The document discusses requirements engineering and requirements elicitation. It defines requirements engineering as the science of analyzing and documenting requirements. Requirements elicitation is the process of discovering, reviewing, articulating, and understanding users' needs. The document describes various techniques for requirements elicitation, including interviews, questionnaires, task analysis, prototyping, and group techniques. It also discusses tools that can be used to support the requirements elicitation process.

![Why are Requirements so important?[2]
4Prepared by: Dr. Hamdan Al-Sabri](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwarerequirementsengineering-170928200102/85/Software-requirements-engineering-4-320.jpg)
![Cumulative number of publications since
[4,2012]
5Prepared by: Dr. Hamdan Al-Sabri](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwarerequirementsengineering-170928200102/85/Software-requirements-engineering-5-320.jpg)
![What is Requirement Engineering?[2]
7Prepared by: Dr. Hamdan Al-Sabri
• Requirement Engineering (RE) is the science and discipline
concerned with analyzing and documenting requirements.
• Requirement:
– (1) A condition or capability needed by a user to solve a problem or
achieve an objective.
– (2) A condition or capability that must be met or possessed by a
system or system component to satisfy a contract, standard,
specification, or other formally imposed documents.
– (3) A documented representation of a condition or capability as in (1)
or (2).
[IEEE-Std-610.12-1990]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwarerequirementsengineering-170928200102/85/Software-requirements-engineering-7-320.jpg)
![A Good Set of Requirements is….[2]
• Correct
• Unambiguous
• Complete
• Consistent
• Ranked for importance and/or stability
• Verifiable
8Prepared by: Dr. Hamdan Al-Sabri
Our objective to study strength and weakness points for the techniques,
approaches , tools and suggested a new one depend on this factors .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwarerequirementsengineering-170928200102/85/Software-requirements-engineering-8-320.jpg)
![The Inputs and Outputs for RE[2]
9Prepared by: Dr. Hamdan Al-Sabri](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwarerequirementsengineering-170928200102/85/Software-requirements-engineering-9-320.jpg)
![Requirement Elicitation[2]
• Requirement Elicitation: the process through which the
customer and developer discover, review, articulate, and
understand the users’ needs and constraints on the software
and development activities
• Requirements elicitation is the process of seeking,
uncovering, acquiring, and elaborating requirements for
computer based systems[3].
10Prepared by: Dr. Hamdan Al-Sabri](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwarerequirementsengineering-170928200102/85/Software-requirements-engineering-10-320.jpg)
![Elicitation Process[2]
• Establish objectives
– Business goals
– Problem to be solved
– System constraints
• Understand background
– Organizational structure
– Application domain
– Existing systems
11Prepared by: Dr. Hamdan Al-Sabri
• Organize knowledge
– Stakeholder identification
– Goal prioritization
– Domain knowledge filtering
• Collect requirements
– Stakeholder requirements
– Domain requirements
– Organizational requirements](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwarerequirementsengineering-170928200102/85/Software-requirements-engineering-11-320.jpg)
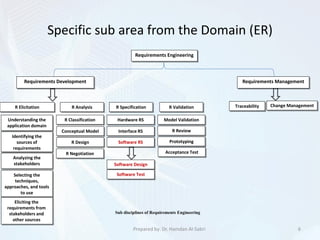
![Requirements Elicitation: Techniques,
Approaches, and Tools[3]
• Requirements Elicitation Techniques.
• Requirements Elicitation Approaches.
• Requirements Elicitation Tools.
12Prepared by: Dr. Hamdan Al-Sabri](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwarerequirementsengineering-170928200102/85/Software-requirements-engineering-12-320.jpg)







![Elicitation Techniques[1]
• Traditional techniques
• Cognitive techniques
• Collaborative techniques
• Contextual approaches
20Prepared by: Dr. Hamdan Al-Sabri](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwarerequirementsengineering-170928200102/85/Software-requirements-engineering-20-320.jpg)



