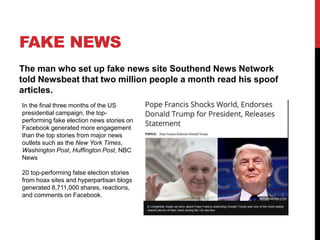
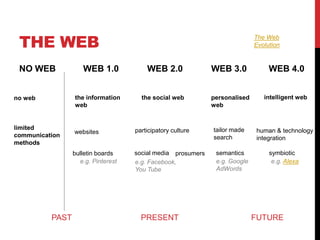
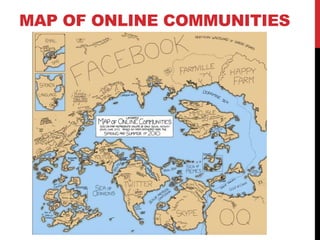
The document discusses how the creation of the web has changed audience behavior and interactions with media. It explores the rise of social media and user-generated content, noting that audiences now participate more actively online as "prosumers" who both consume and produce media. This has resulted in a blurred line between audiences and producers. The document also examines concepts like citizen journalism, fake news, and debates different perspectives on the impact of these changes.









![ACTIVITY
Numa numa http://www.newgrounds.com/portal/view/206373
Tay Zonday http://tayzonday.ning.com/
Memes http://www.freshnetworks.com/blog/2010/12/6-social-media-memes-of-2010/
Mashups http://videomashup.blogspot.com/
Pick one of the above and do a case study on a Googledoc Presentation
Include:
1. What it is (definition)
2. When and how it began
3. What was the response
4. Examples of how it has developed (via the Web)
5. Future? –what do you predict could follow as a result? [extension]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2017newmedia-170522120249/85/2017-new-media-10-320.jpg)