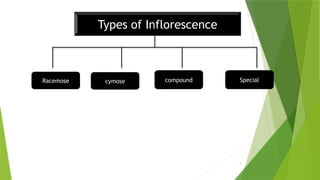
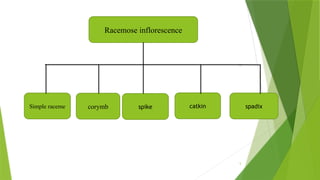
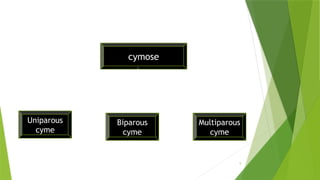
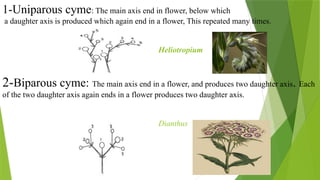
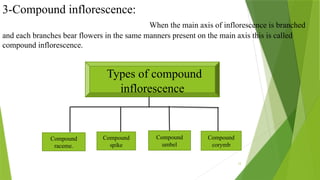
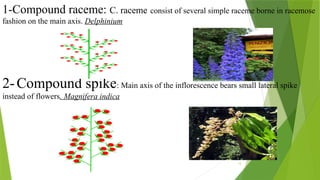
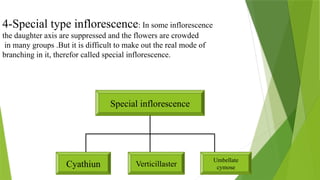
The document describes inflorescences, which are groups of flowers arranged on a stem or branch, detailing their types including racemose, cymose, and compound inflorescences. It explains characteristics and examples of each type, such as the growth patterns and arrangements of flowers. Additionally, it highlights special types of inflorescences like cyathium, hypanthodium, and verticellaster.