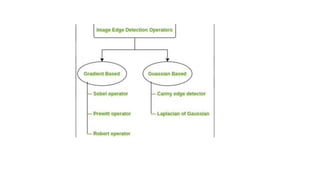
The document discusses digital image processing with a focus on edge detection, highlighting the significance of edges as boundaries in images and the various methods for detecting them, such as gradient and Gaussian-based operators. It also describes edge linking algorithms, categorizing them into local and global linkers, and introduces segmentation principles like automatic thresholding and region growing techniques for effective image interpretation. The process involves grouping connected pixels with similar properties to accurately represent different regions or objects within an image.