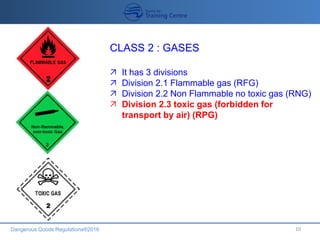
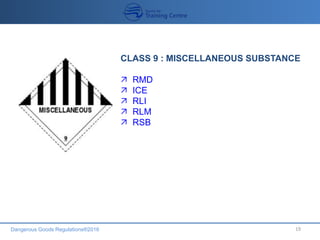
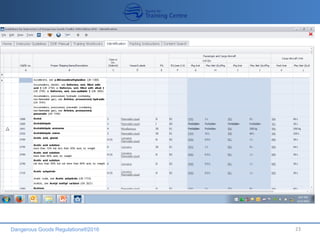
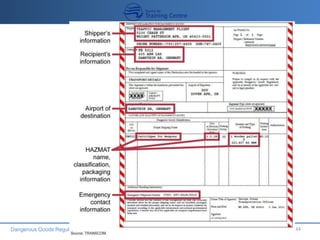
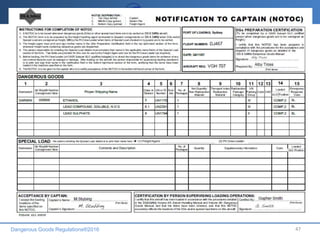
This document provides an overview of dangerous goods regulations for transportation by air. It outlines the objectives of dangerous goods training which include identifying dangerous goods and their classes, understanding regulations and philosophy, recognizing labels, and emergency response procedures. It then details the 9 classes of dangerous goods and their divisions and hazards. The document emphasizes that the shipper bears primary responsibility for classifying, packing, marking and documenting dangerous goods in accordance with regulations. It explains that key documents for transporting dangerous goods include the shipper's declaration, notification to the pilot, and material safety data sheets.