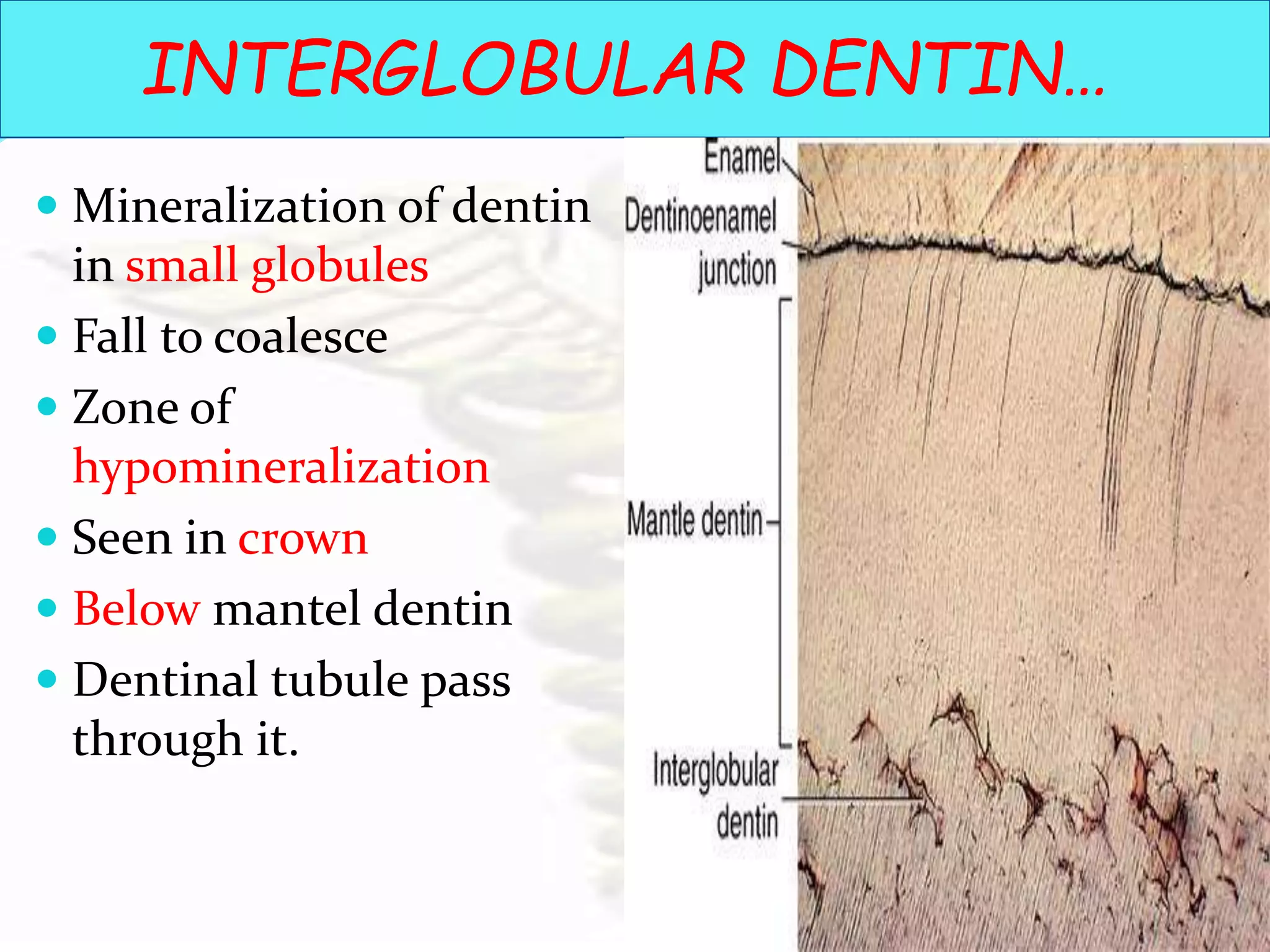
The document provides an overview of dentin, including its composition, structure, types, properties and historical discoveries. Some key points summarized:
1. Dentin makes up the bulk of teeth and is composed of 65-70% organic material including collagen, and 20-25% inorganic material including calcium phosphate. It contains dentinal tubules that branch throughout.
2. There are three types of dentin - primary, secondary, and tertiary. Primary dentin forms most of the tooth, secondary develops after root formation, and tertiary is produced in response to damage or irritation.
3. Dentin has physical properties including a thickness of 3-10mm, hardness of 68KHN, and permeability