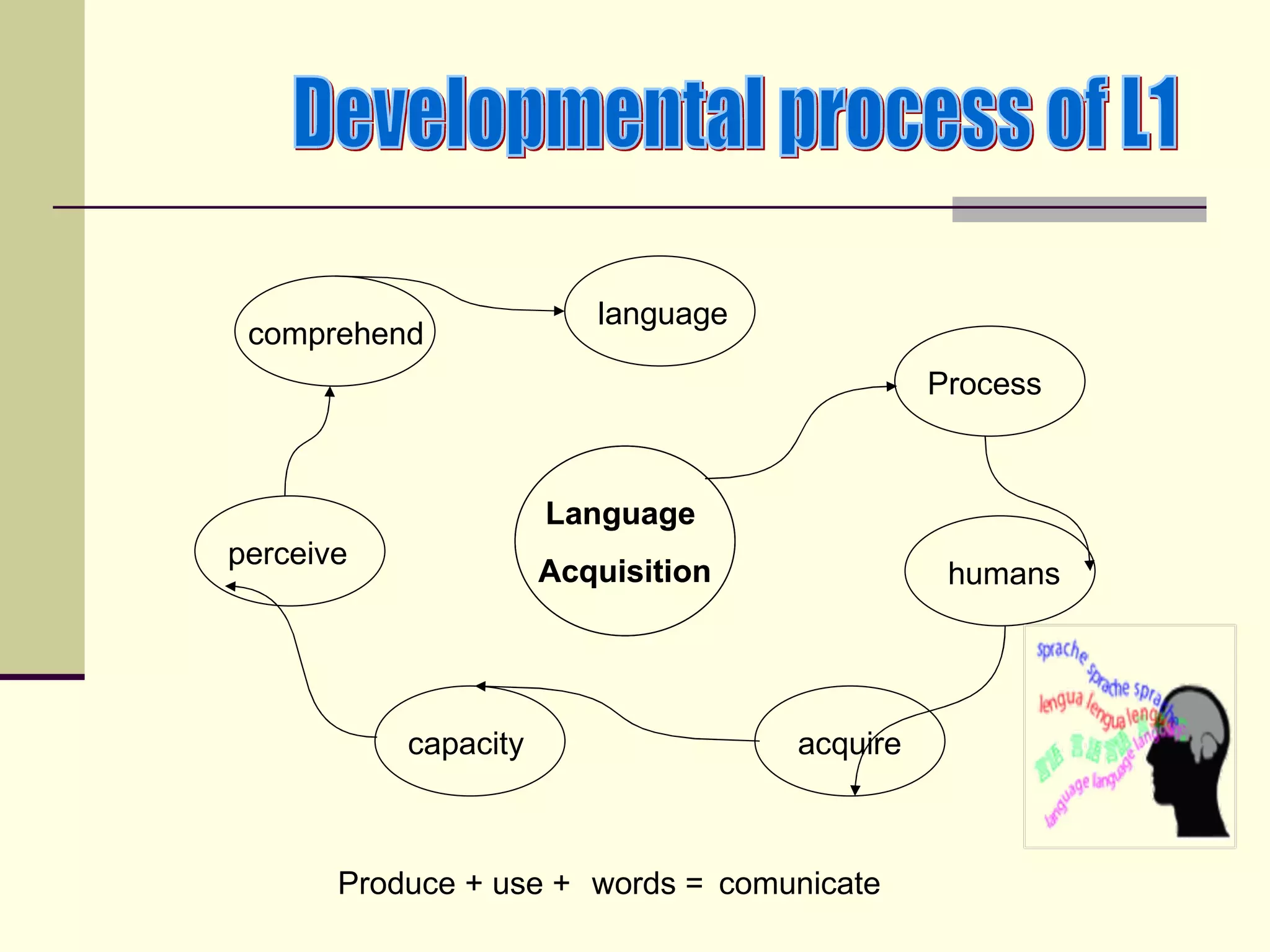
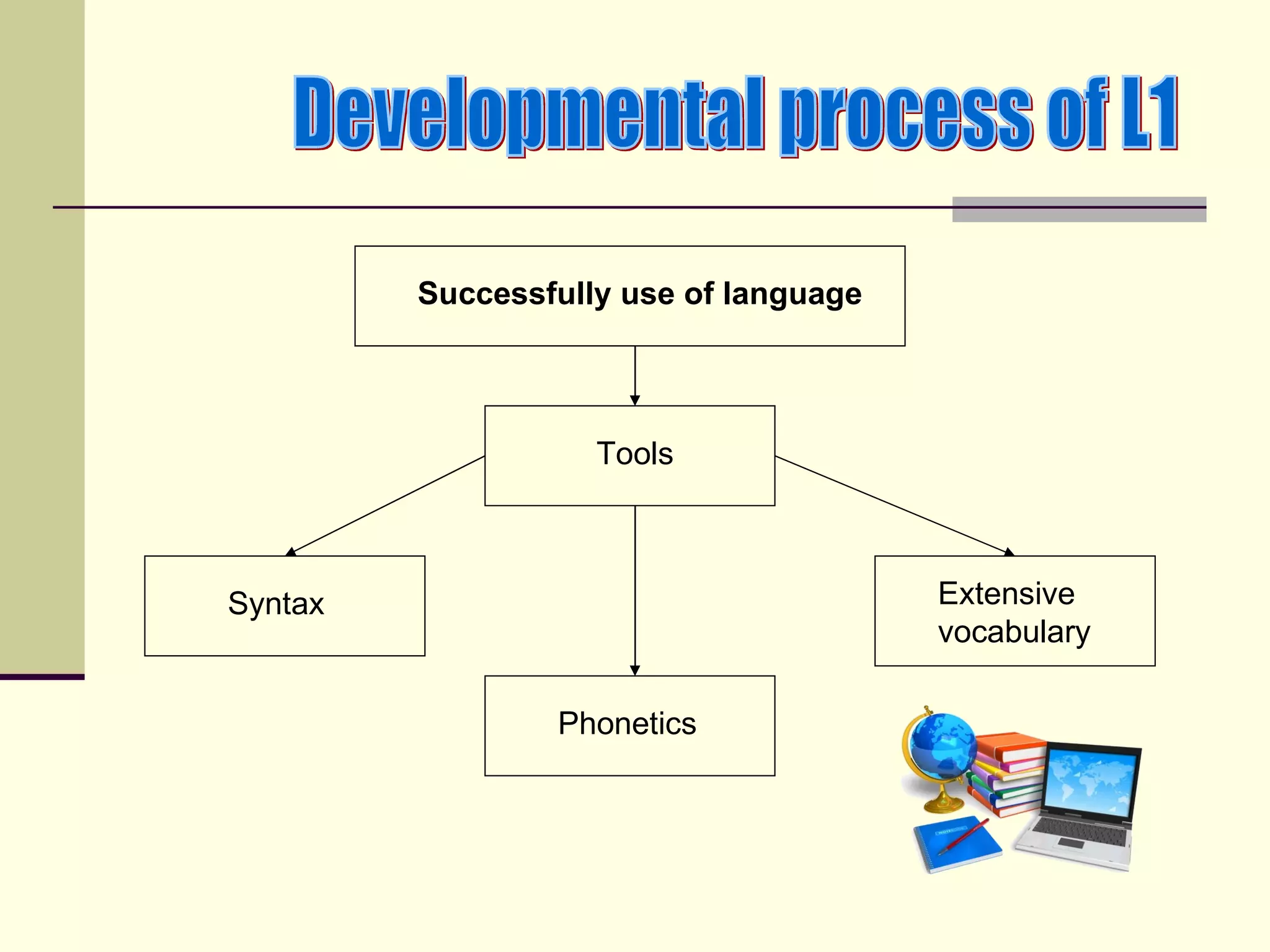
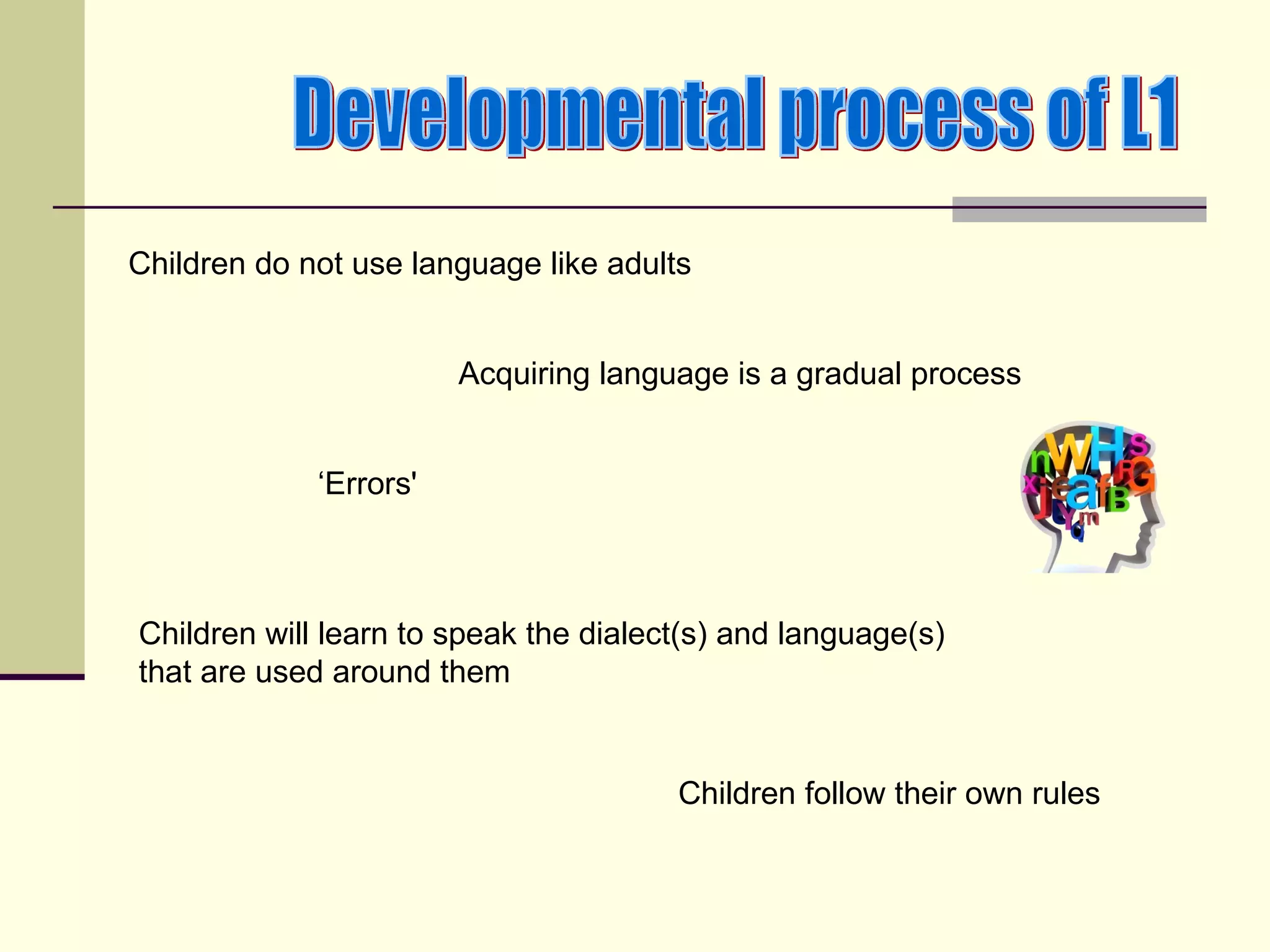
The document discusses language acquisition in children, emphasizing that it is a gradual process influenced by their environment, with children developing their own strategies and rules as they learn to communicate. It highlights that children do not learn language in the same way as adults and experience individual rates of acquisition based on their physical and cognitive development. Resources for further learning on this topic, including books by David Crystal and Eve Clark, are recommended.