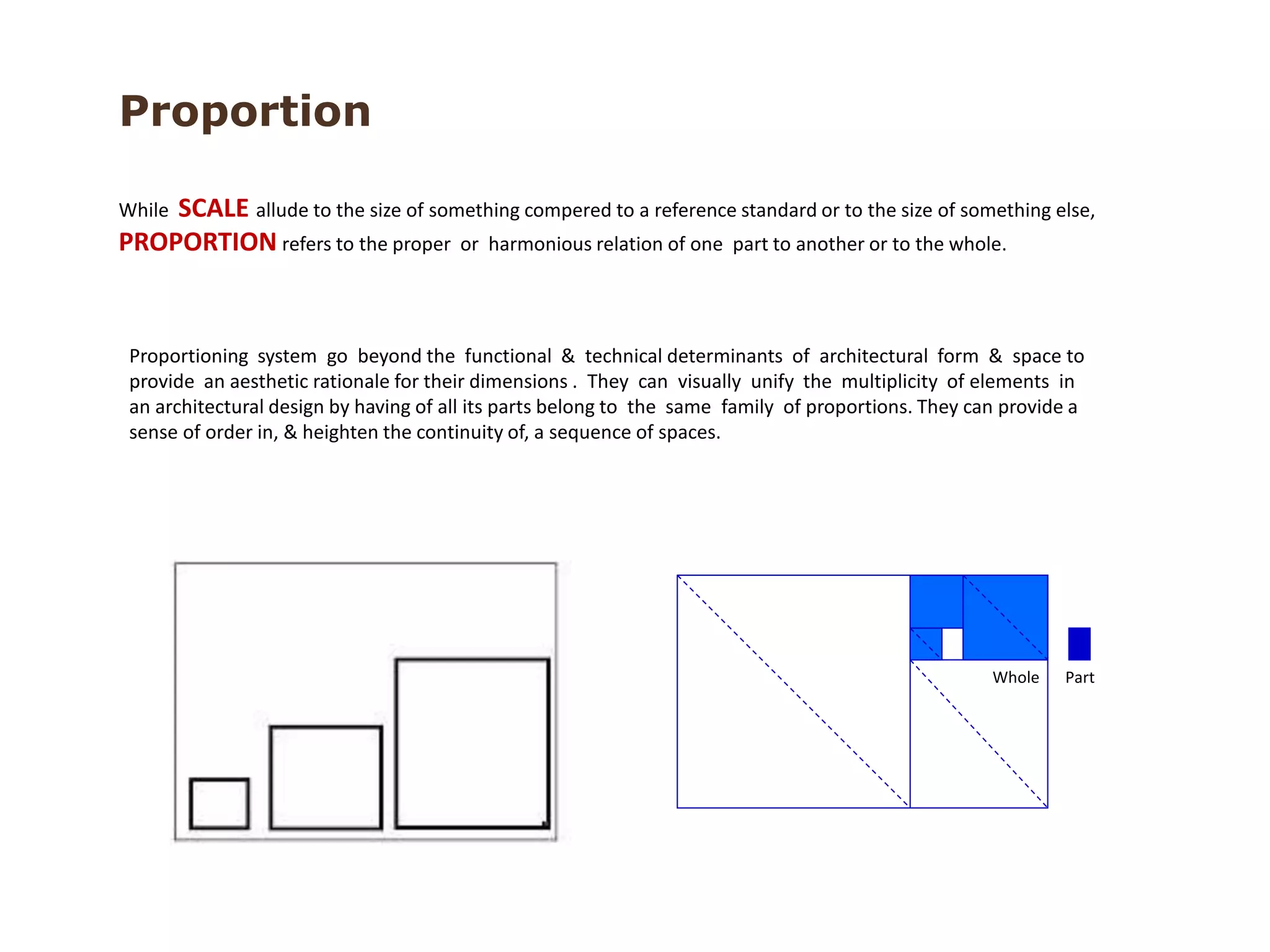
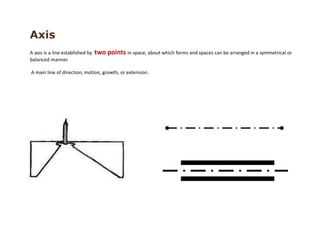
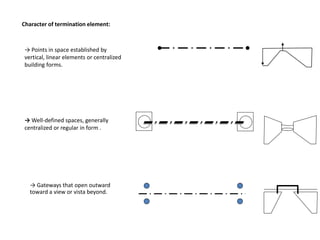
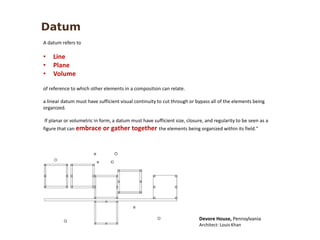
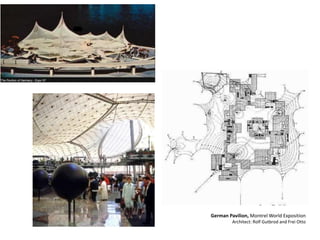
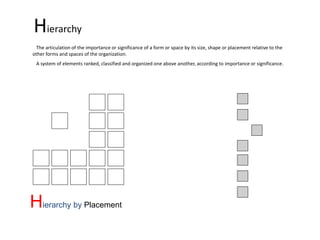
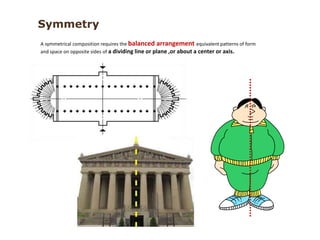
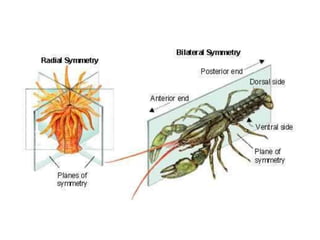
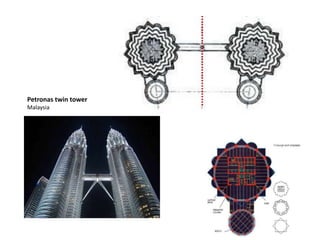
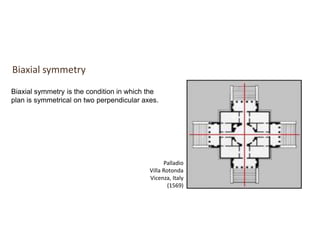
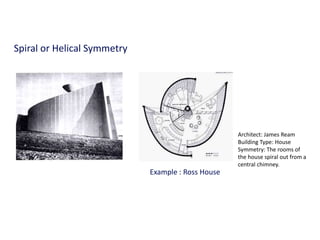
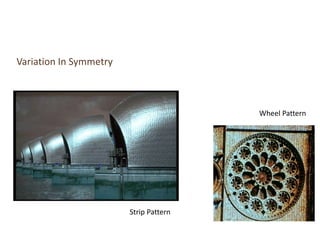
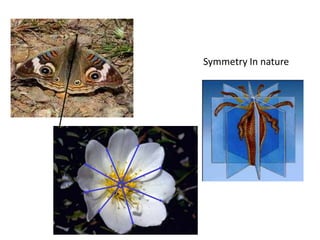
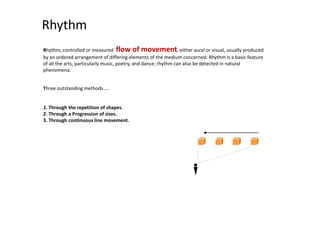
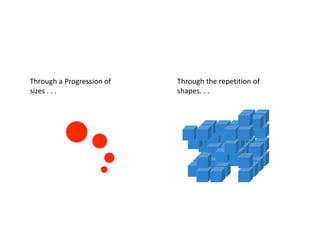
The document discusses several key concepts in architectural design including scale, proportion, human scale, hierarchy, symmetry, rhythm, and axis. It provides definitions and examples to illustrate each concept. Scale refers to size relative to a standard, while proportion is the relationship between parts and the whole. Elements like windowsills and door frames give buildings a human scale. Hierarchy is expressed through varying size, shape or placement of elements to show importance. Symmetry involves balanced patterns around a center. Rhythm uses repetition of shapes, progression of sizes, or line movement. An axis establishes a line of organization.