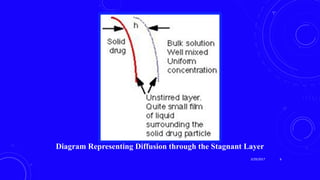
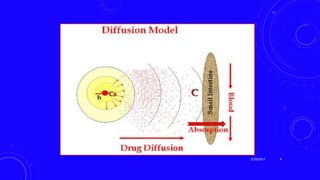
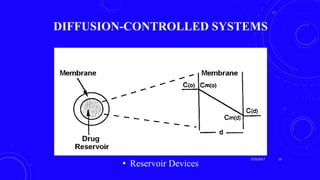
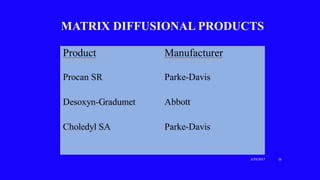
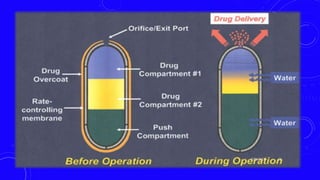
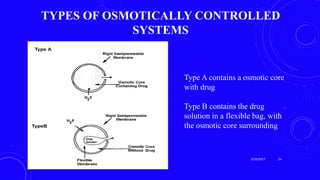
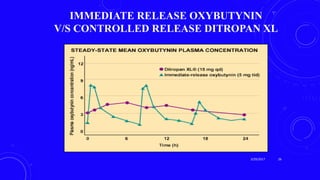
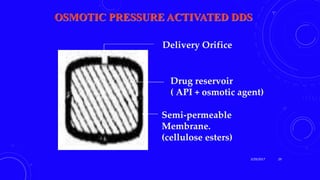
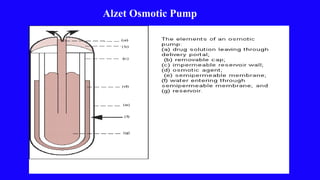
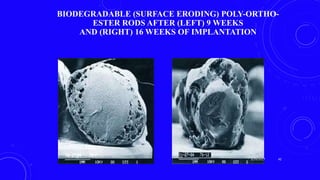
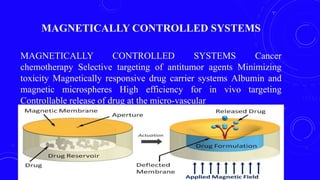
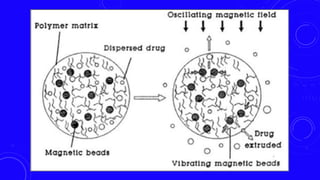
This document provides an overview of different controlled release polymer systems, including diffusion-controlled systems, solvent-activated systems, and chemically controlled systems. Diffusion-controlled systems use a reservoir or matrix to control the diffusion of a drug. Solvent-activated systems use osmotic pressure or polymer swelling to control drug release. Chemically controlled systems link drugs to polymers or use biodegradable polymers so the drug releases as the polymer breaks down. Magnetically controlled systems can also be used to selectively and controllably release drugs using magnetic fields.