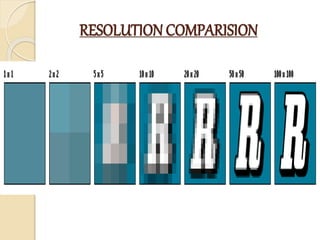
This document discusses the specifications of digital cameras. It begins with a brief history of digital cameras, invented in 1975 by Steven Sasson at Kodak. There are three main types: point and shoot, mega zoom, and DSLR. Key specifications that determine camera quality include sensor type and size (larger is better but more expensive), image processor brand, resolution in megapixels, aperture size of the lens (lower number means larger aperture), ISO sensitivity range (higher means better in low light), shutter speed range, and video capabilities like frames per second (higher is smoother). Other factors include screen size and quality, zoom range, storage options, battery life, connectivity and camera size/weight. Overall image