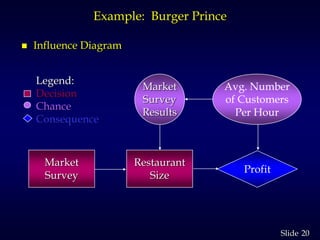
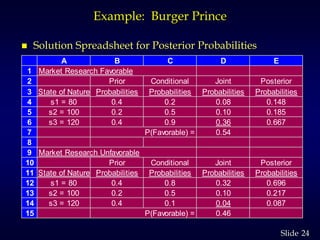
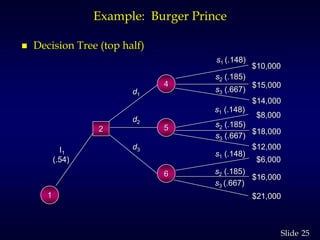
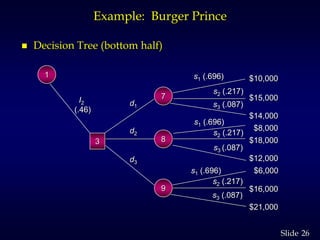
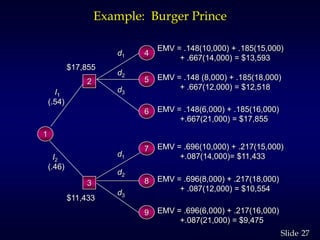
1. The document discusses quantitative decision making methods, including expected value, decision trees, and expected value of perfect and sample information.
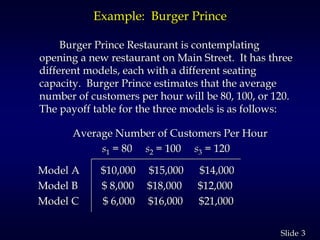
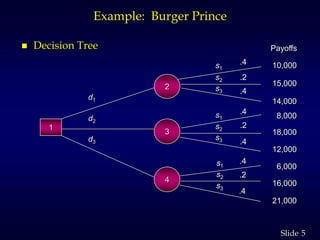
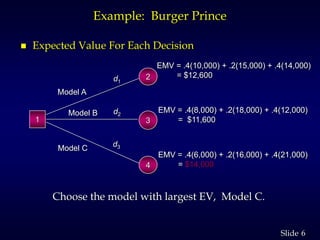
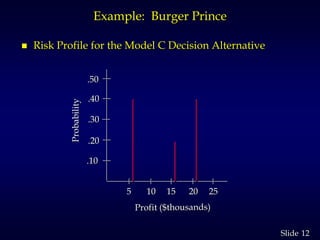
2. It provides an example of a restaurant choosing between three models based on expected number of customers. It calculates expected values and shows the optimal choice is Model C.
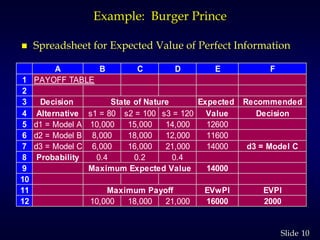
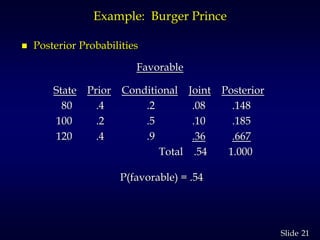
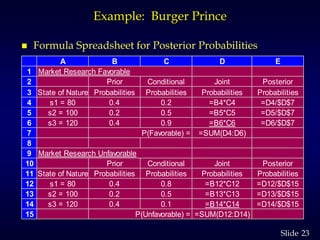
3. It then calculates the expected value of perfect information as $2,000, the increase in profit if the true customer number was known for certain. Obtaining a marketing survey costs $1,000 but only provides an expected value of sample information of $900.88, so the survey should not be purchased.