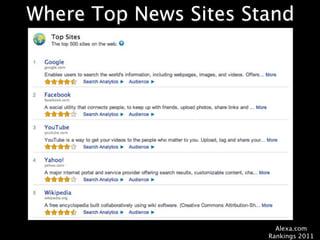
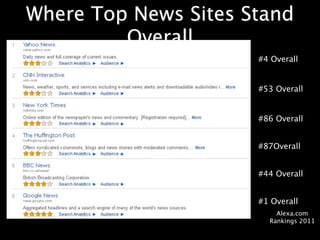
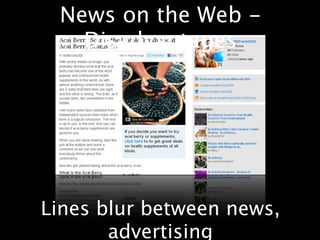
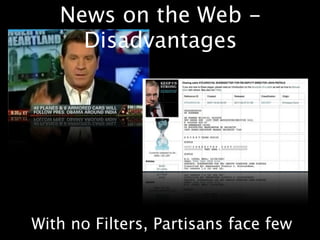
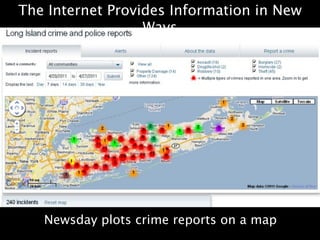
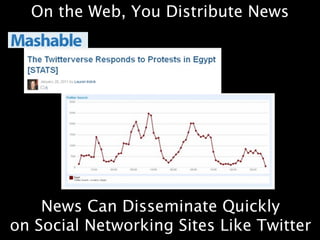
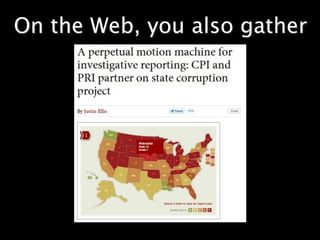
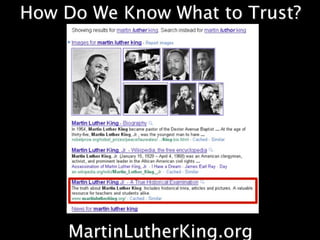
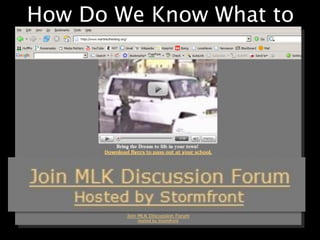
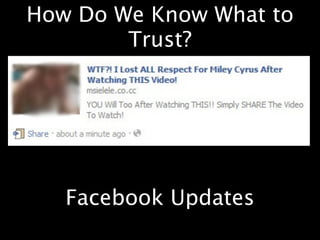
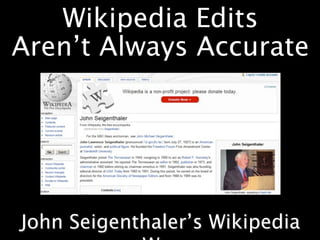
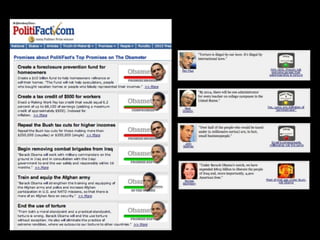
This document provides an overview of news literacy in the information age. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of finding information online, how to identify reliable sources, and how to minimize disadvantages. Key points include: the growth of internet usage, top news sites, information overload online, challenges like inaccurate information and blurred lines between news and opinion, and how to evaluate websites based on factors like date of content, citations, independence, and transparency of authorship. The document emphasizes that popularity and speed do not guarantee reliability and provides tips for fact checking information found online.