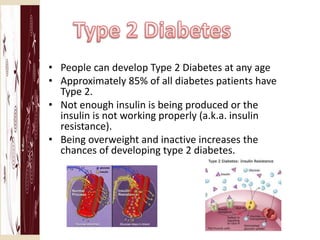
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the body destroys the cells that produce insulin. It usually develops in childhood and requires daily insulin injections. Type 2 diabetes involves the body not producing enough insulin or cells resisting insulin. It is often prevented through diet and exercise and sometimes requires medication. The key difference is that type 1 diabetes involves destroyed insulin-producing cells while type 2 involves insulin resistance or deficiency.