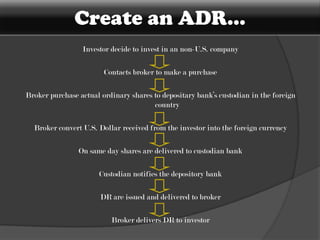
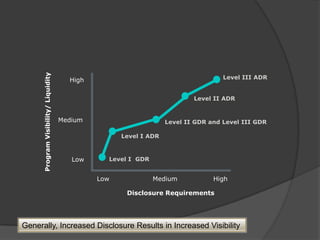
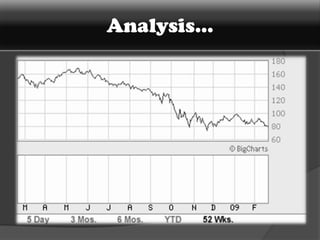
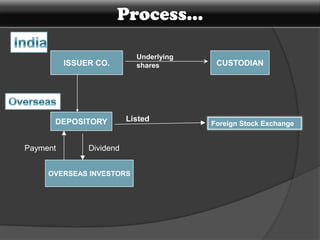
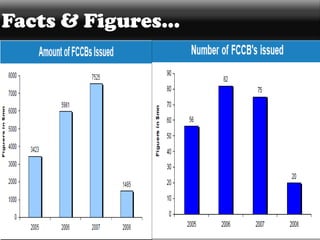
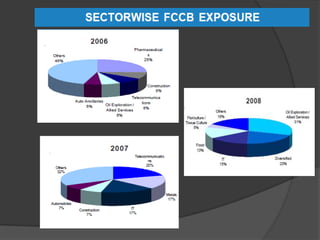
American Depository Receipts (ADRs), Global Depository Receipts (GDRs), and Foreign Currency Convertible Bonds (FCCBs) allow Indian companies to raise capital from foreign markets. ADRs/GDRs represent shares of an Indian company trading on a foreign stock exchange. FCCBs are bonds issued in foreign currency that are convertible into shares. Key benefits include increased visibility, flexibility to list abroad, and diversifying investor base. Key risks include currency exchange rate fluctuations and lack of familiarity with foreign markets. Regulatory approvals from SEBI, RBI, and relevant foreign authorities are required for issuing these instruments.