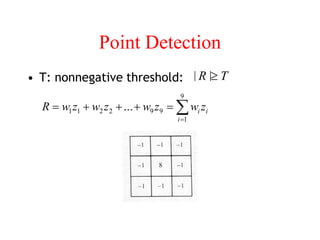
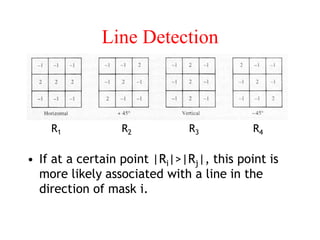
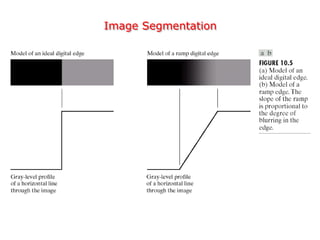
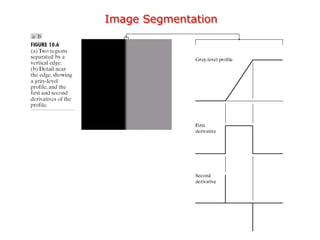
The document discusses image segmentation techniques. It describes image segmentation as the process of subdividing an image into constituent regions or objects. Some common segmentation methods mentioned include edge detection, boundary detection, region growing, and region merging. Segmentation can be based on discontinuities in intensity values using edges, or on similarities in regions using thresholding or region-based approaches. Edge detection computes derivatives to find boundaries between distinct regions.