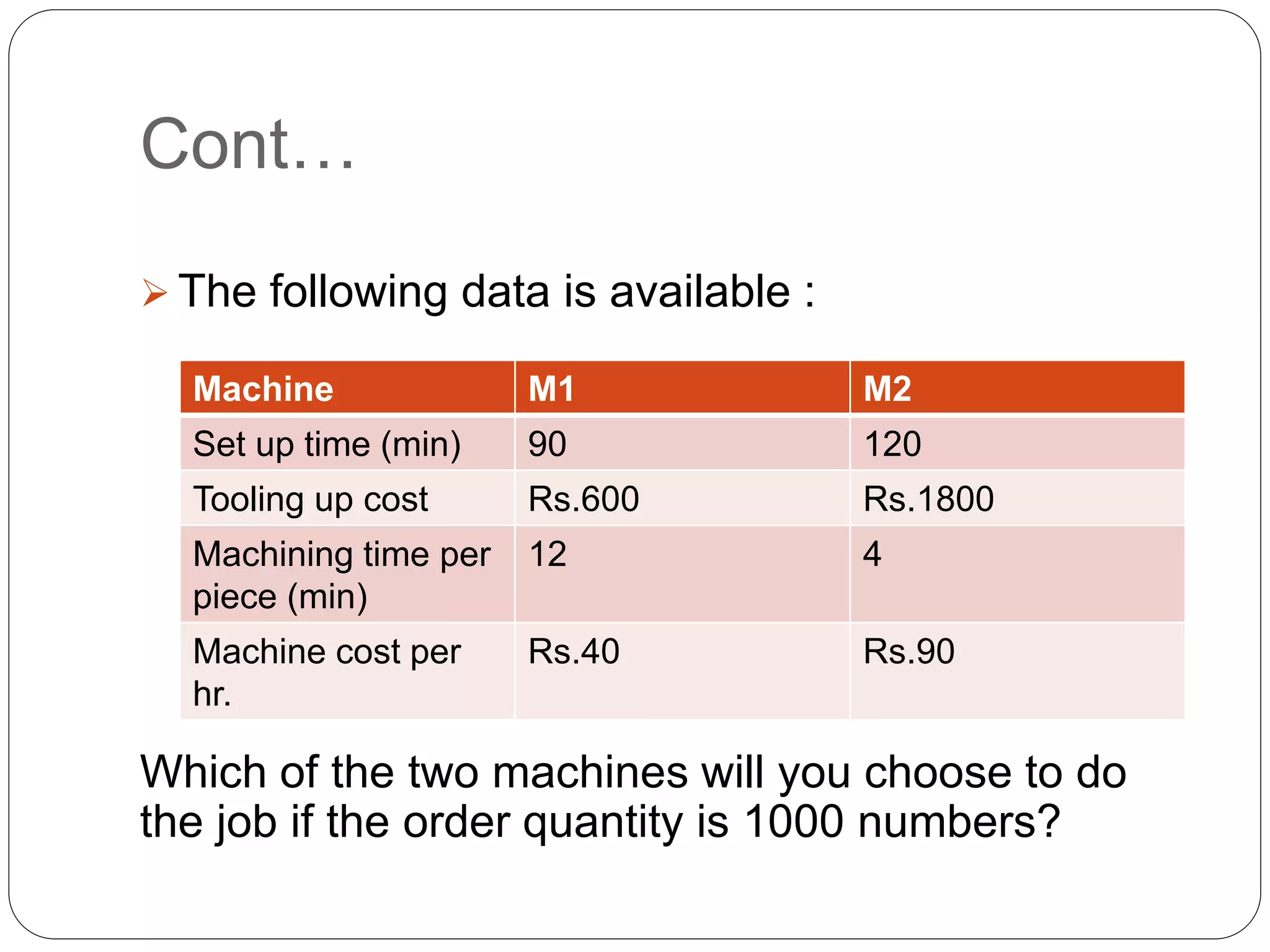
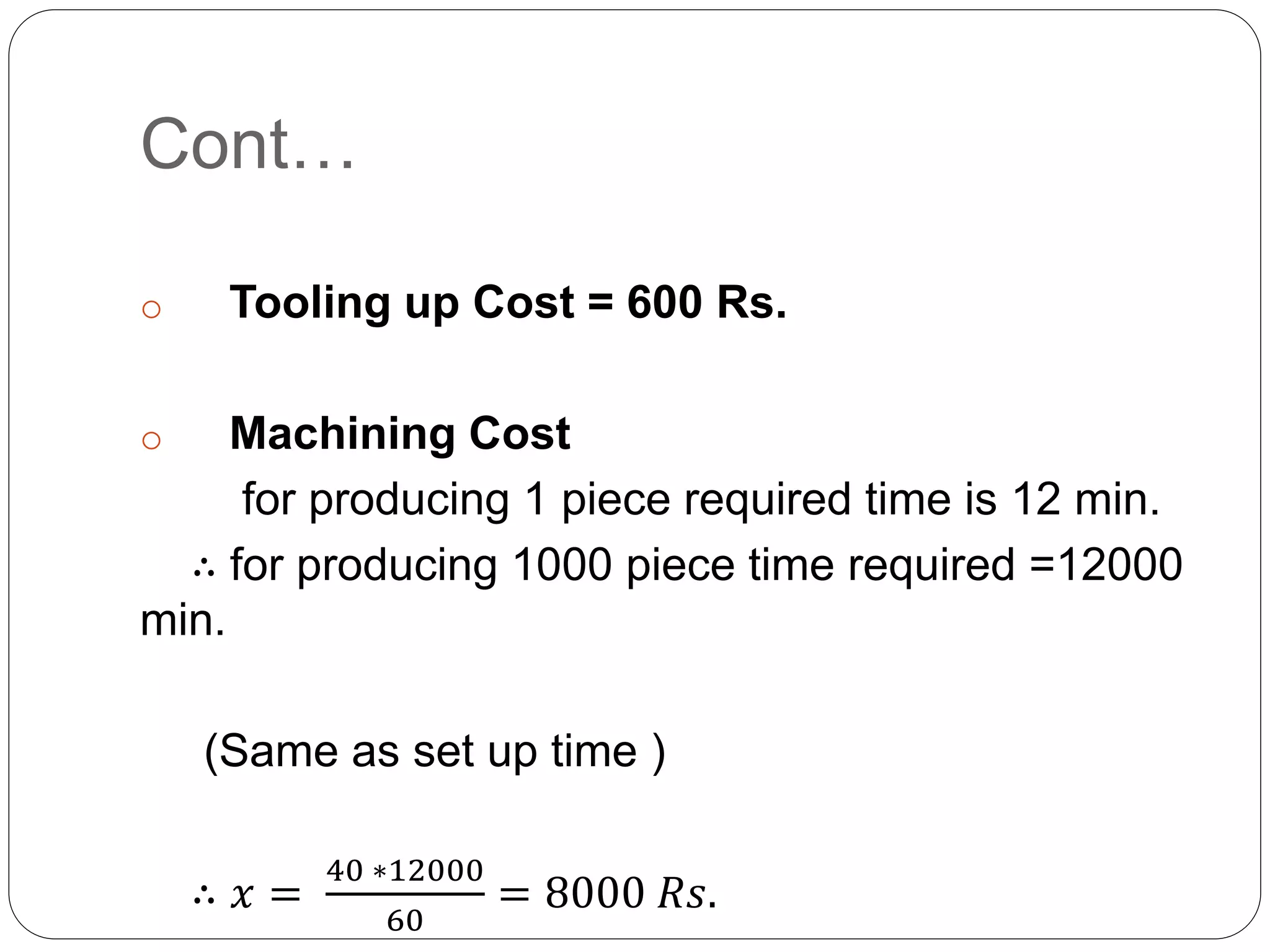
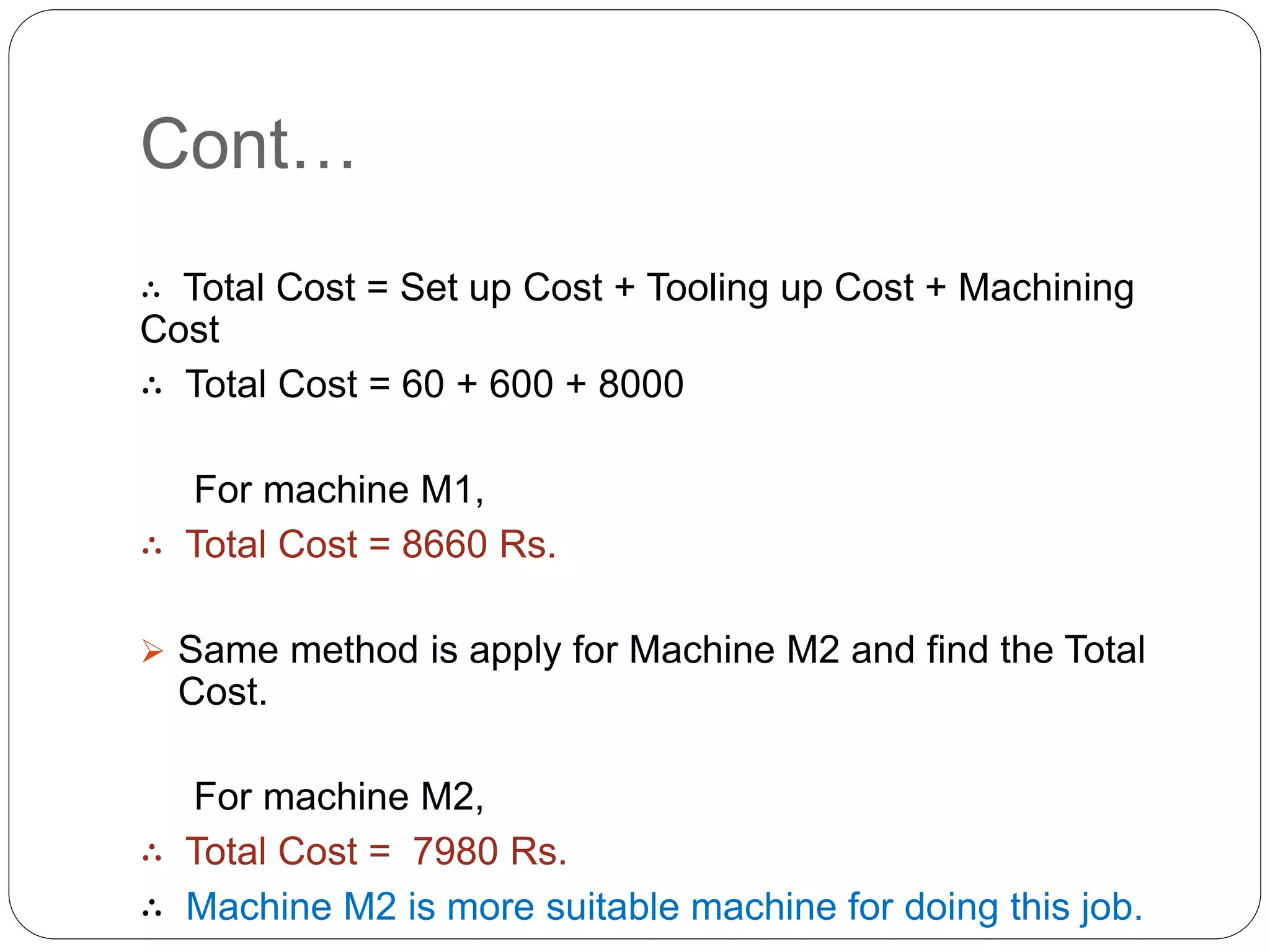
This document introduces decision theory and decision-making under certainty. It defines decision theory as a descriptive and prescriptive approach to classify levels of knowledge when making decisions. Under certainty, a decision maker has perfect information about outcomes for each alternative, allowing them to choose the best option. An example is provided where a manufacturer must choose between two machines, M1 and M2, to process an order of 1000 units. All costs are known for each machine's setup time, tooling costs, and machining time per unit. Calculations show the total cost is lower to use machine M2, so it is the best choice under the certain conditions given.