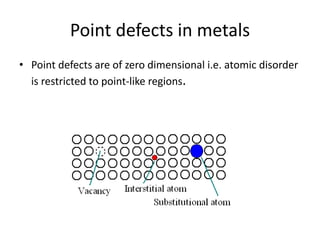
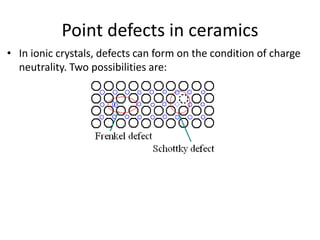
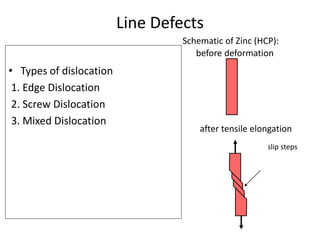
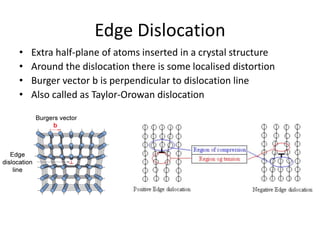
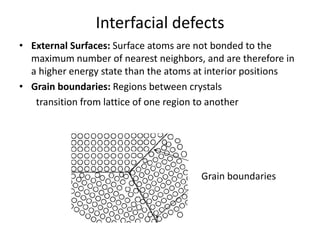
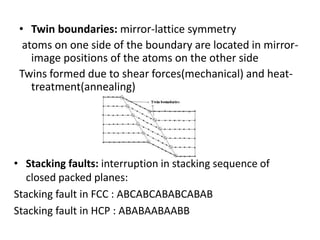
This document discusses different types of crystal defects including point defects, line defects, interfacial defects, and bulk defects. It describes point defects as atomic disorders restricted to point regions, and line defects as dislocations including edge dislocations from extra half planes of atoms, screw dislocations from shear deformation, and mixed dislocations containing both. Interfacial defects are defined as surfaces, grain boundaries between crystal regions, twin boundaries of mirror-image atoms, and stacking faults interrupting closed packed plane sequences.