Embed presentation
Download to read offline
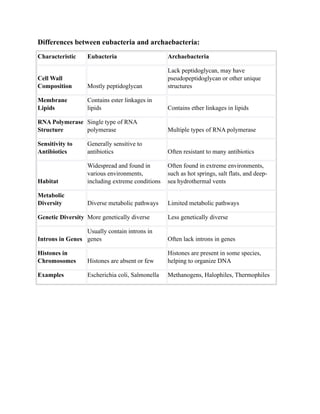
Eubacteria and archaebacteria differ in their cell wall composition, membrane lipids, RNA polymerase structure, antibiotic sensitivity, and habitats. Eubacteria typically have peptidoglycan cell walls, contain ester linkages in their lipids, have a single type of RNA polymerase, are generally sensitive to antibiotics, and are widespread including in extreme environments. Archaebacteria lack peptidoglycan, have ether linkages in their lipids, have multiple RNA polymerases, are often resistant to antibiotics, and are typically found in extreme habitats like hot springs.
