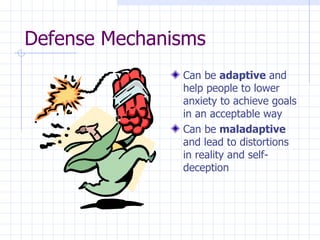
Defense mechanisms are automatic psychological processes that protect individuals from anxiety and awareness of internal or external dangers. They can be adaptive in helping people lower anxiety to achieve goals, but can also be maladaptive and lead to distortions. Freud identified major defenses like suppression, altruism, humor, and sublimation that manage conflict on a relatively unconscious level. Defenses range from mature to neurotic to immature, with mature defenses being the most adaptive and psychotic defenses involving denial of reality.