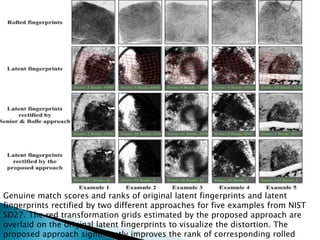
This document discusses challenges in fingerprint recognition related to low quality fingerprints and distortions. It summarizes approaches to detect distorted fingerprints and rectify them for fingerprint matching. The key approaches discussed are:
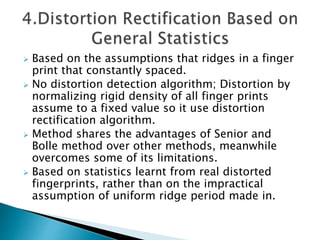
1. Detecting distortions by analyzing registered ridge orientation and period maps of fingerprints as feature vectors.
2. Rectifying distortions by searching a reference database of distorted fingerprints to find the nearest neighbor and corresponding distortion field to inverse transform the input fingerprint.
3. Evaluating these approaches on benchmark datasets shows improved detection of distorted fingerprints and higher matching accuracy after rectification compared to previous methods.








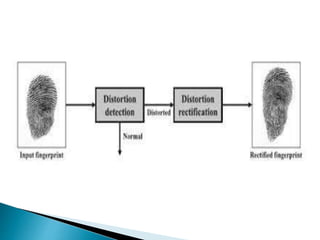











![Experiment
1st evaluate the detection algorithm.
Evaluate the rectification algorithm.
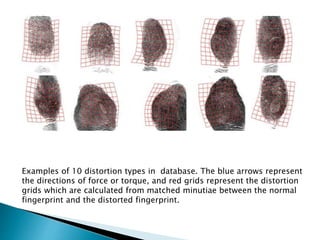
Performance of distorted delectation
Three distorted examples. Our previous algorithm [1] fails to detect their
distortion, while the current algorithm can detect their distortion
correctly. The red transformation grids estimated by the proposed
algorithm are overlaid on them. The blue numbers show the matching
scores without/with rectification.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/detectionandrectificationofdistortedfingerprint-161108072059/85/Detection-and-rectification-of-distorted-fingerprint-23-320.jpg)