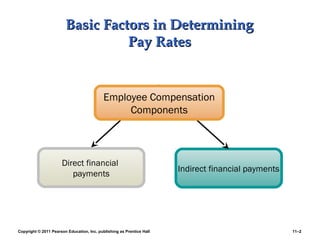
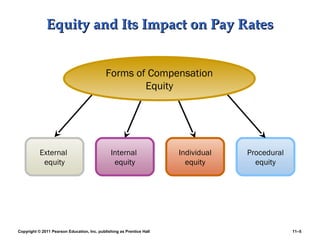
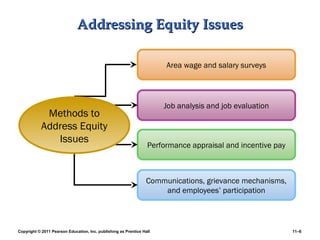
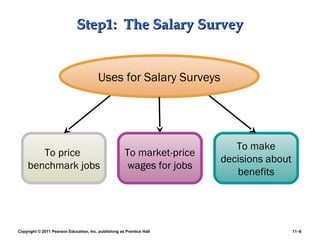
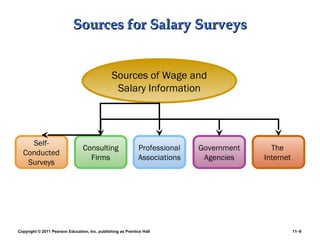
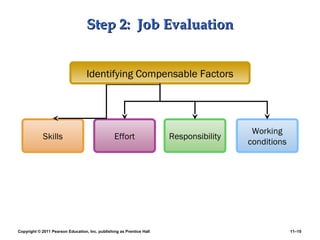
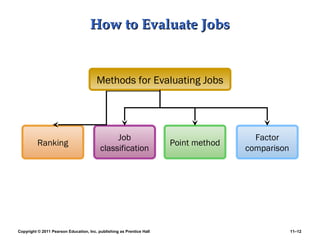
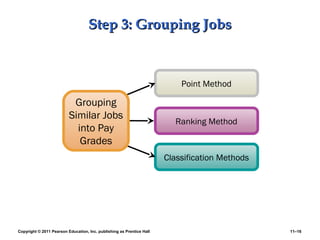
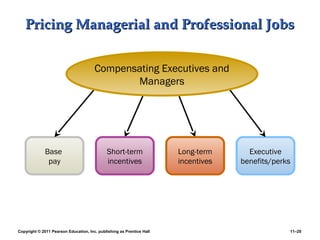
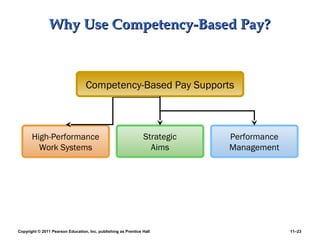
This PowerPoint presentation discusses establishing strategic pay plans. It covers topics such as determining pay rates based on factors like internal equity, conducting salary surveys, job evaluation methods, grouping jobs into pay grades, using wage curves to price grades, and fine-tuning pay rates. It also addresses issues like compensation for managers and professionals, competency-based pay, broadbanding, the gender pay gap, and automating compensation administration. The overall presentation provides an overview of developing compensation systems aligned with business strategy.