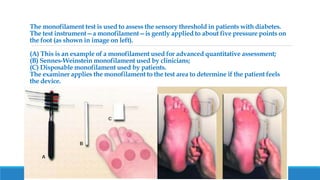
This document discusses foot problems in people with diabetes, including that over 50% of lower extremity amputations are due to diabetes and are often preventable with proper foot care. Neuropathy, peripheral vascular disease, and hyperglycemia can impair wound healing. Daily foot inspections are important to catch injuries or infections early. Preventative care includes foot exams, nail trimming, moisturizing, proper shoes, and treating conditions like calluses.