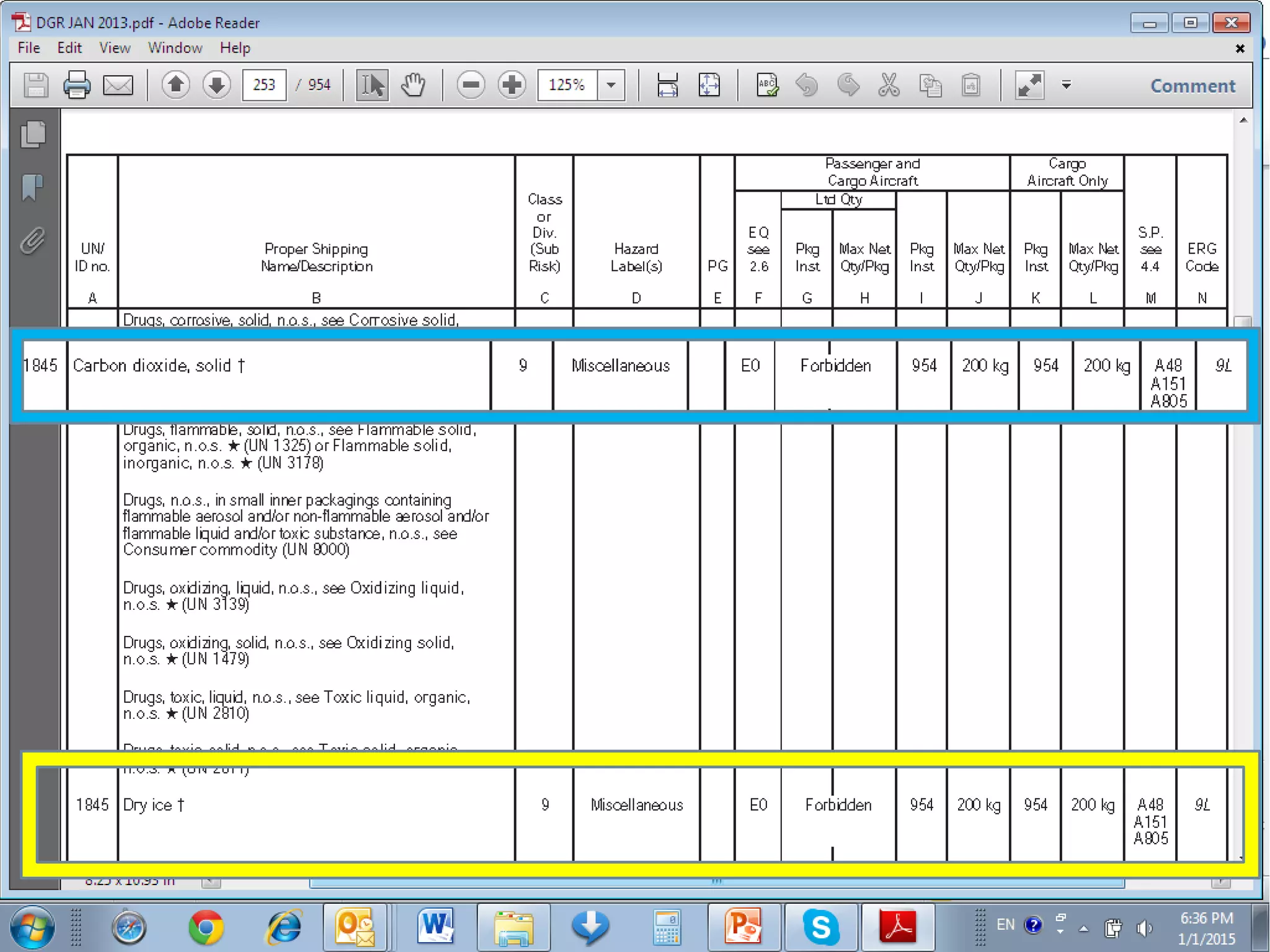
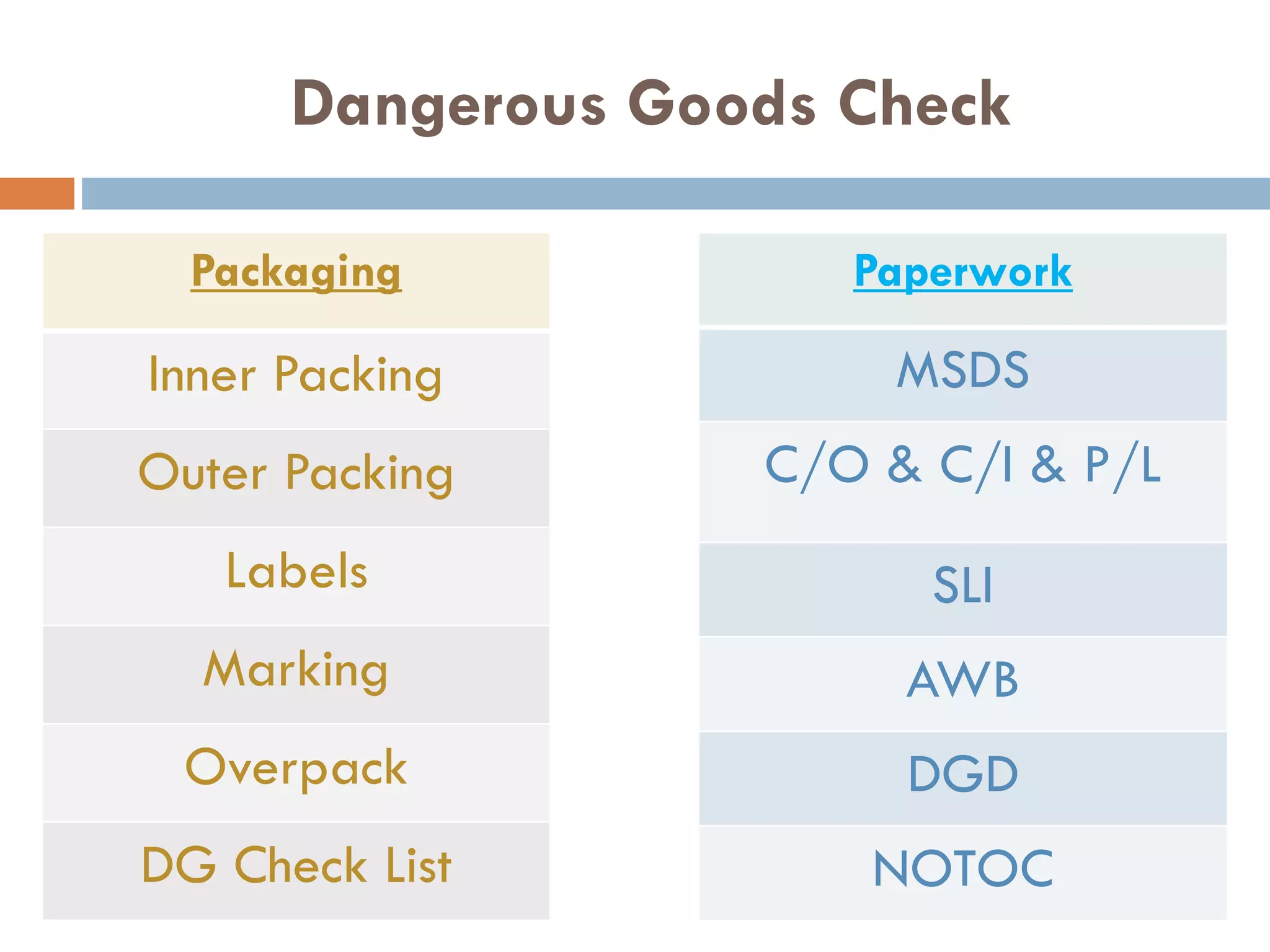
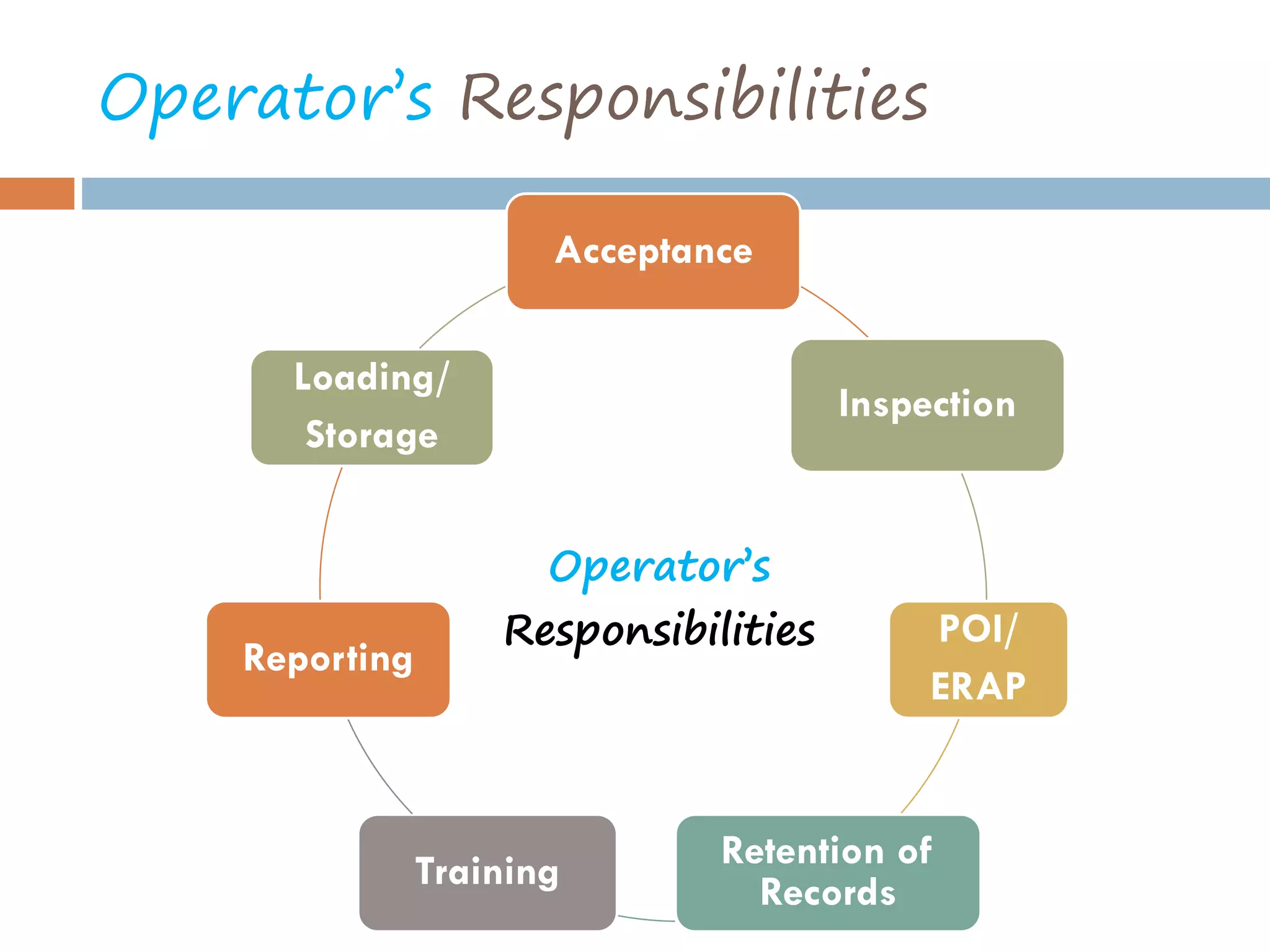
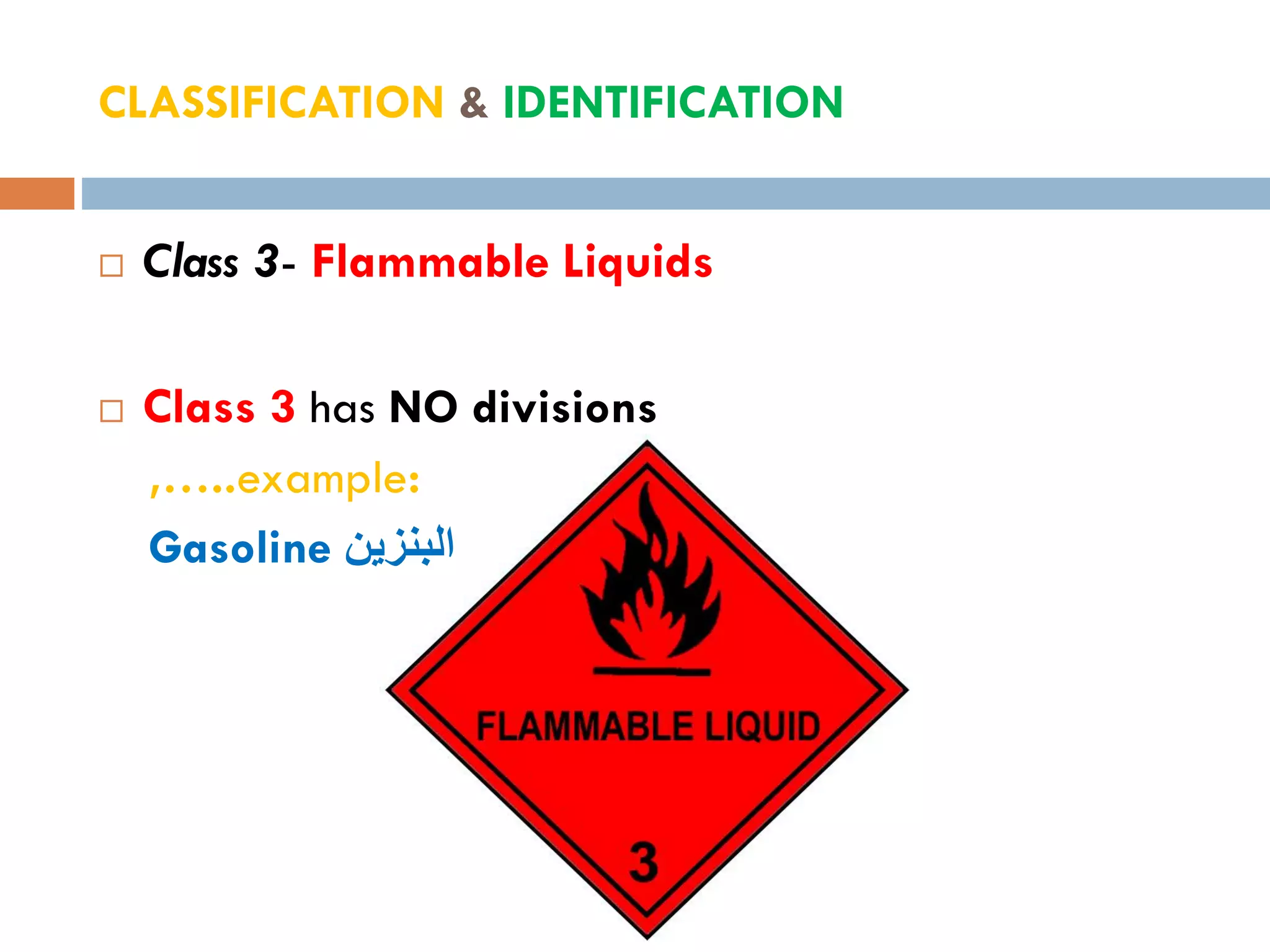
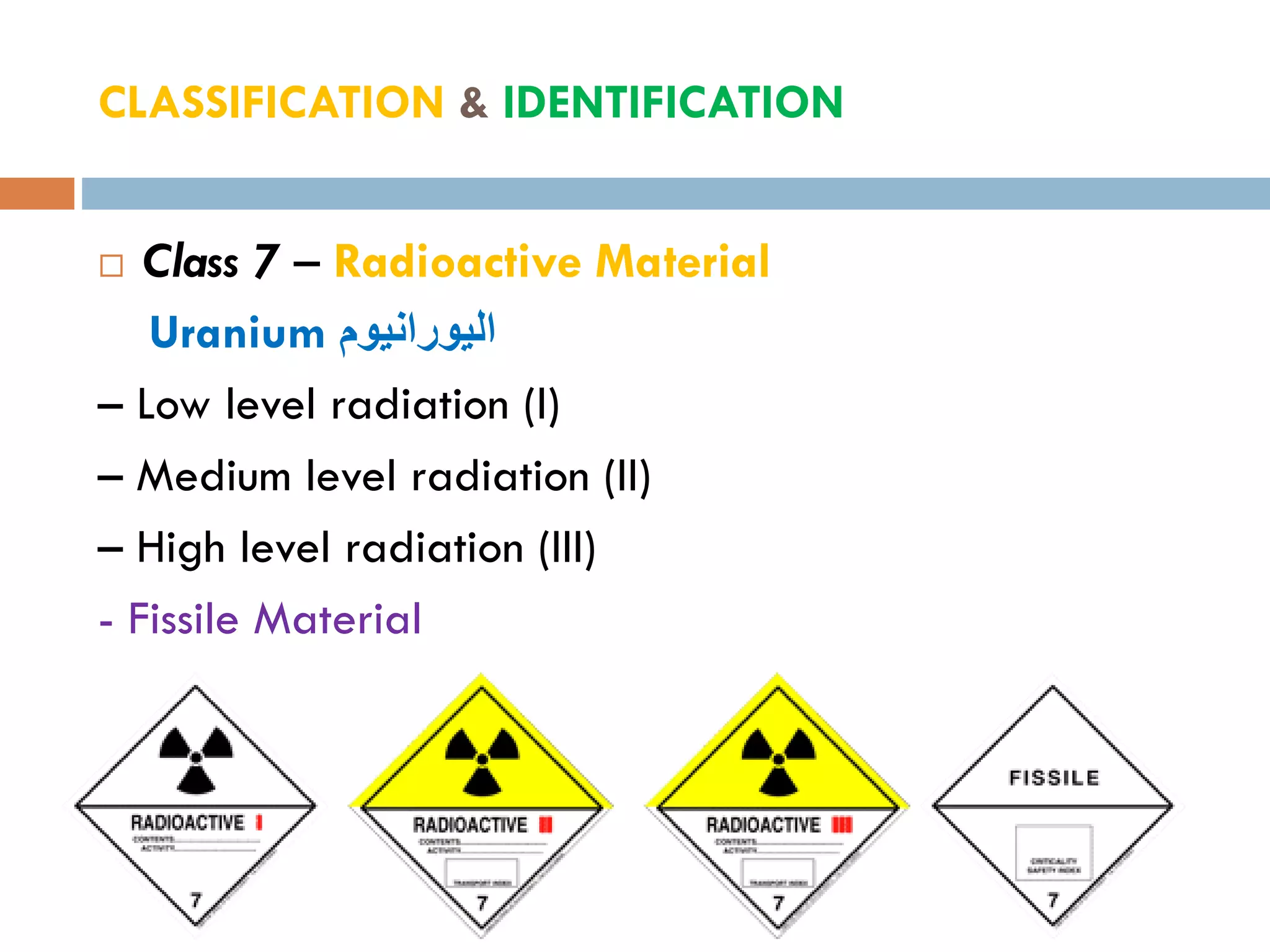
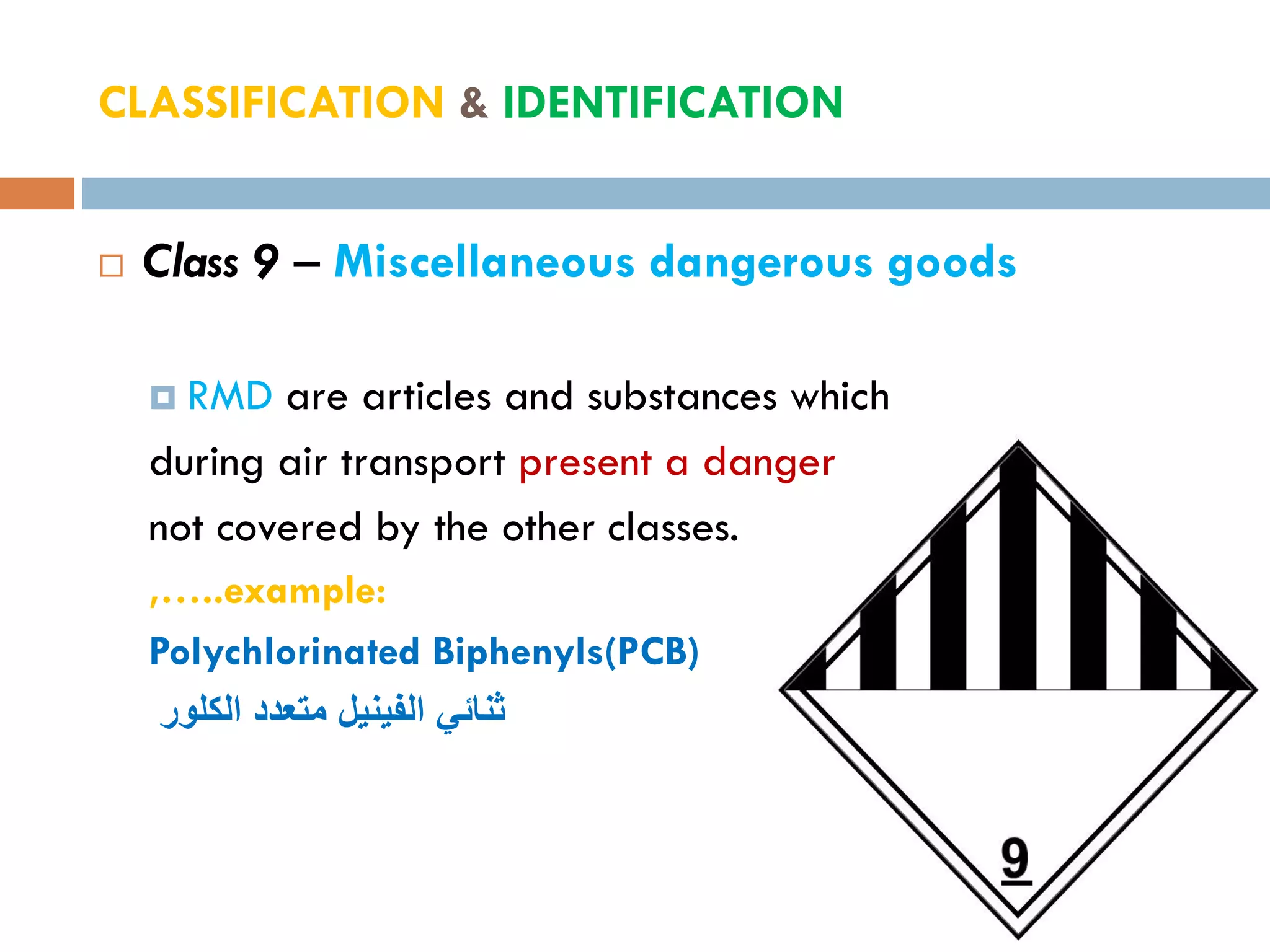
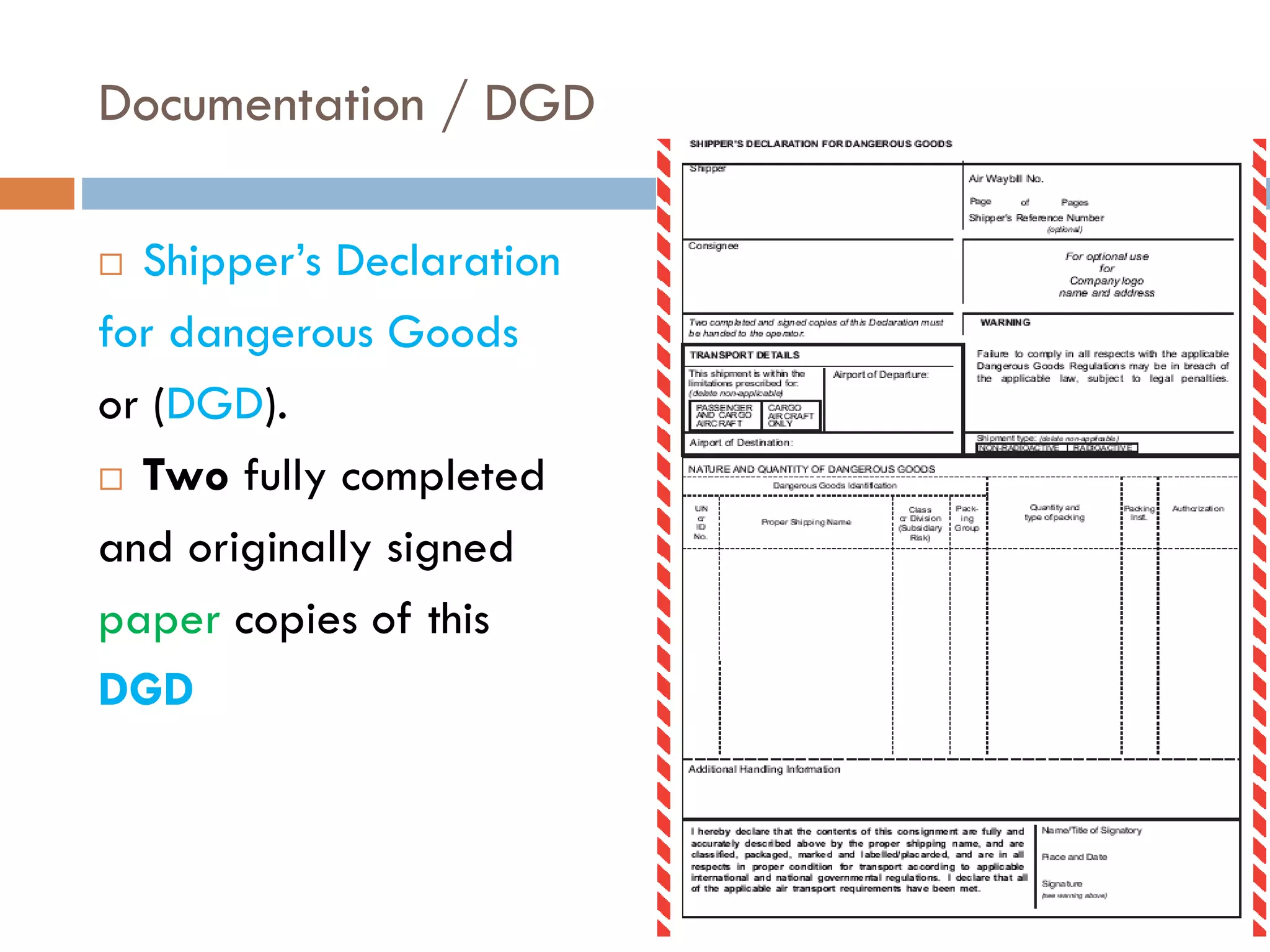
This document provides an overview of dangerous goods regulations. It defines key organizations like IATA and key terms like overpack. It describes shipper and operator responsibilities. Nine hazard classes are described including examples like explosives, gases, and corrosives. Proper packaging, marking, labeling and documentation like the shipper's declaration are outlined. Classification identifies the hazard and packing group. Regulations cover packing methods, UN codes, and permitted dangerous goods on passengers.