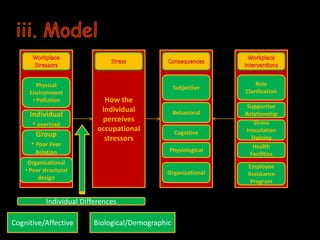
The document outlines various interventions for career planning and development, workforce diversity, and employee stress and wellness. It emphasizes the importance of managing career stages, individual and organizational goals in career development, and the necessity of addressing workforce diversity to improve employee satisfaction and productivity. Additionally, it highlights the significance of addressing employee wellness and stress through supportive organizational practices and interventions.






















![Leave Encashment [annual leaves]
Medical Leaves
Casual Leaves
Problems:
Turnover
Absenteeism
Low performance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/developingandassistingmembersinorganizationaldevelopment-130224093119-phpapp01/85/Developing-and-Assisting-Members-in-organizational-development-23-320.jpg)