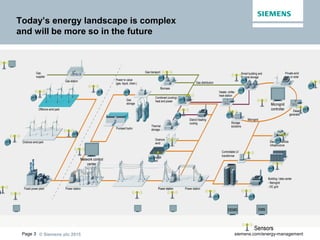
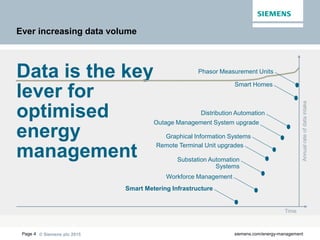
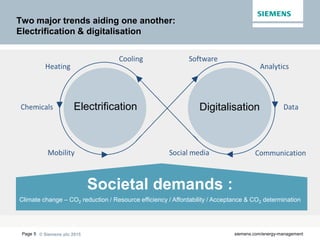
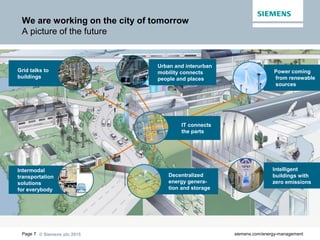
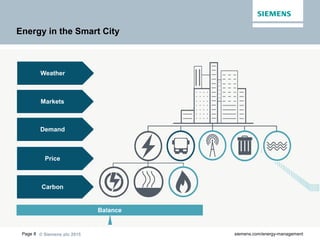
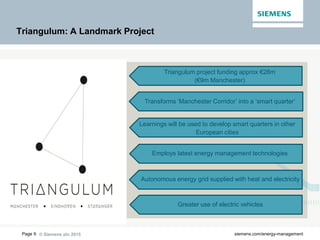
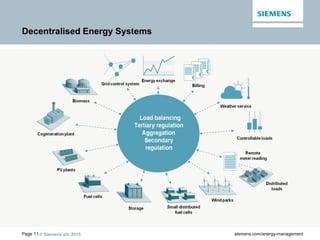
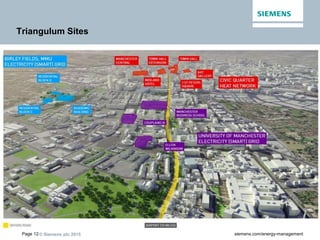
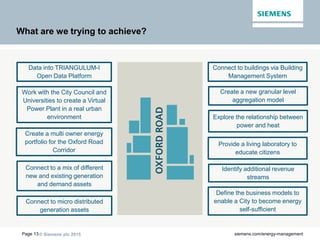
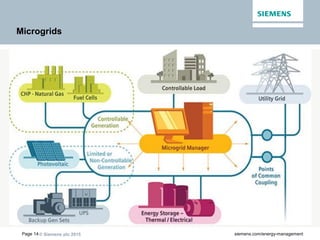
The document discusses digitalization of energy management and decentralized energy systems. It summarizes that increasing data volume is key to optimized energy management. Two major trends aiding this are electrification and digitalization to meet societal demands around issues like climate change and affordability. Examples provided include the Triangulum project transforming Manchester into a smart quarter using latest energy technologies and microgrids like one created at the University of Genoa campus.