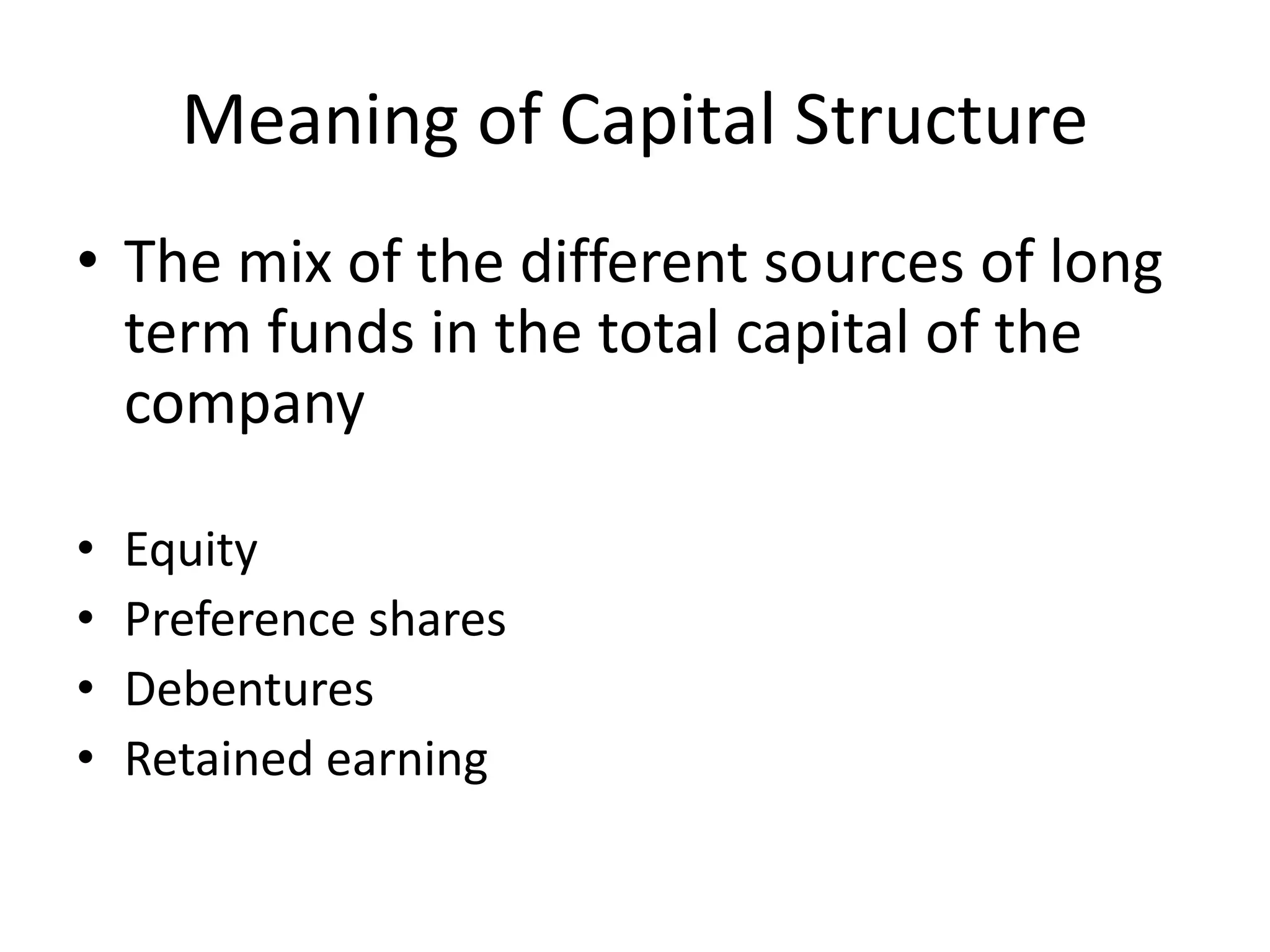
This document discusses capital structure and its key aspects. It defines capital structure as the mix of long-term funding sources for a company, including equity, preference shares, debentures, and retained earnings. It outlines features like return, risk, simplicity and flexibility. Factors affecting capital structure are also examined, such as trading on equity, government policy, and purpose of financing. The merits and demerits of different capital structure options are analyzed, such as no fixed liability but dilution of control with equity shares.