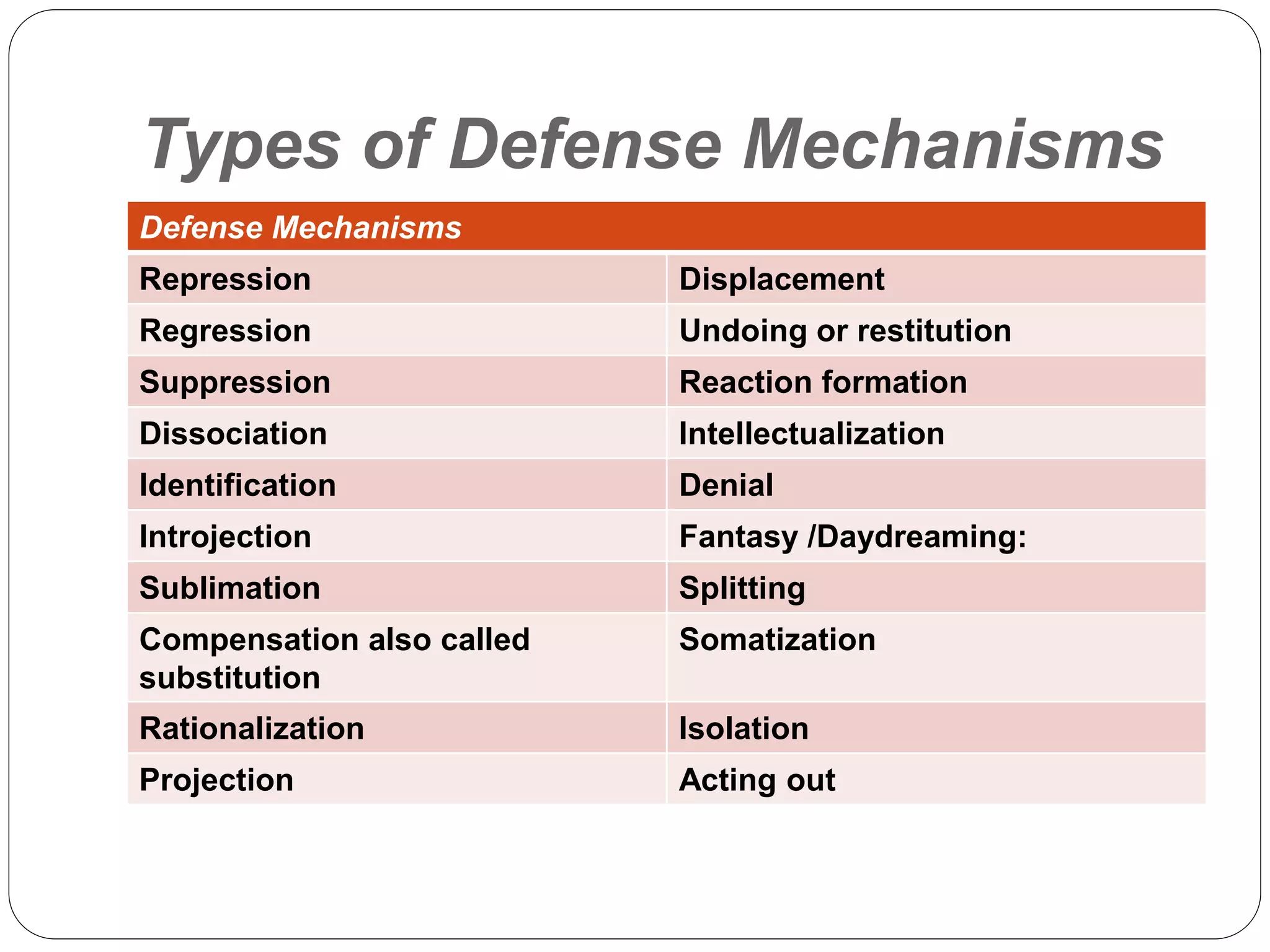
Defense mechanisms are unconscious coping strategies that help reduce anxiety and protect self-esteem. They include repression of unwanted thoughts, displacement of feelings onto safer targets, and rationalization through unrealistic excuses. The document outlines various defense mechanisms ranging from highly adaptive mechanisms like sublimation to immature ones like denial, as well as examples of how each might manifest.