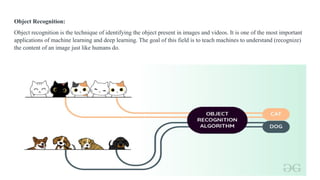
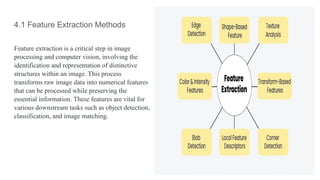
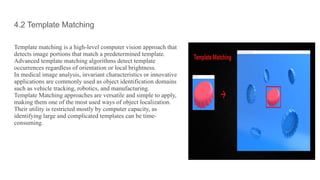
This document discusses techniques in object recognition and classification, including feature extraction methods like edge, corner, blob detection, and texture analysis, which transform raw image data into numerical features. It also explains template matching and deep learning approaches, emphasizing their role in automating tasks such as image recognition and data analysis across various applications. Additionally, it highlights the importance of deep learning in AI and its uses in fields like automotive, medical research, and natural language processing.