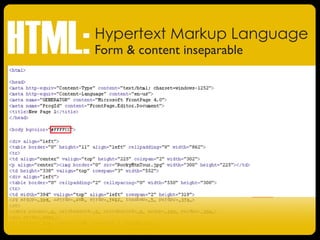
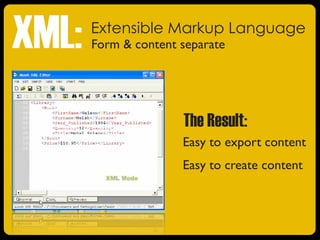
The document discusses the evolution of journalism and communication from a top-down model to a participatory model driven by user-generated content, marking the emergence of 'Web 2.0.' It highlights the transition from HTML to XML, and the role of social media in altering the control of messaging, enabling ordinary people to create and share content. The new digital landscape brings both challenges and opportunities for journalists as it transforms storytelling and audience interaction.





![- Richard Edelman (President & CEO of Edelman PR)
The media, communications, and marketing
landscape in which the PR industry was developed
is being knocked down. [...]
It is the decline of media based on a top-down
model of communications. [...] This model is
premised on the audience being passive receptors
for the message [...]
In the emerging model, as epitomized by YouTube,
MySpace, Oh My News and Wikipedia, ordinary
people provide content to others. Ideas and
information are passed virally. This consumer
generated content alters the laws of control of
message. Many are calling this new social and user
driven media ‘Web 2.0.’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch1-240828213608-6b7db83a/85/Digital-Journalism-Digital-Storytelling-7-320.jpg)