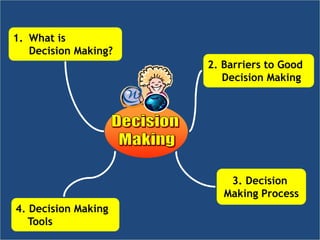
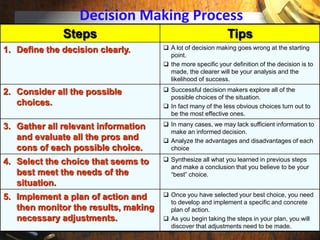
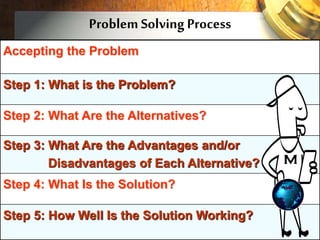
The document discusses the decision-making process and problem-solving techniques, outlining their significance and components. It highlights barriers to effective decision-making, the six C's of decision-making, and a structured process for both decision-making and problem-solving. Various tools and strategies for improving these skills are also presented.