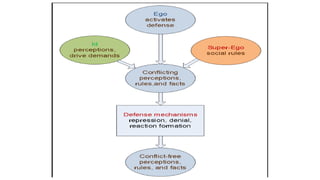
Freud began investigating ego defense mechanisms in his early works. Anna Freud later provided more comprehensive descriptions of individual defense mechanisms in her landmark book. Defense mechanisms operate unconsciously to resolve conflicts and reduce anxiety when the id is in serious conflict with the ego and superego. They can be classified as either positive or negative depending on their results. Positive defenses include compensation, substitution, sublimation, rationalization, repression, undoing, identification, and intellectualization. Negative defenses include suppression, displacement, projection, regression, fixation, fantasy, reaction formation, conversion, dissociation, and denial.