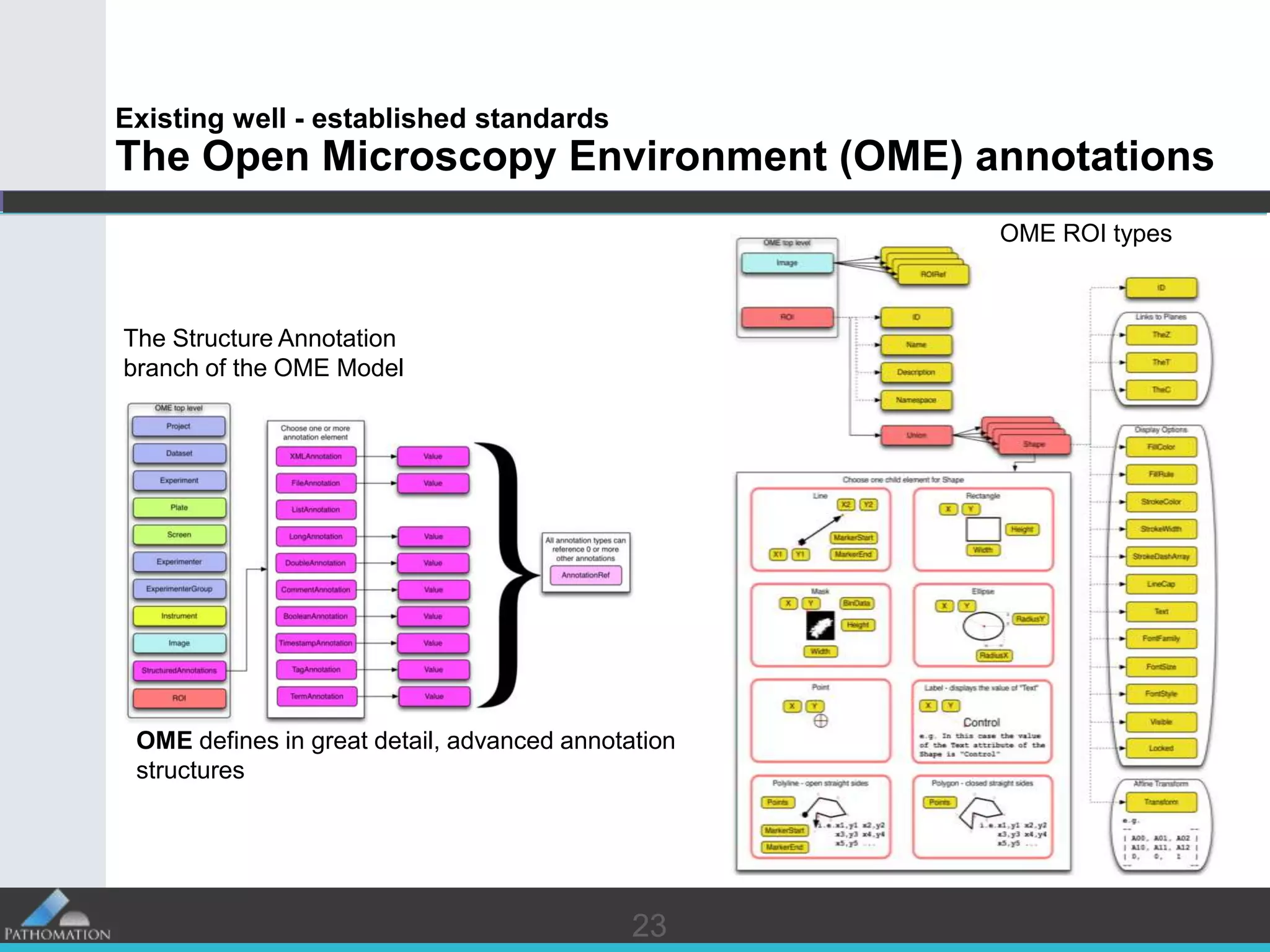
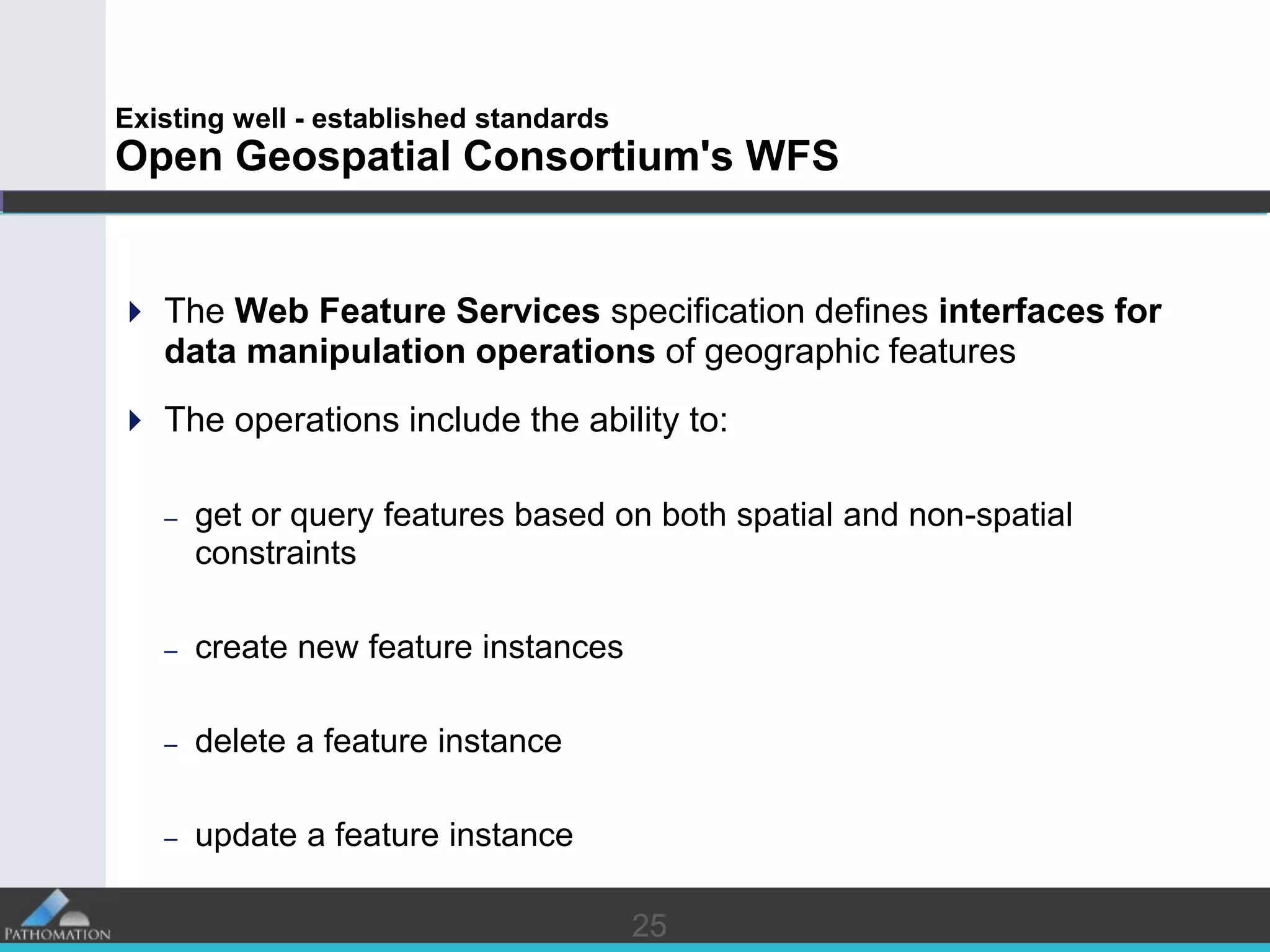
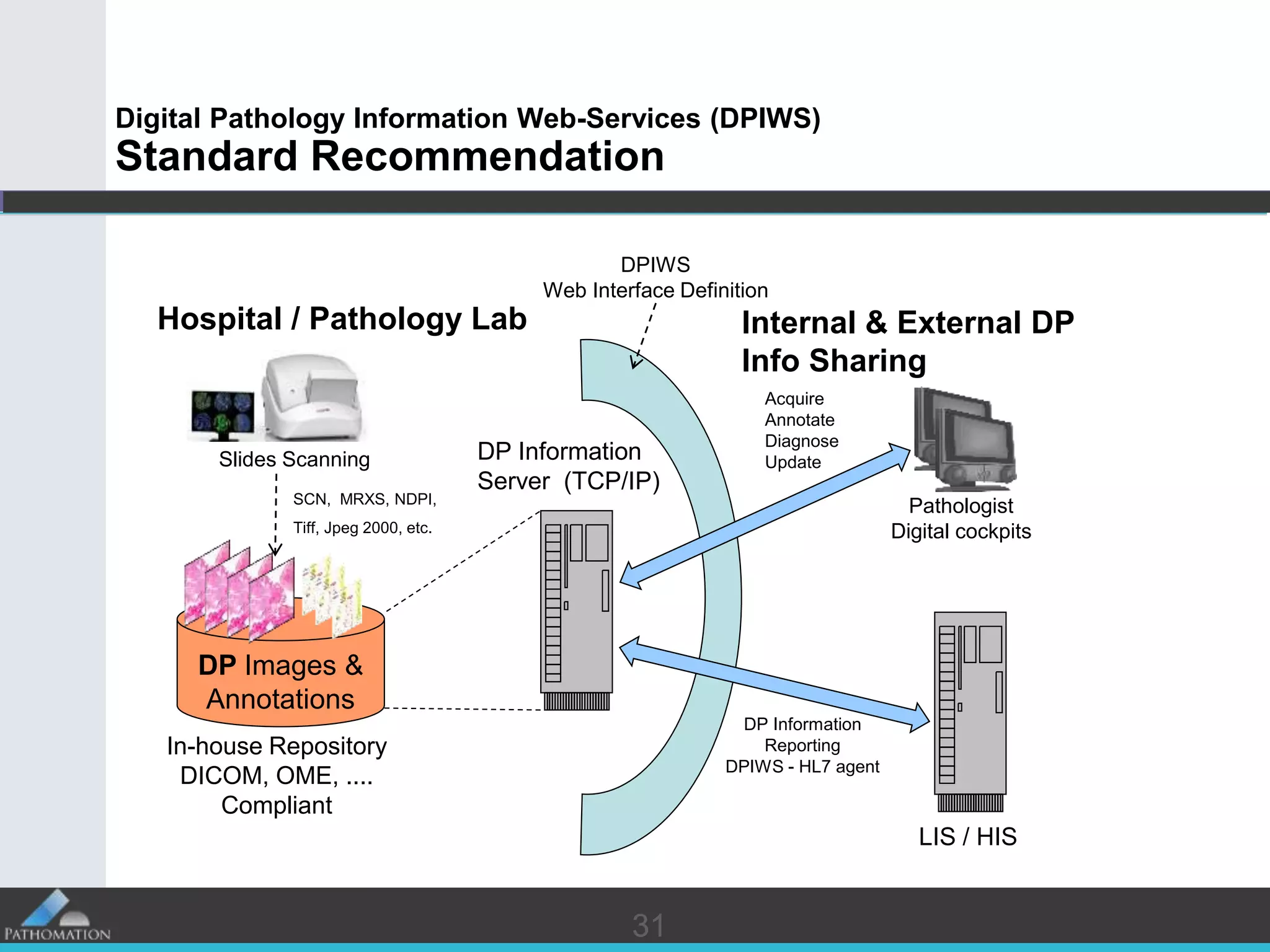
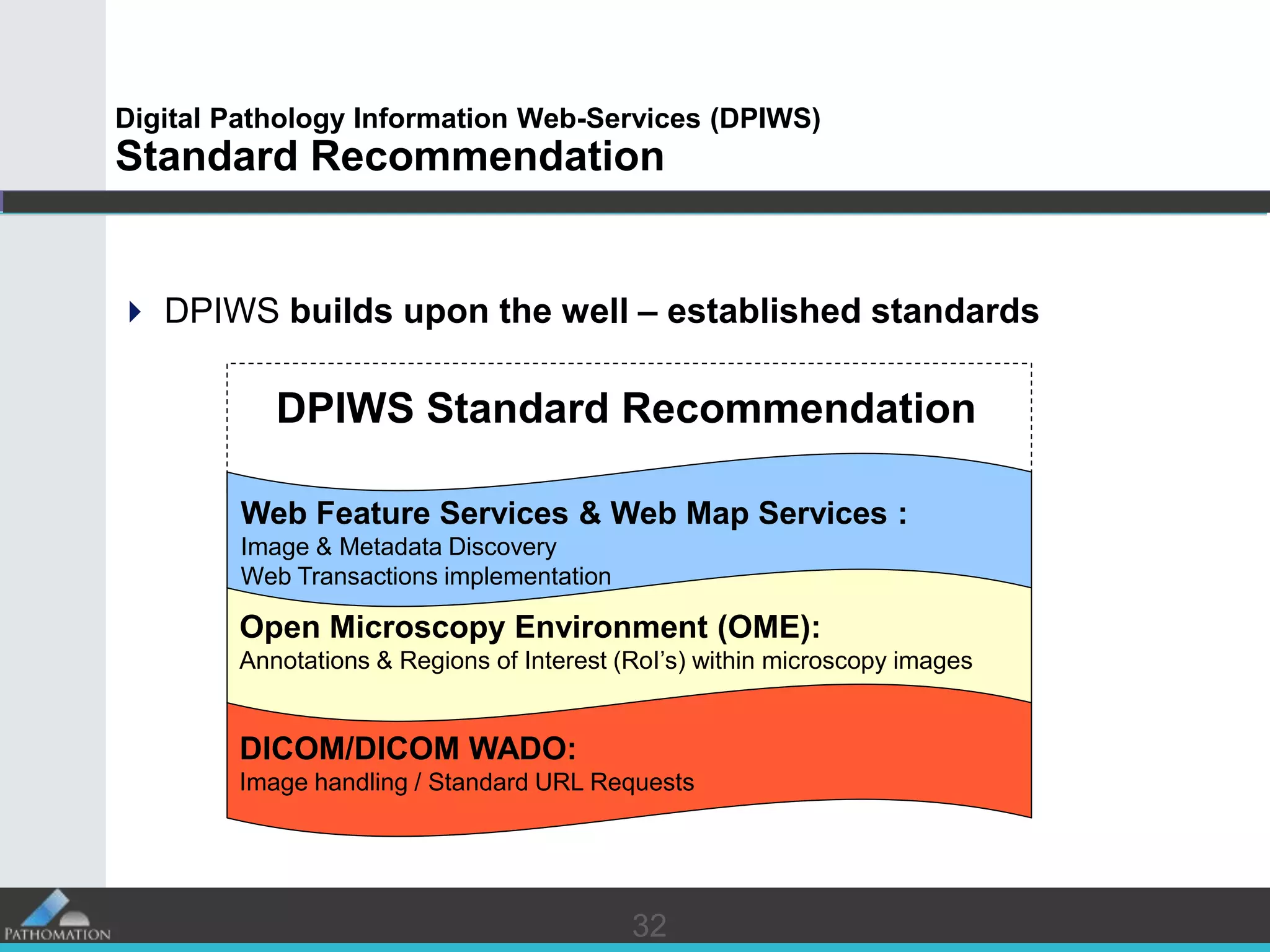
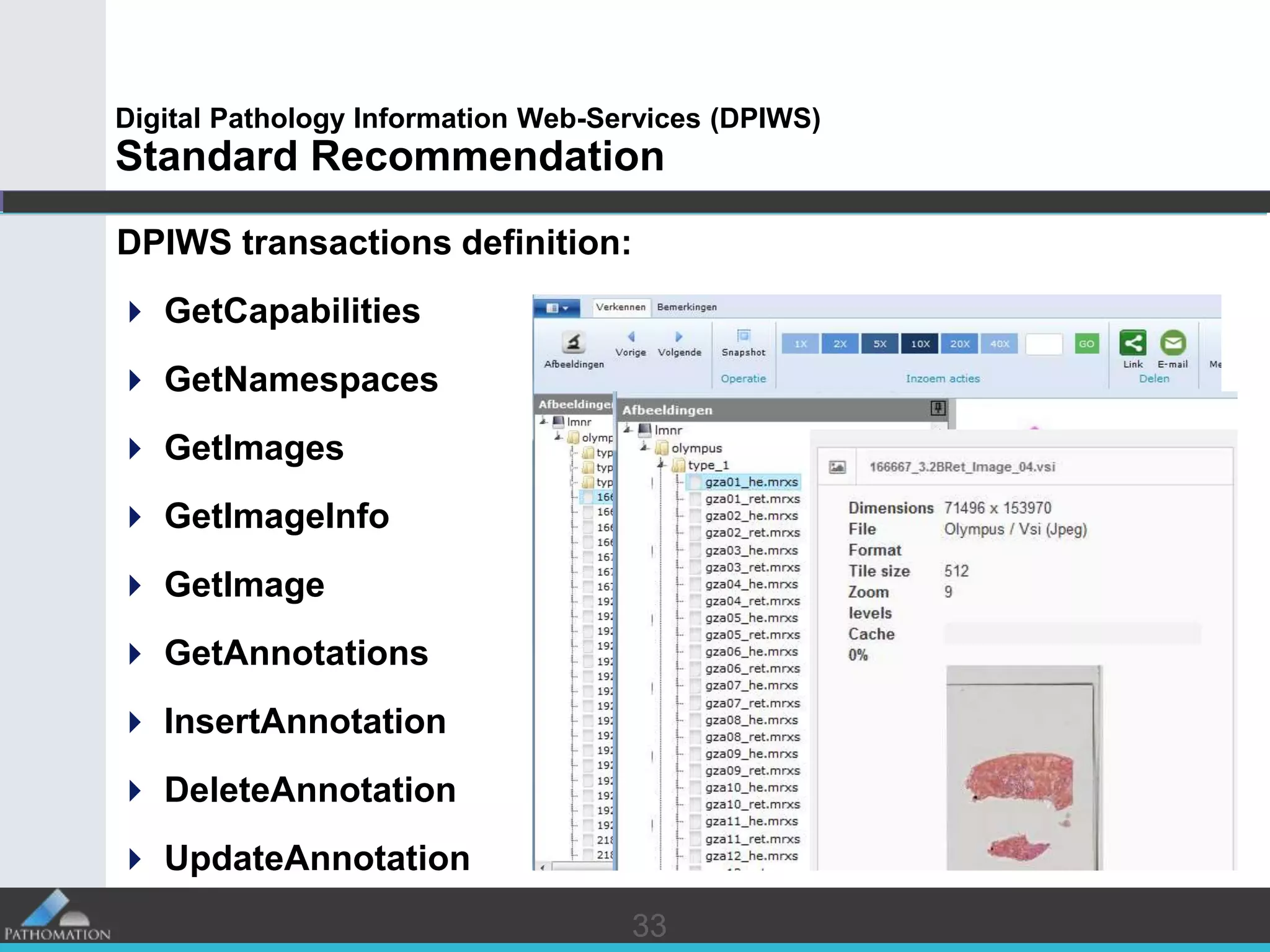
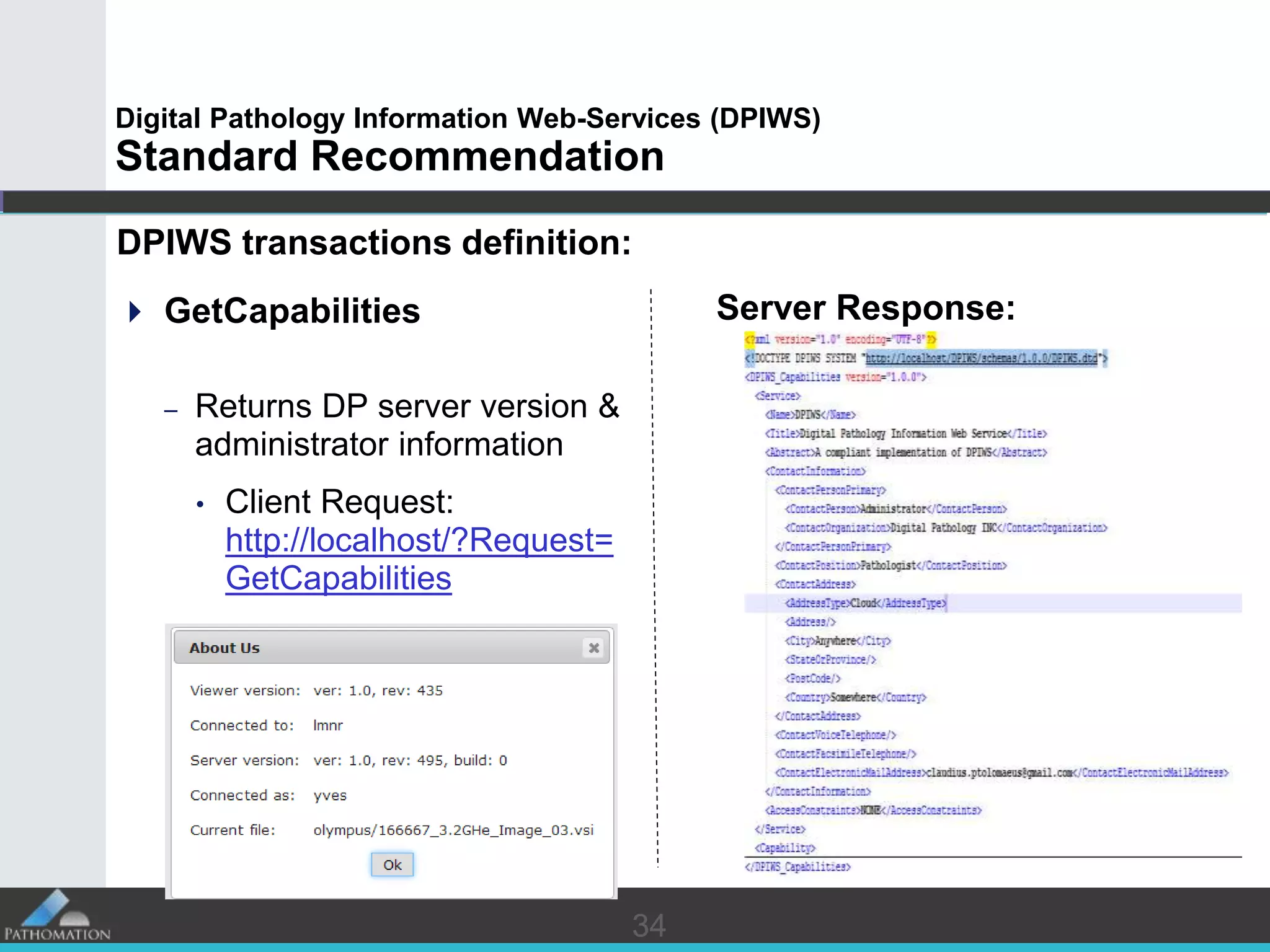
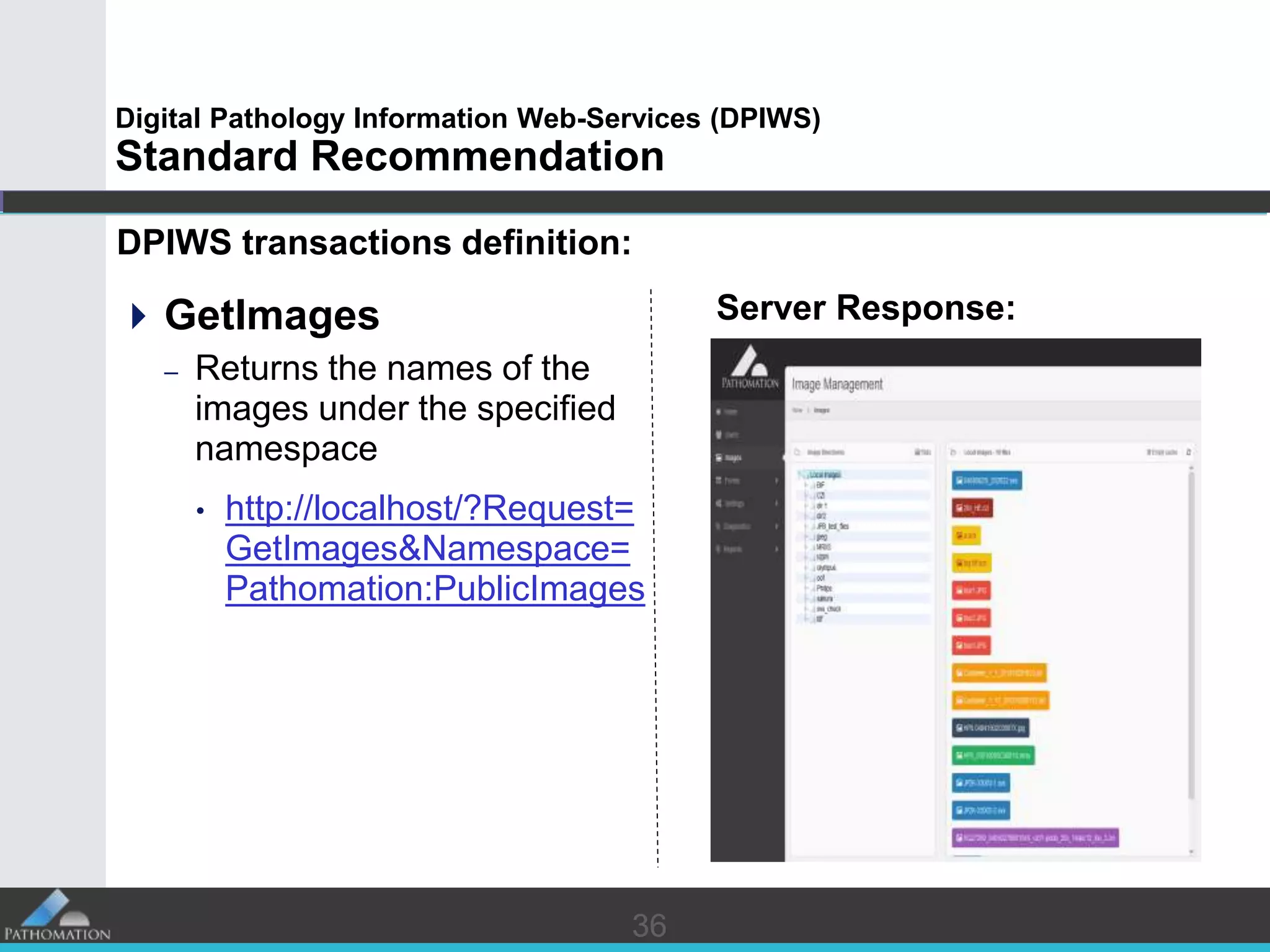
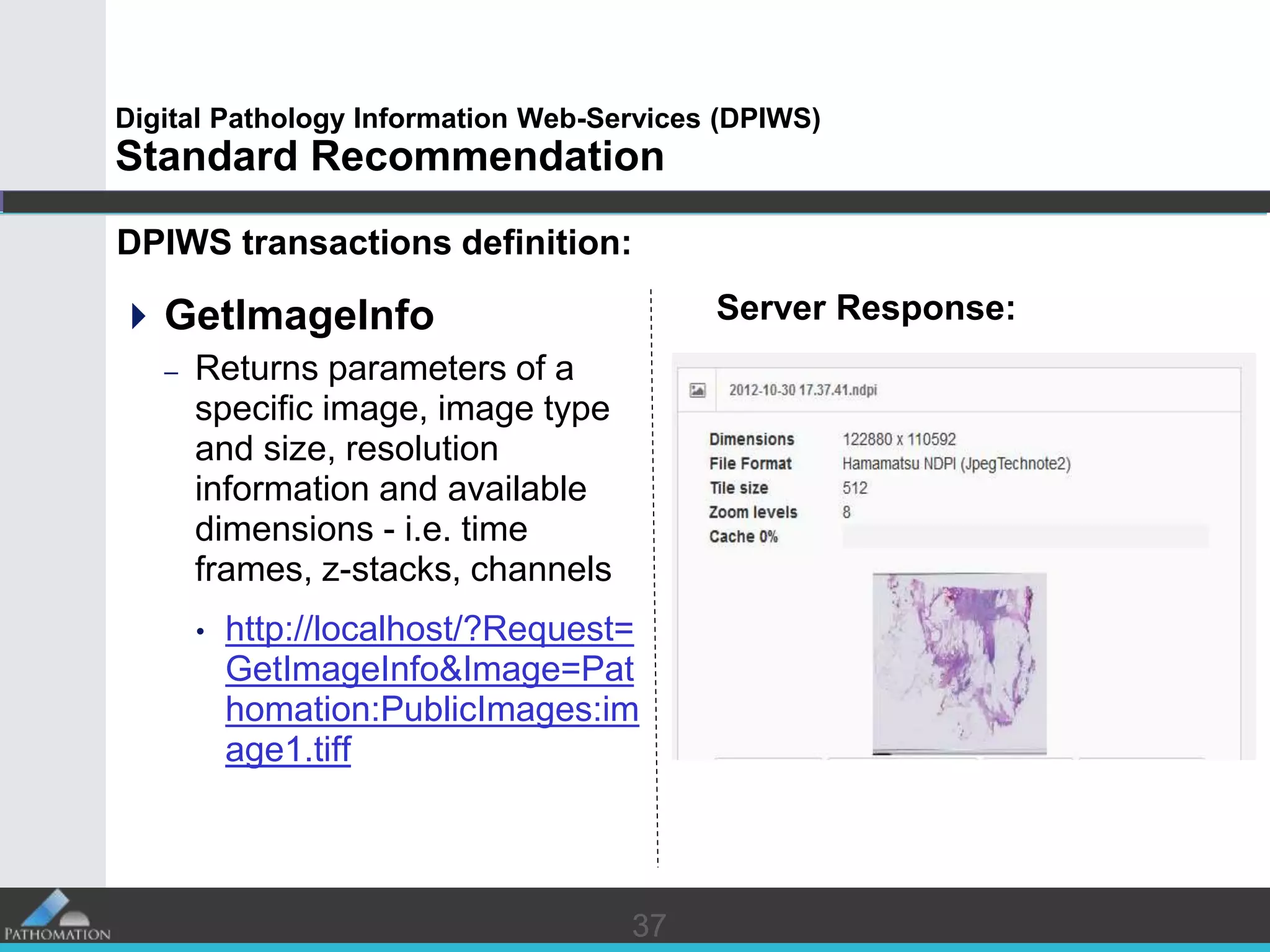
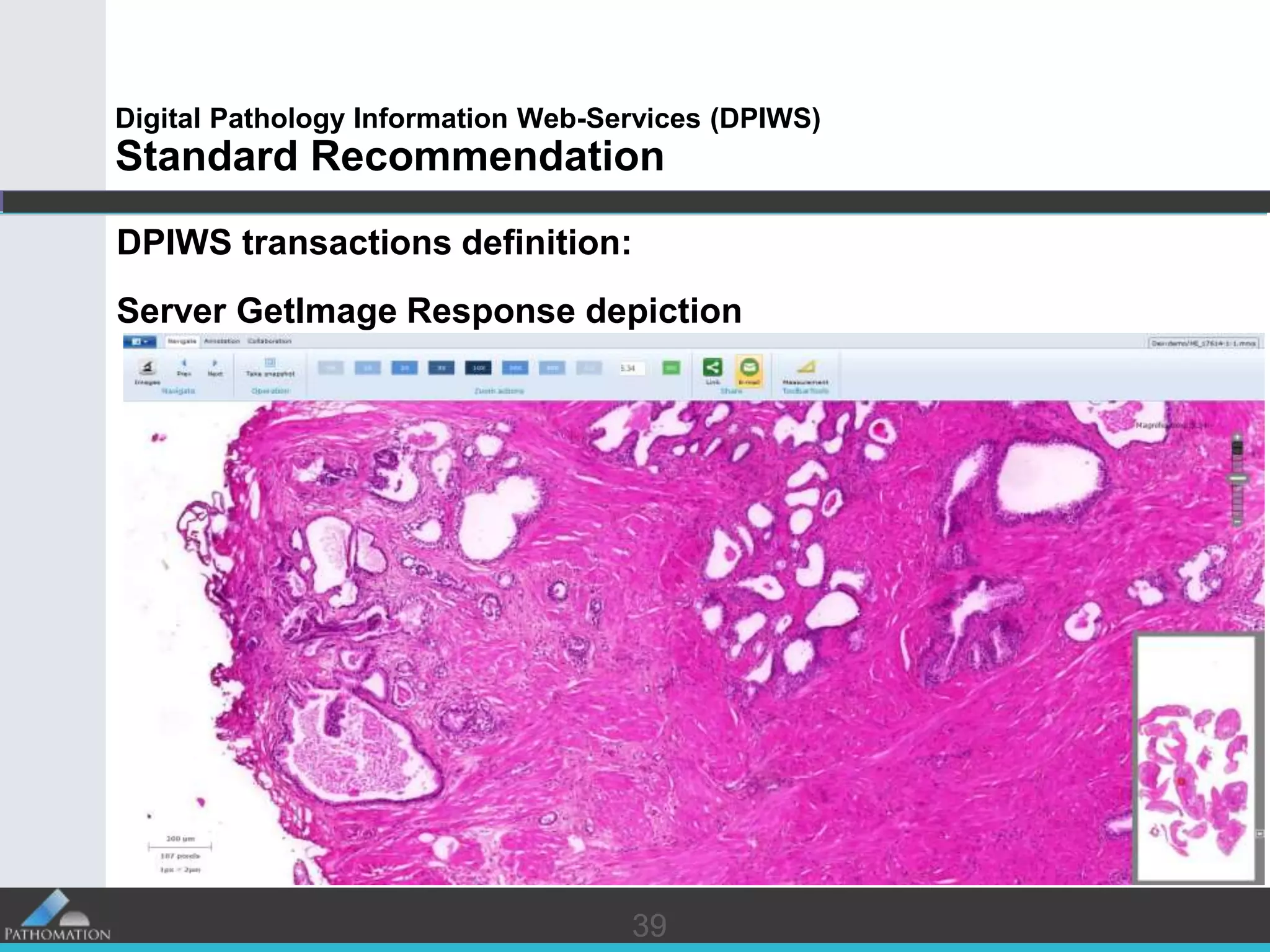
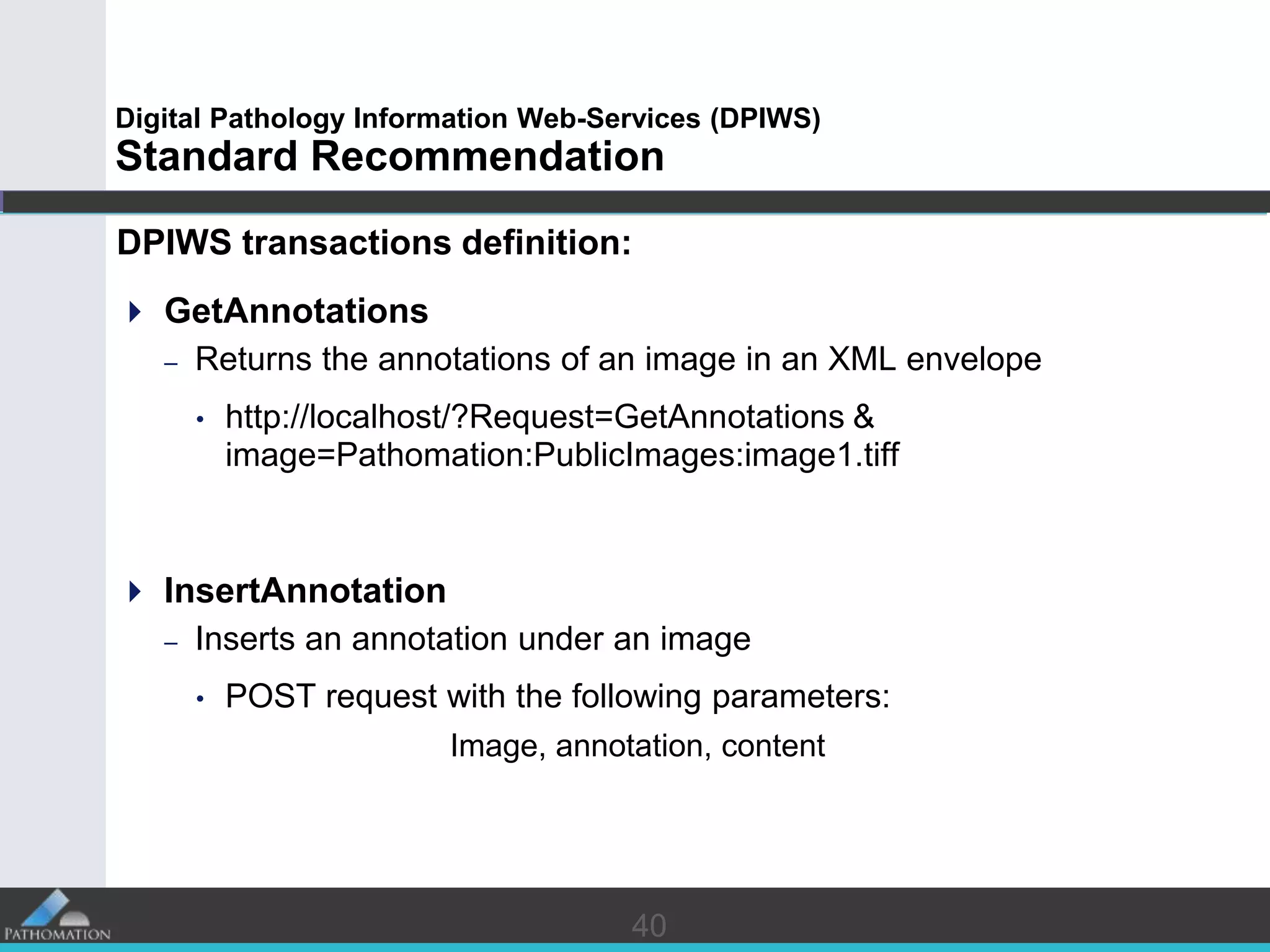
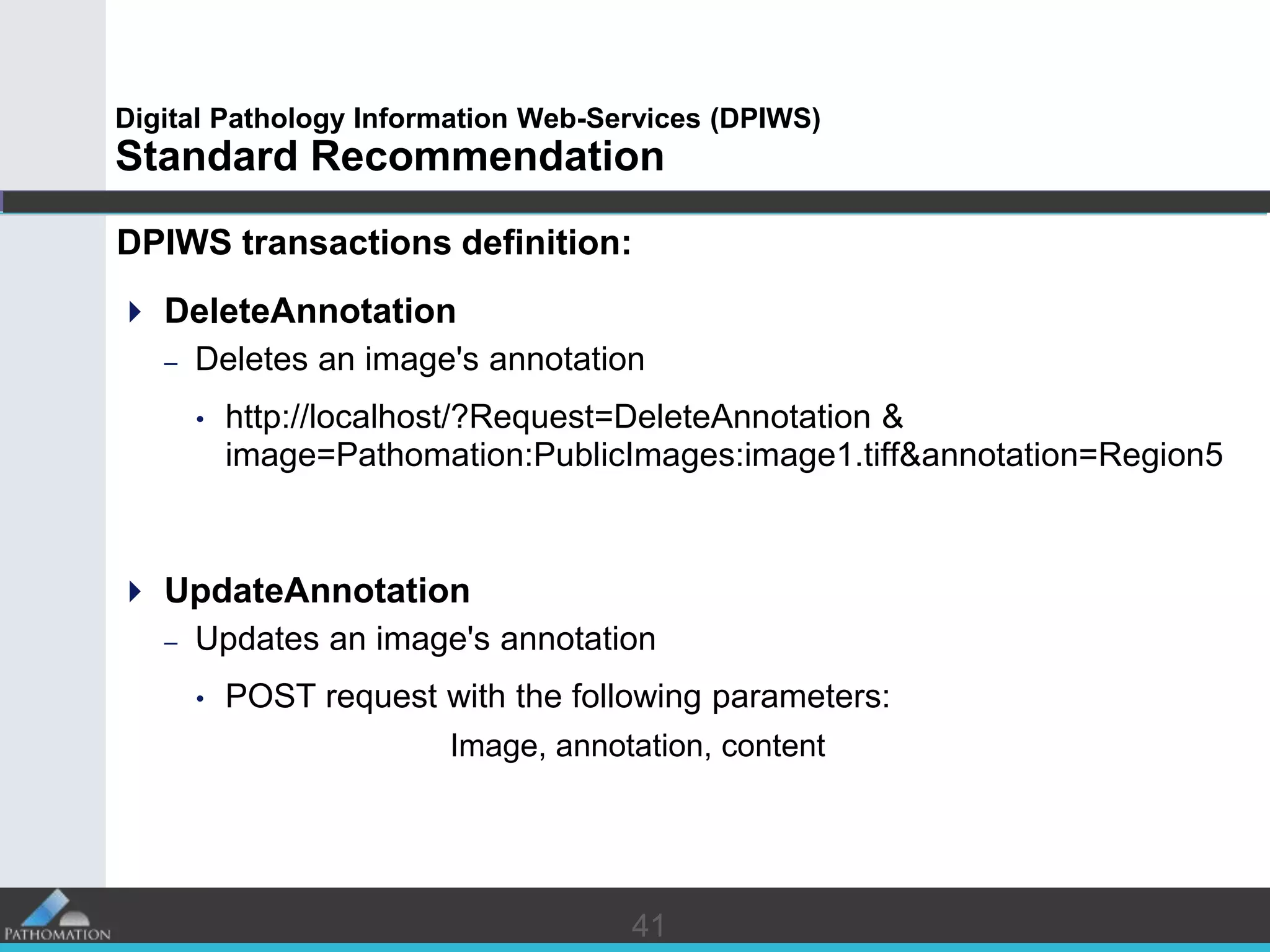
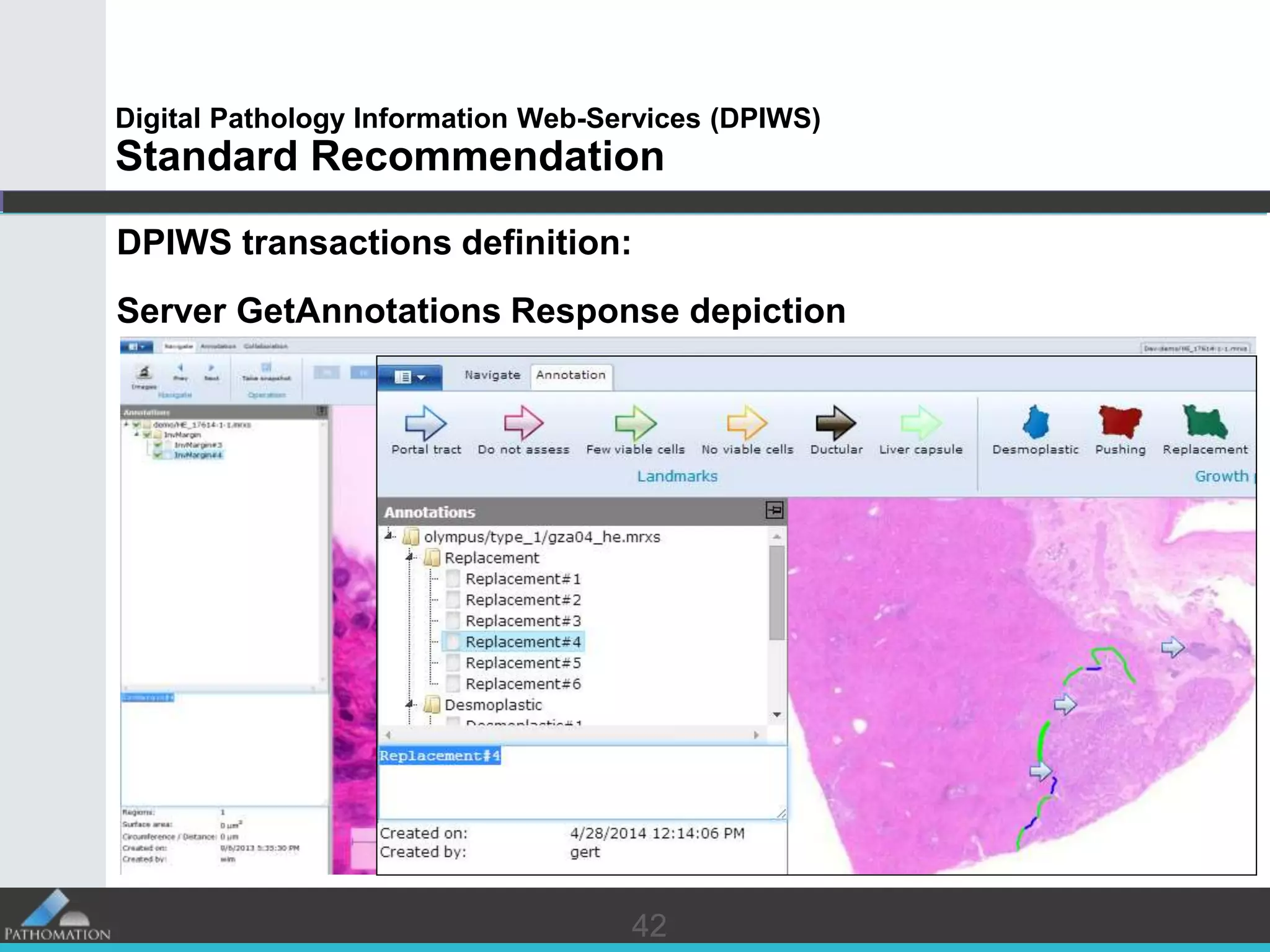
The document proposes a standard called Digital Pathology Information Web-Services (DPIWS) to facilitate data sharing of digital pathology information over the web. DPIWS defines a minimum set of operations, such as getting images and annotations, that a digital pathology content server must support. It builds upon existing standards like DICOM, OME, WFS, and WMS, and defines URL requests and server responses for common transactions. The goal of DPIWS is to enable platform-independent and format-agnostic exchange of digital pathology data.