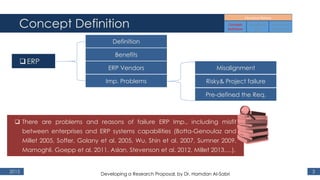
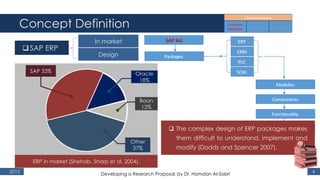
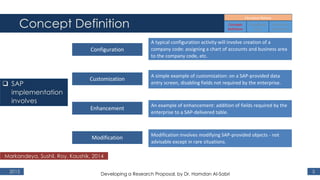
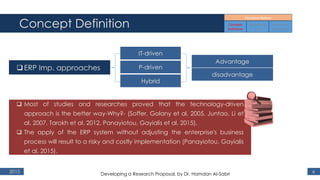
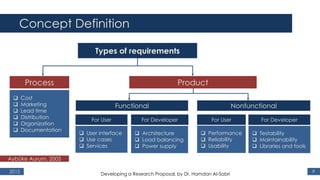
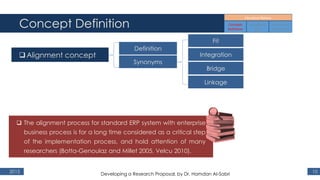
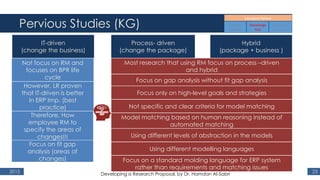
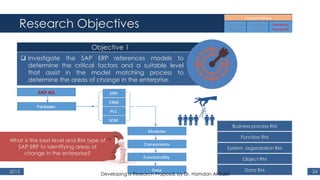
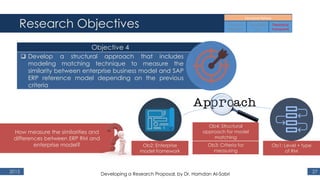
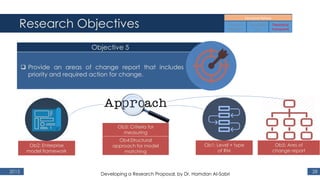
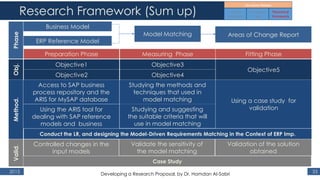
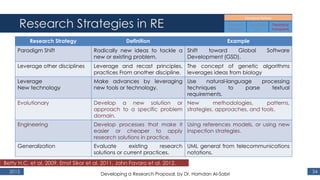
The document outlines a research proposal by Dr. Hamdan M. Al-Sabri focusing on model-driven requirements matching in software engineering, particularly around the implementation of Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) ERP systems like SAP. It discusses key elements such as previous studies on ERP implementation, challenges faced by businesses, and the importance of aligning business processes with ERP functionalities. The proposal also sets specific research objectives aimed at developing frameworks for effective model matching and enhancing ERP implementation success.