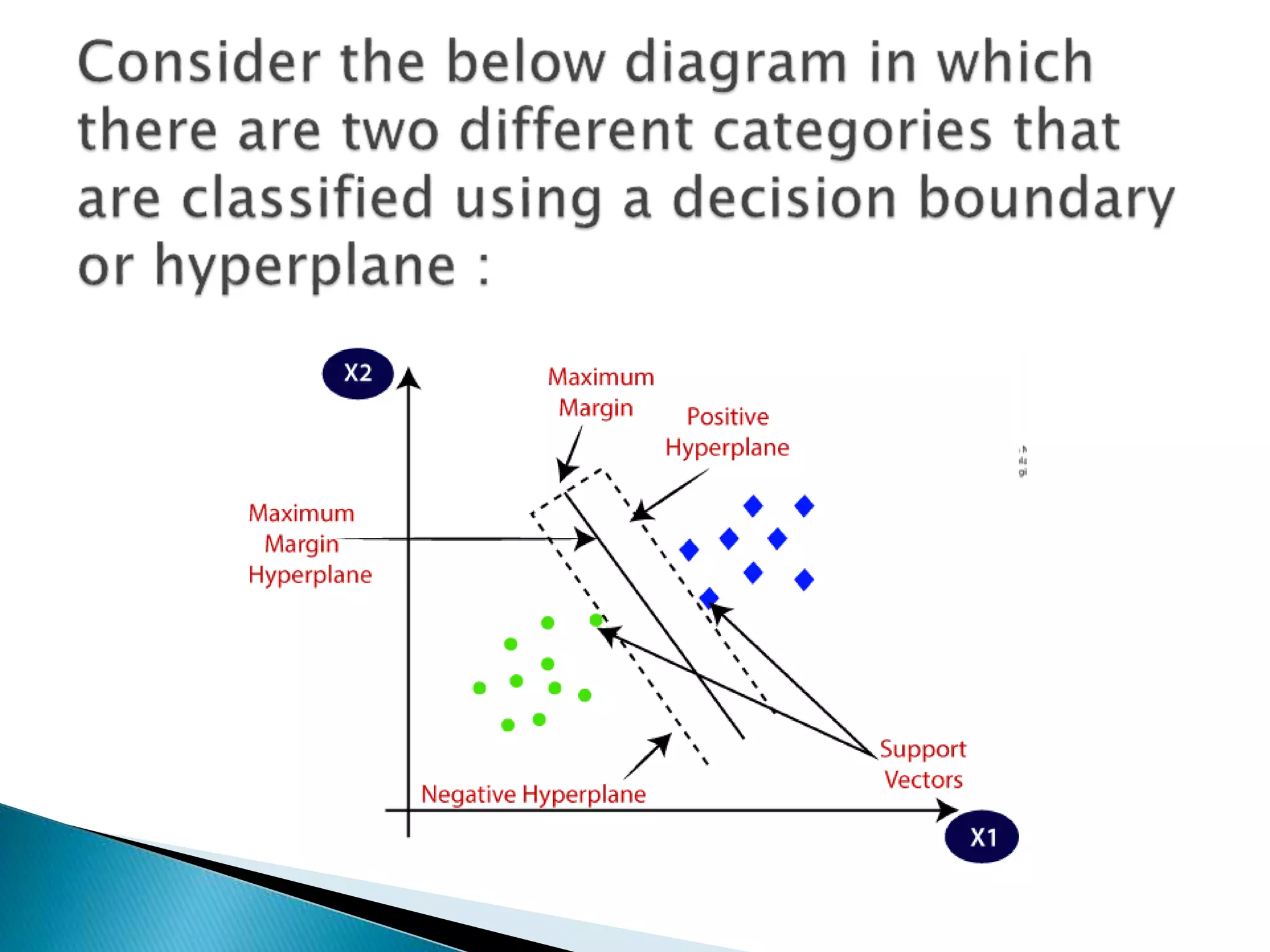
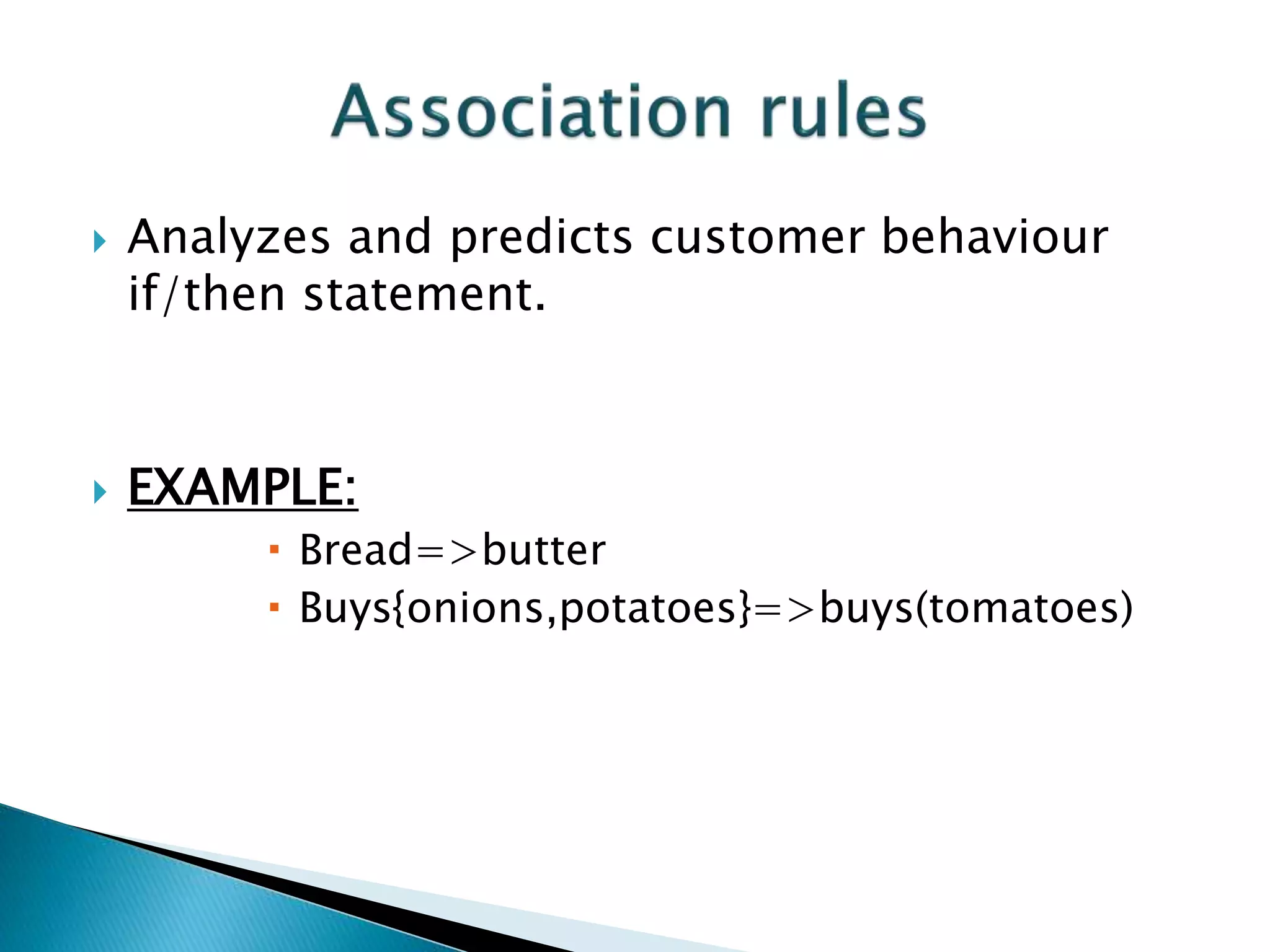
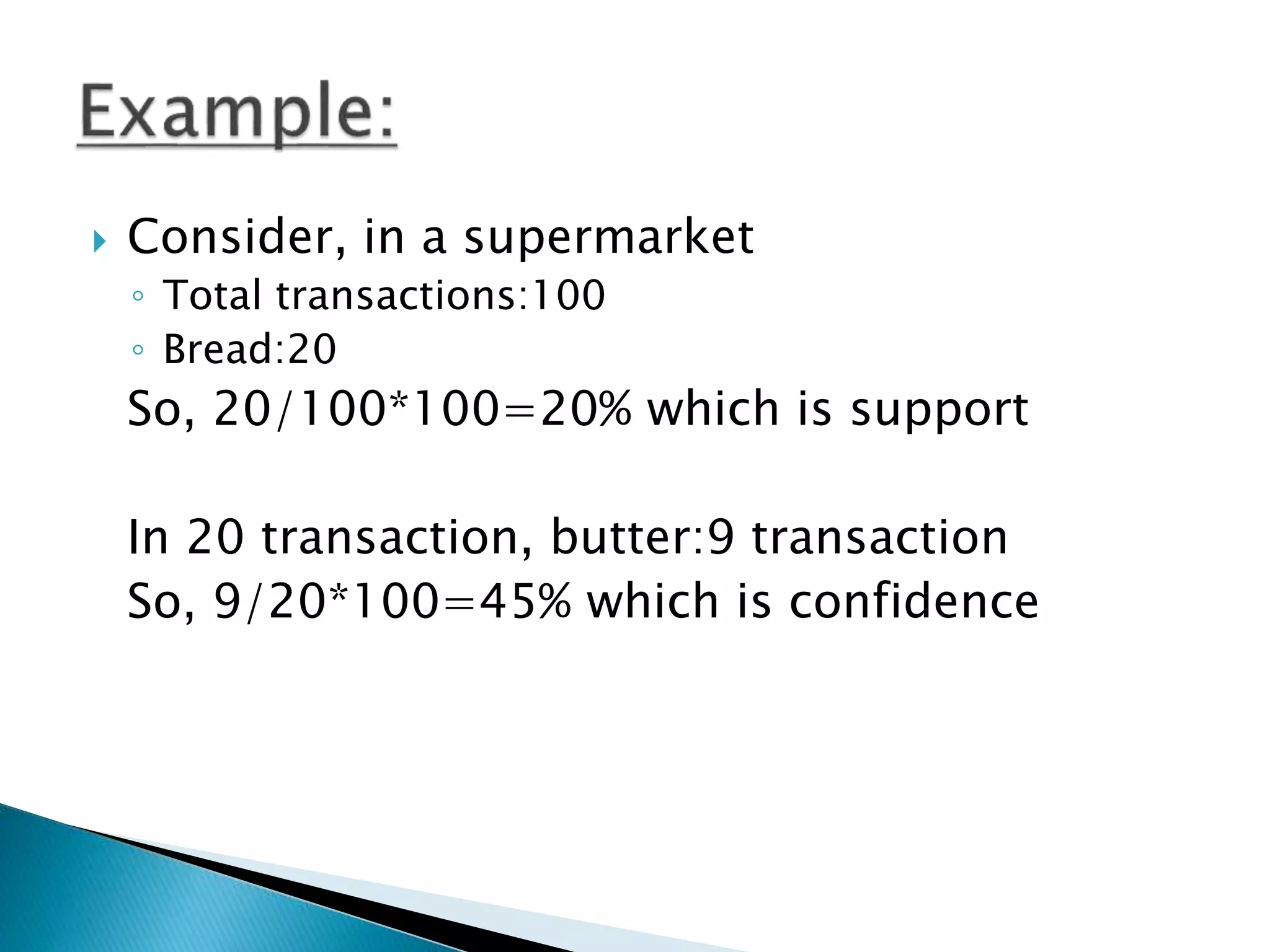
The document introduces Support Vector Machine (SVM) algorithms, primarily used for classification problems in machine learning, focusing on the creation of hyperplanes to segregate data. It discusses linear and non-linear SVMs for different types of data, along with the classification of association rules like support and confidence in consumer behavior. Additionally, it covers applications of SVMs in various fields, including web usage mining and market analysis.