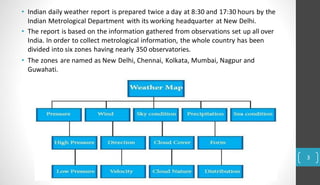
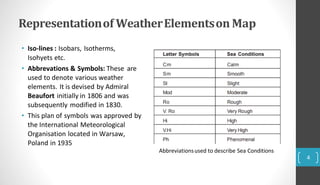
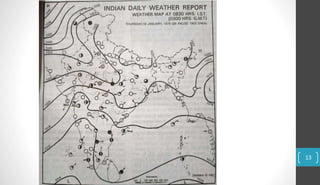
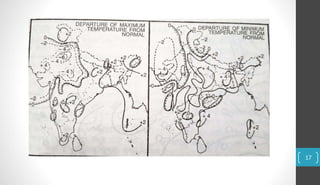
A weather map represents current weather conditions over a region. It shows six key elements: temperature, rainfall, atmospheric pressure, wind direction, wind speed, cloud cover, and humidity. Meteorological departments use weather maps to forecast weather by analyzing these elements. Maps use lines, symbols, and abbreviations to depict elements like pressure (isobars), winds, clouds, and precipitation. Interpreting daily weather maps involves examining features like areas of high and low pressure, wind patterns, cloud cover, rainfall amounts and distribution, sea conditions, and how temperatures compare to normal levels for that area.