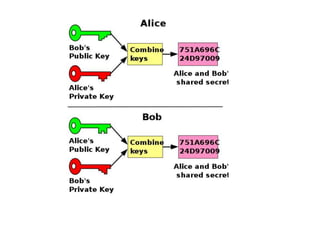
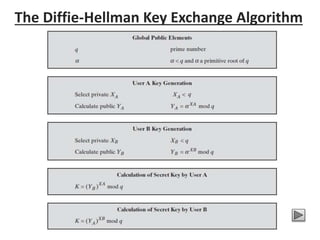
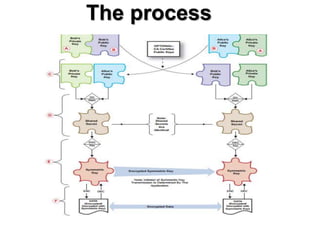
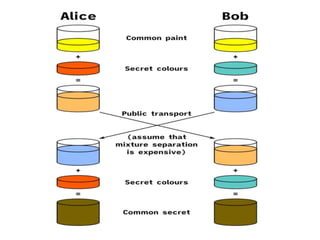
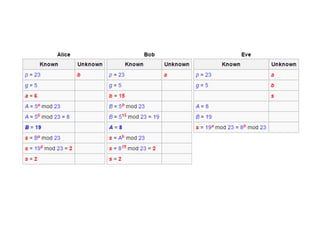
Diffie-Hellman key exchange is a cryptographic protocol that allows two parties to establish a shared secret over an unsecured communication channel. It was one of the first practical examples of key exchange and predates public-key infrastructure. The security of the Diffie-Hellman protocol relies on the difficulty of calculating discrete logarithms, though it lacks authentication and is susceptible to man-in-the-middle attacks. While an important historical algorithm, Diffie-Hellman may not scale sufficiently for future needs as key sizes would need to continually increase over time to maintain security levels.