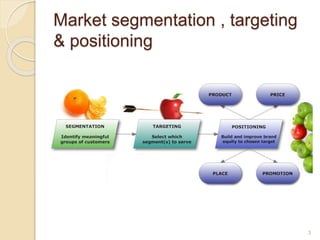
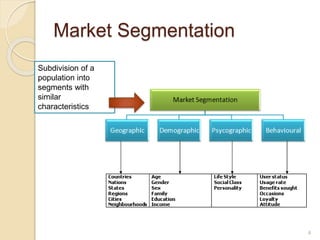
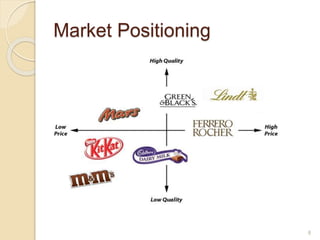
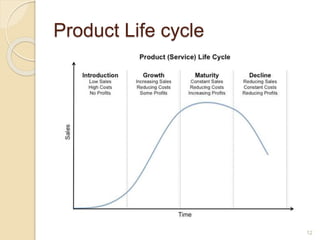
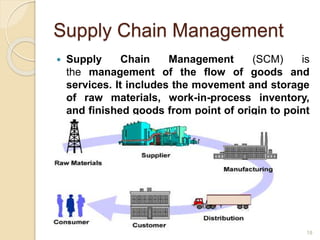
This document discusses various marketing strategies including market segmentation, targeting, positioning, the marketing mix (product, price, place, promotion), branding, packaging, labeling, distribution channels, supply chain management, and the use of celebrity endorsements. It provides examples and definitions for key marketing terms and concepts. The case study examines David Beckham's career and popularity, and asks how celebrity endorsements can benefit companies by associating products with popular or admired public figures.