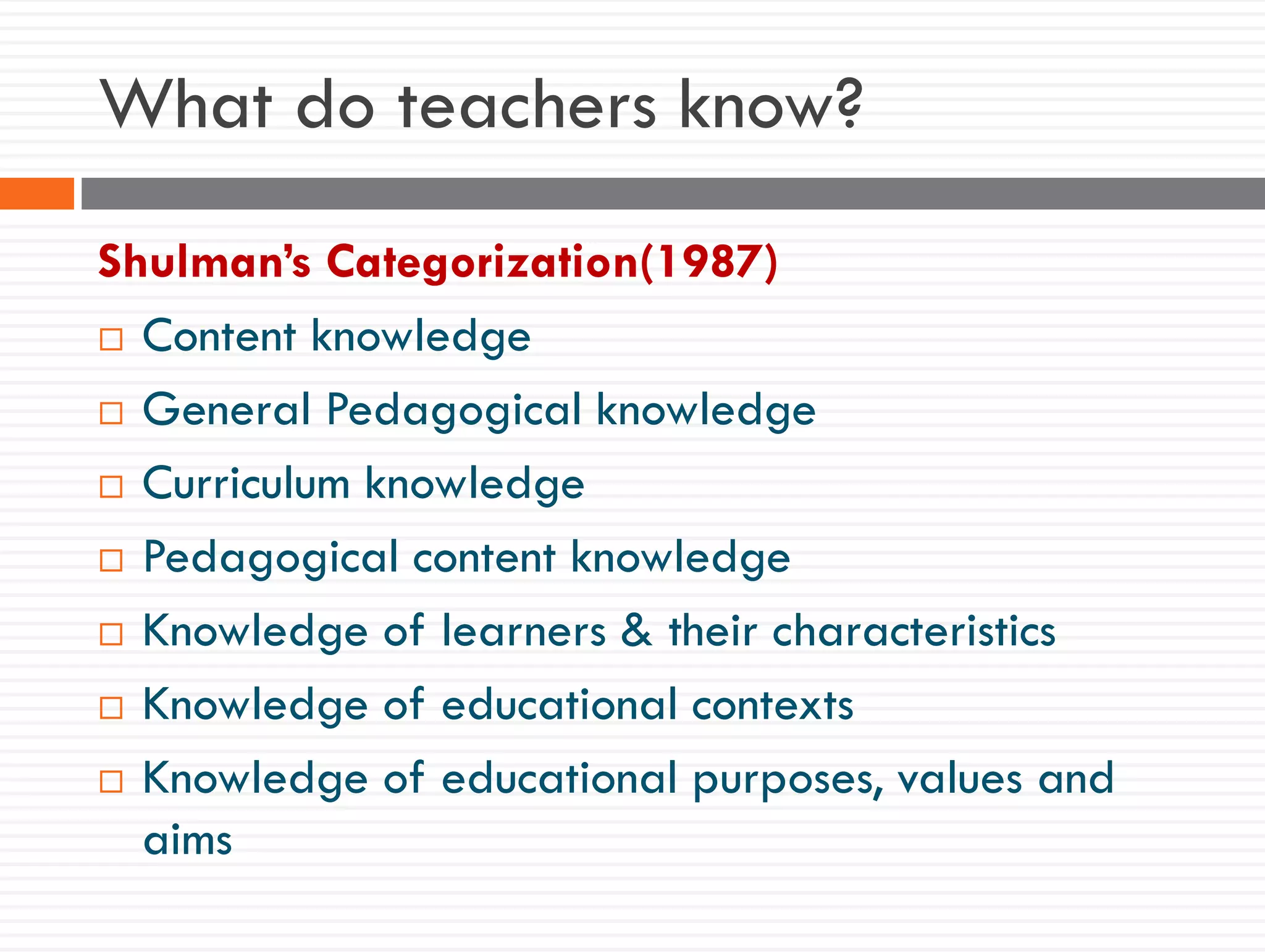
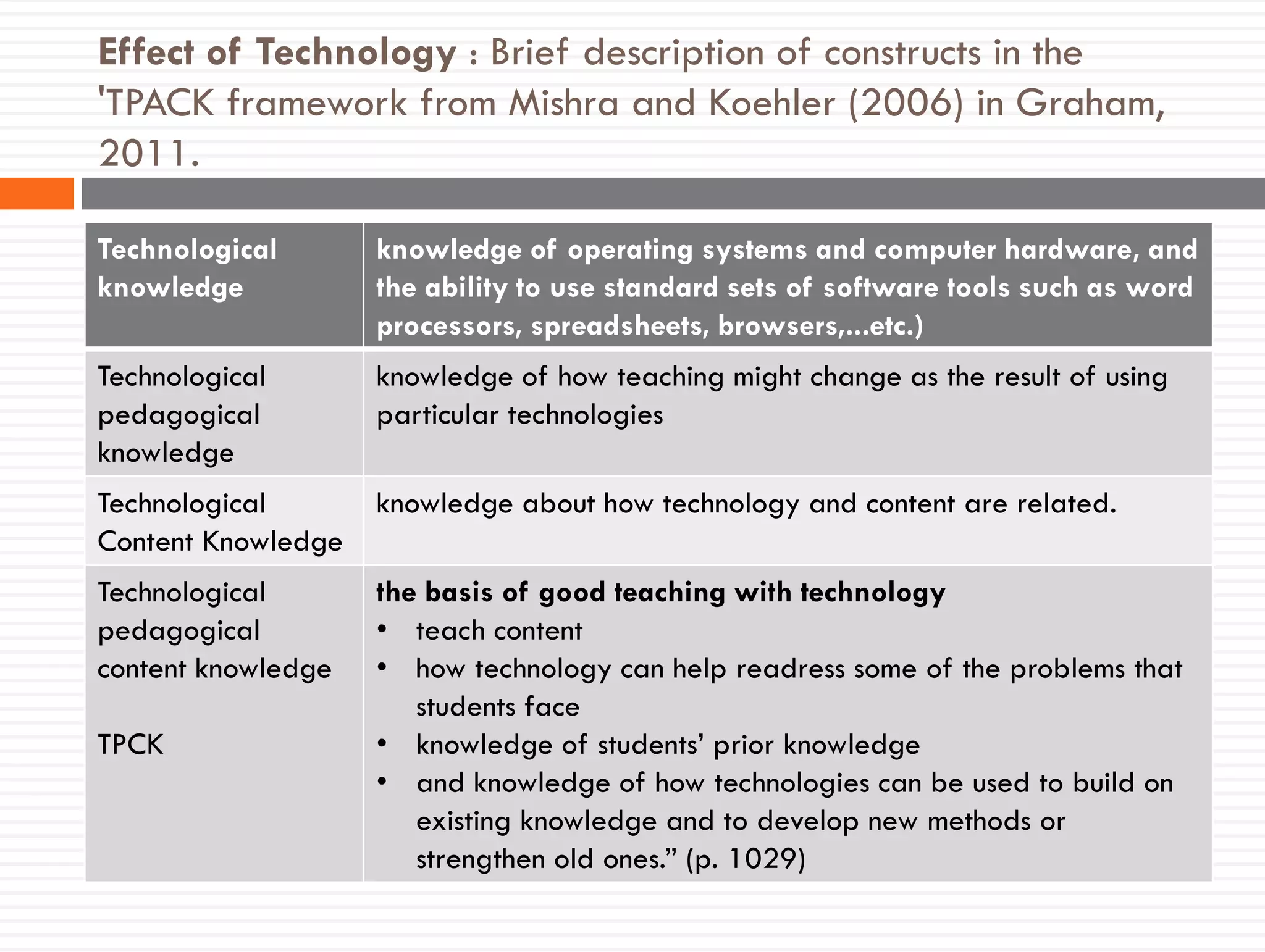
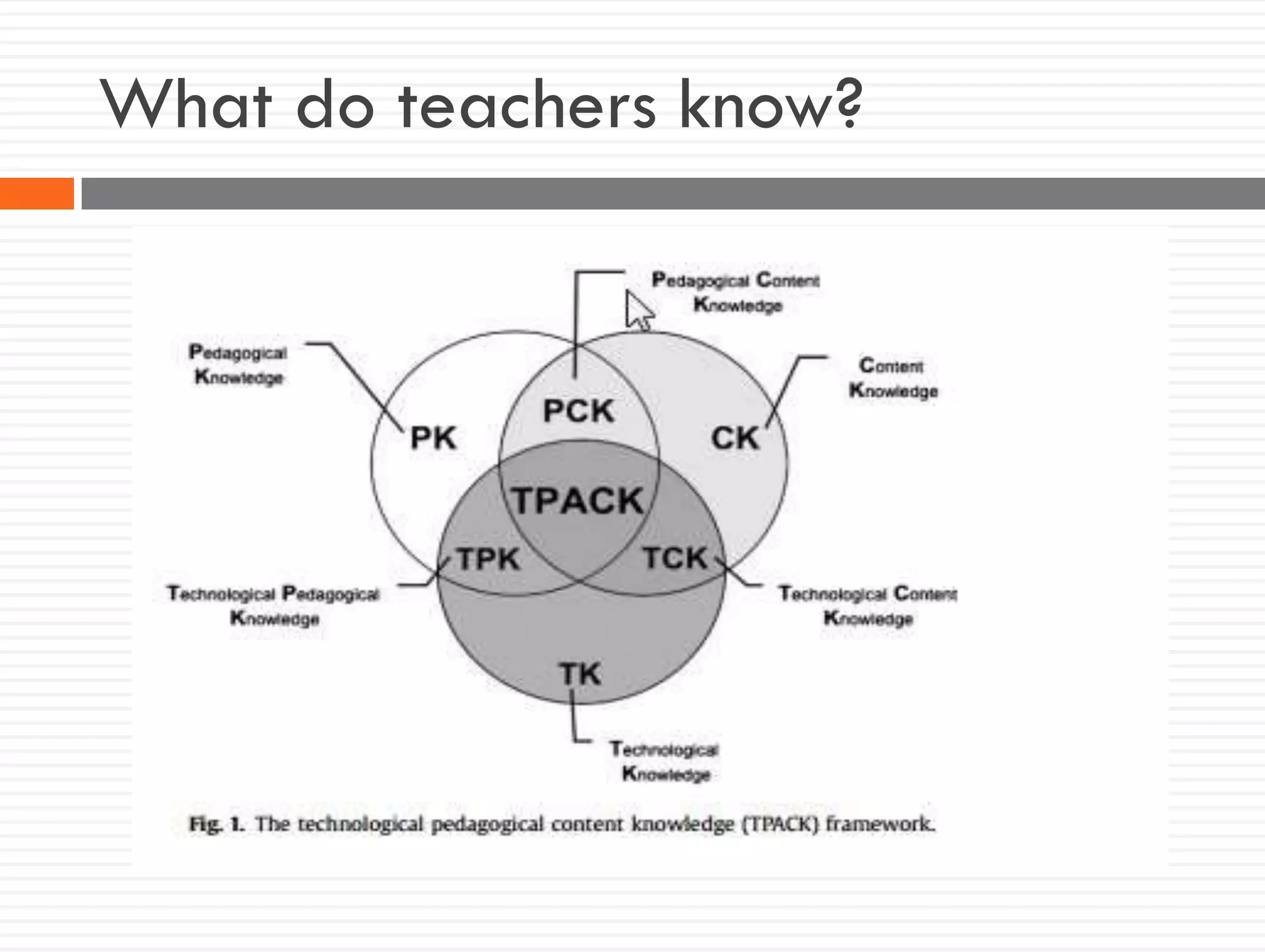
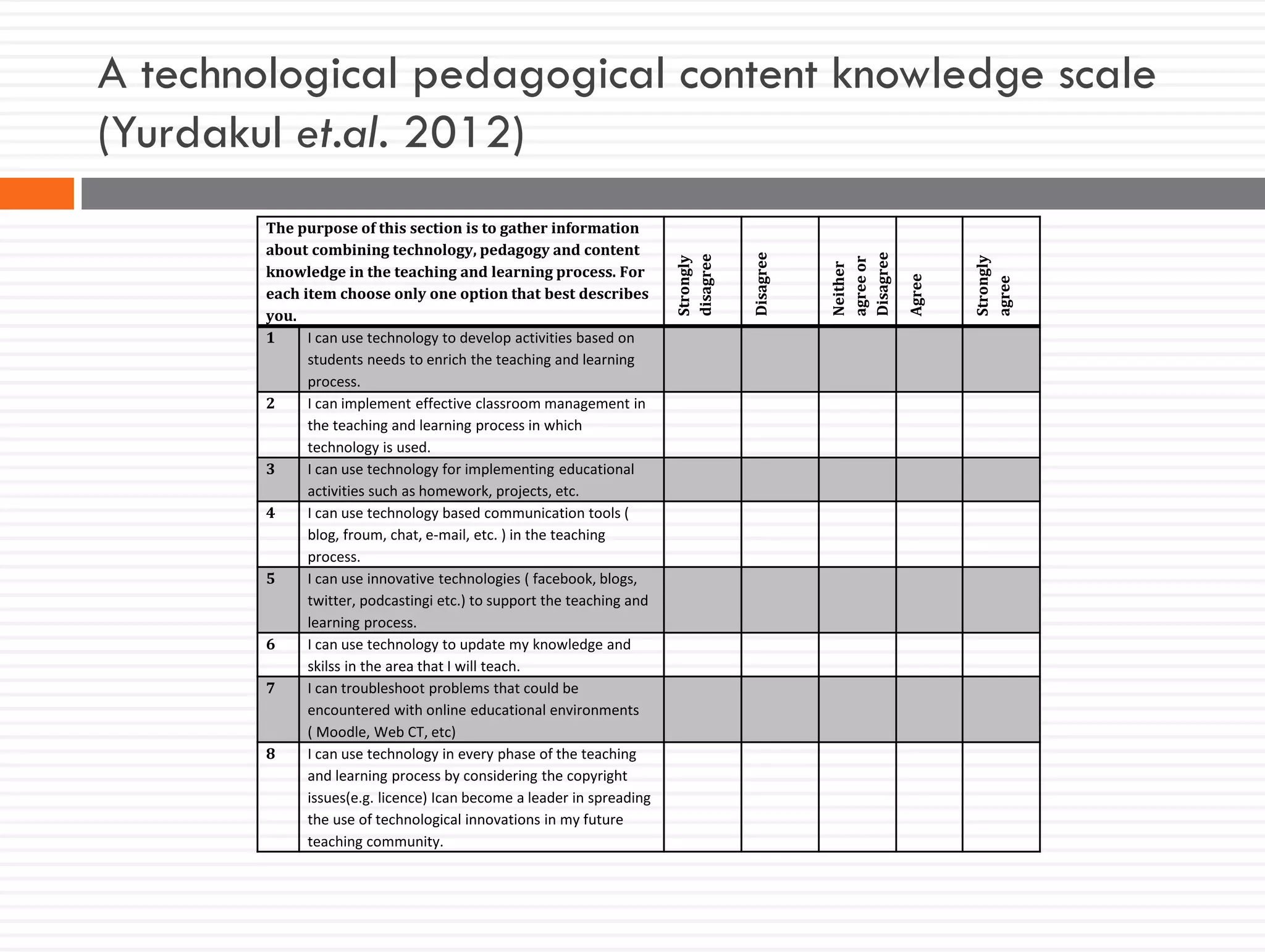
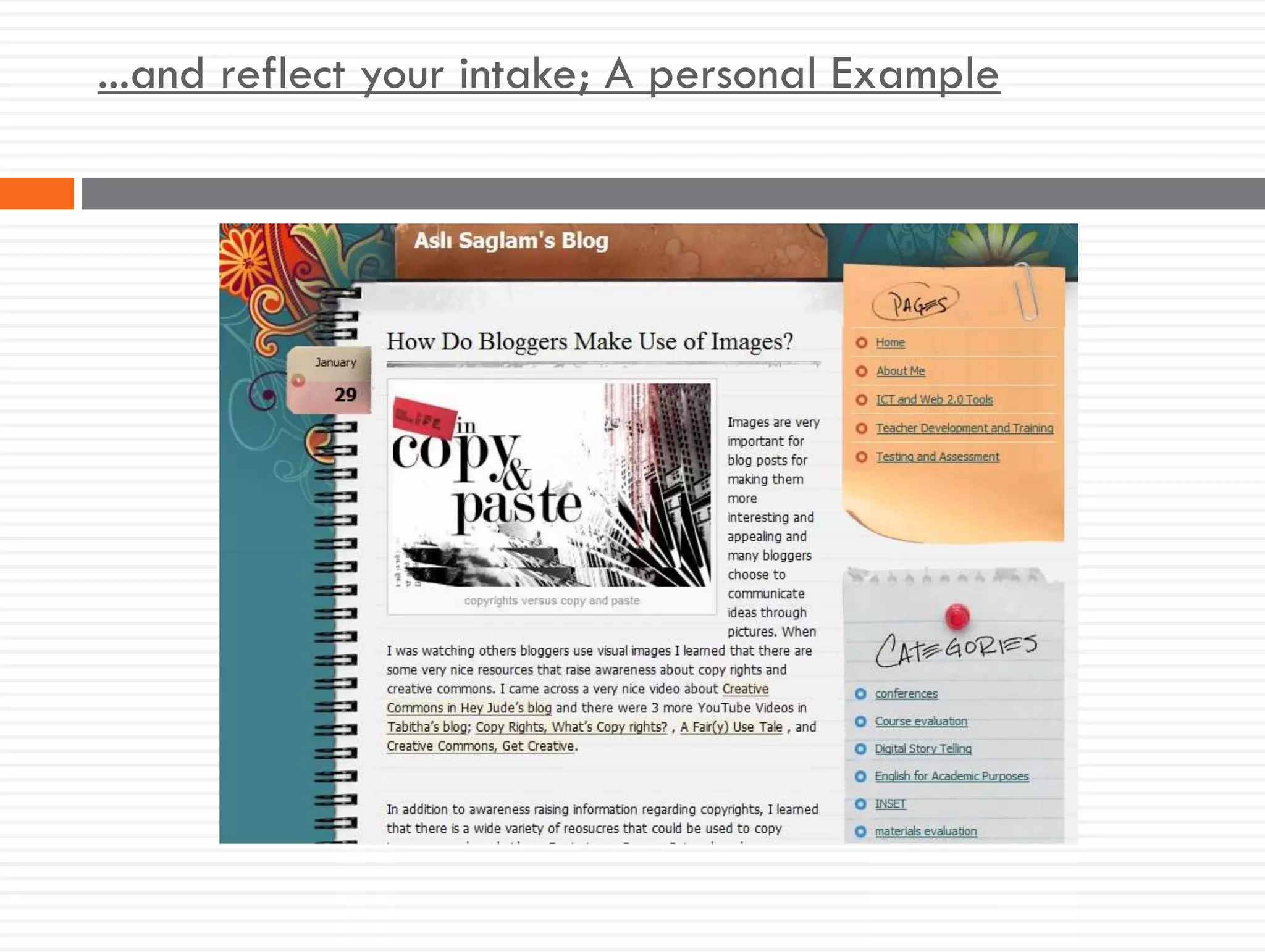
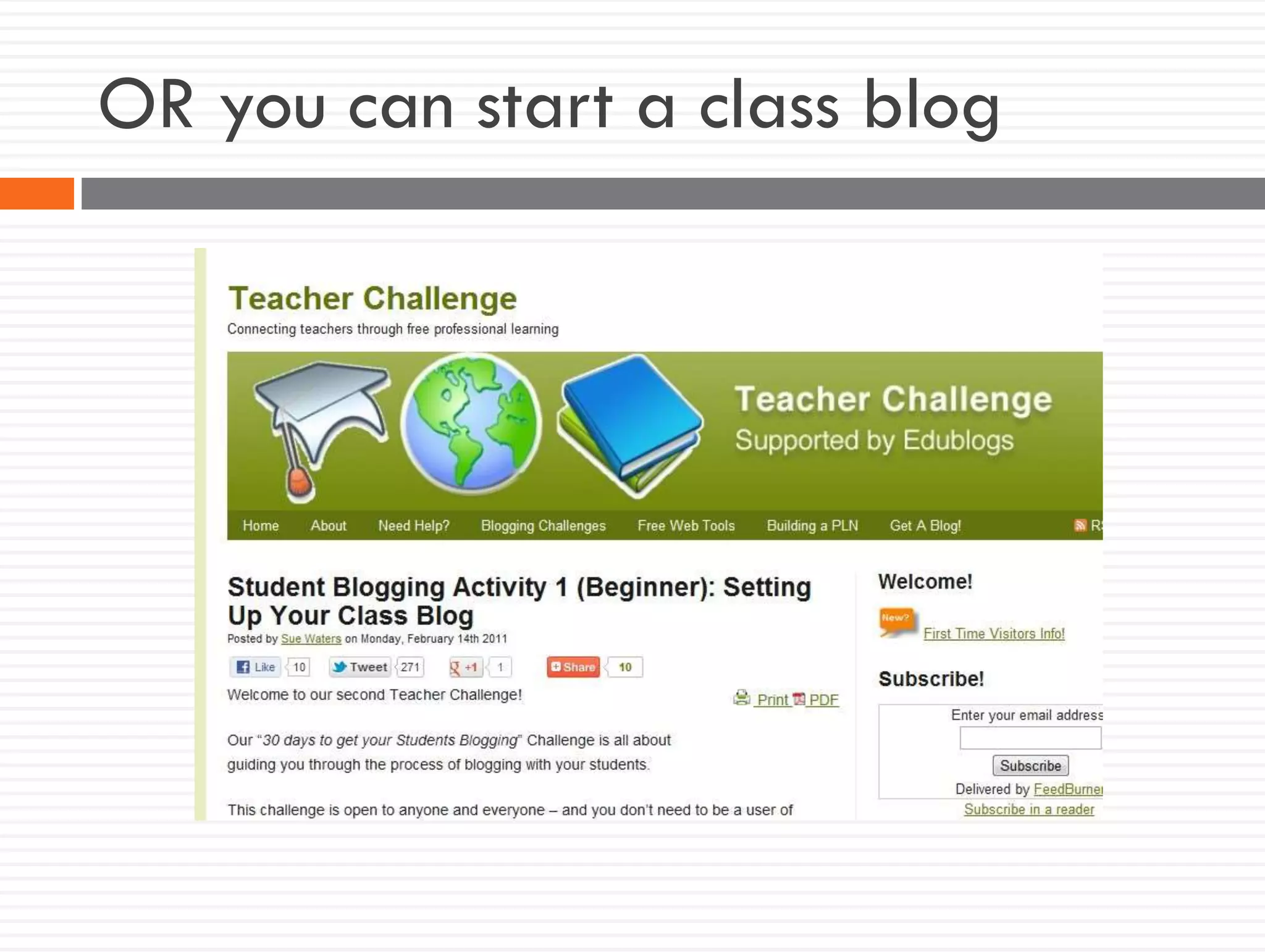
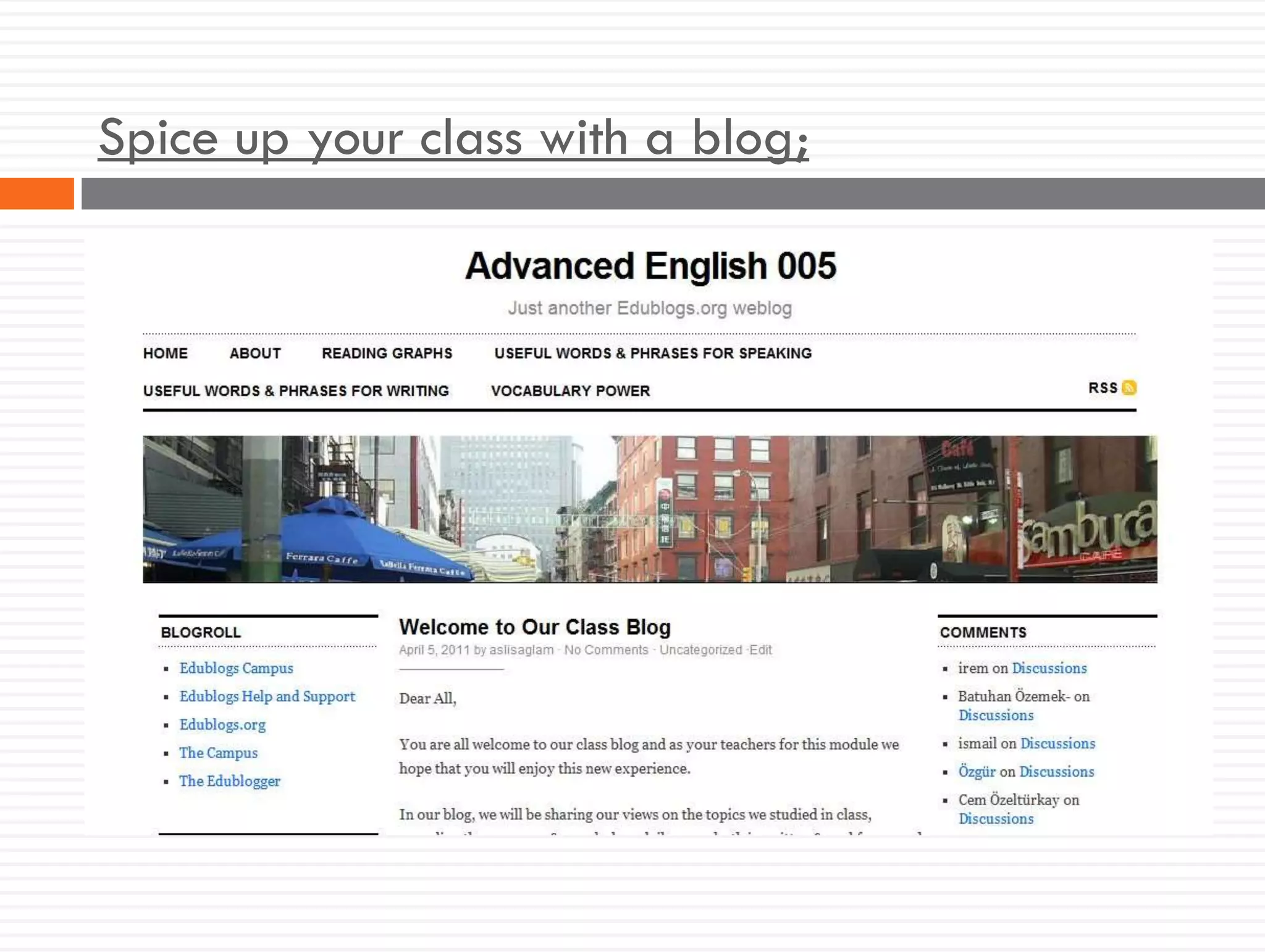
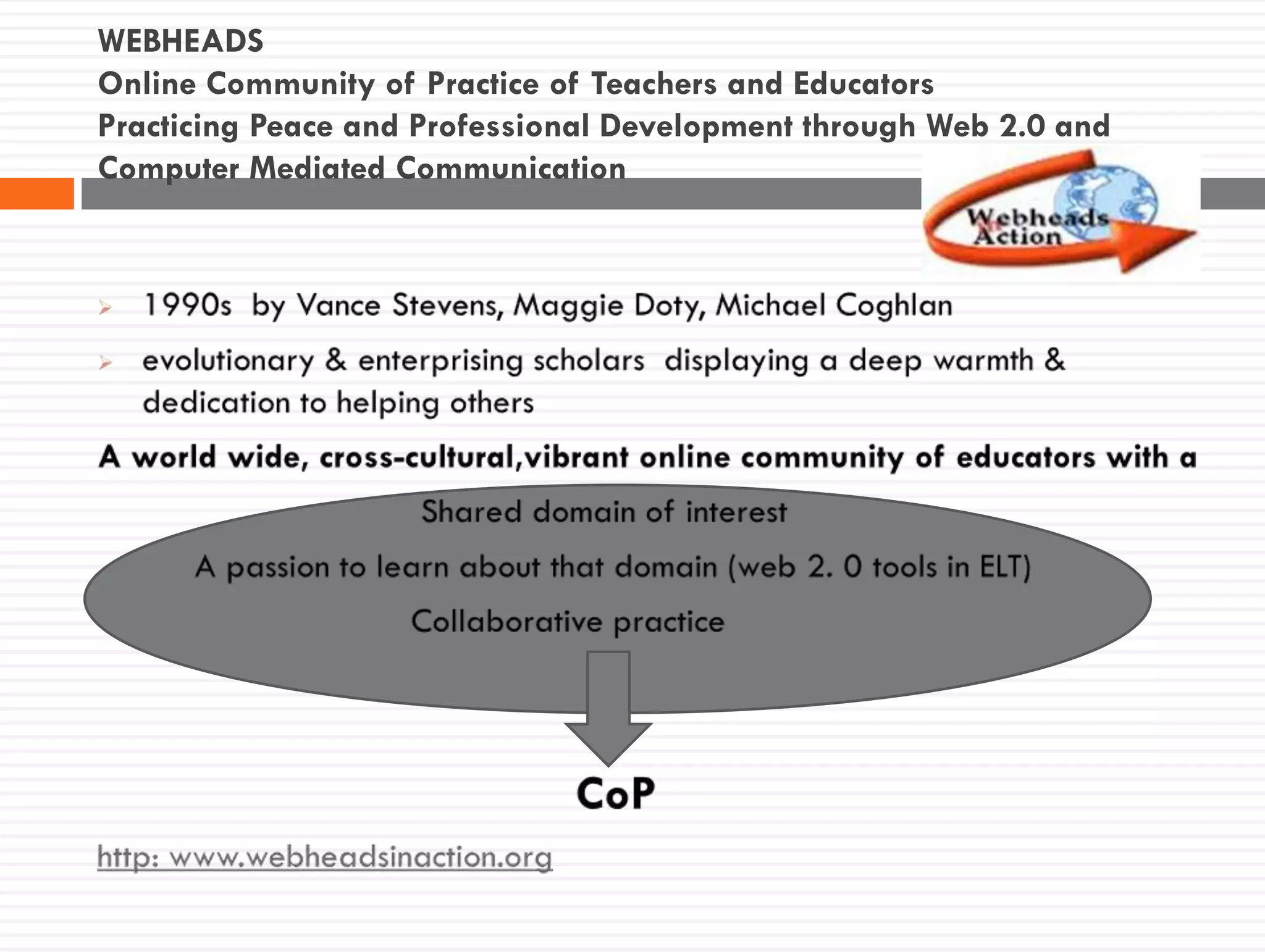
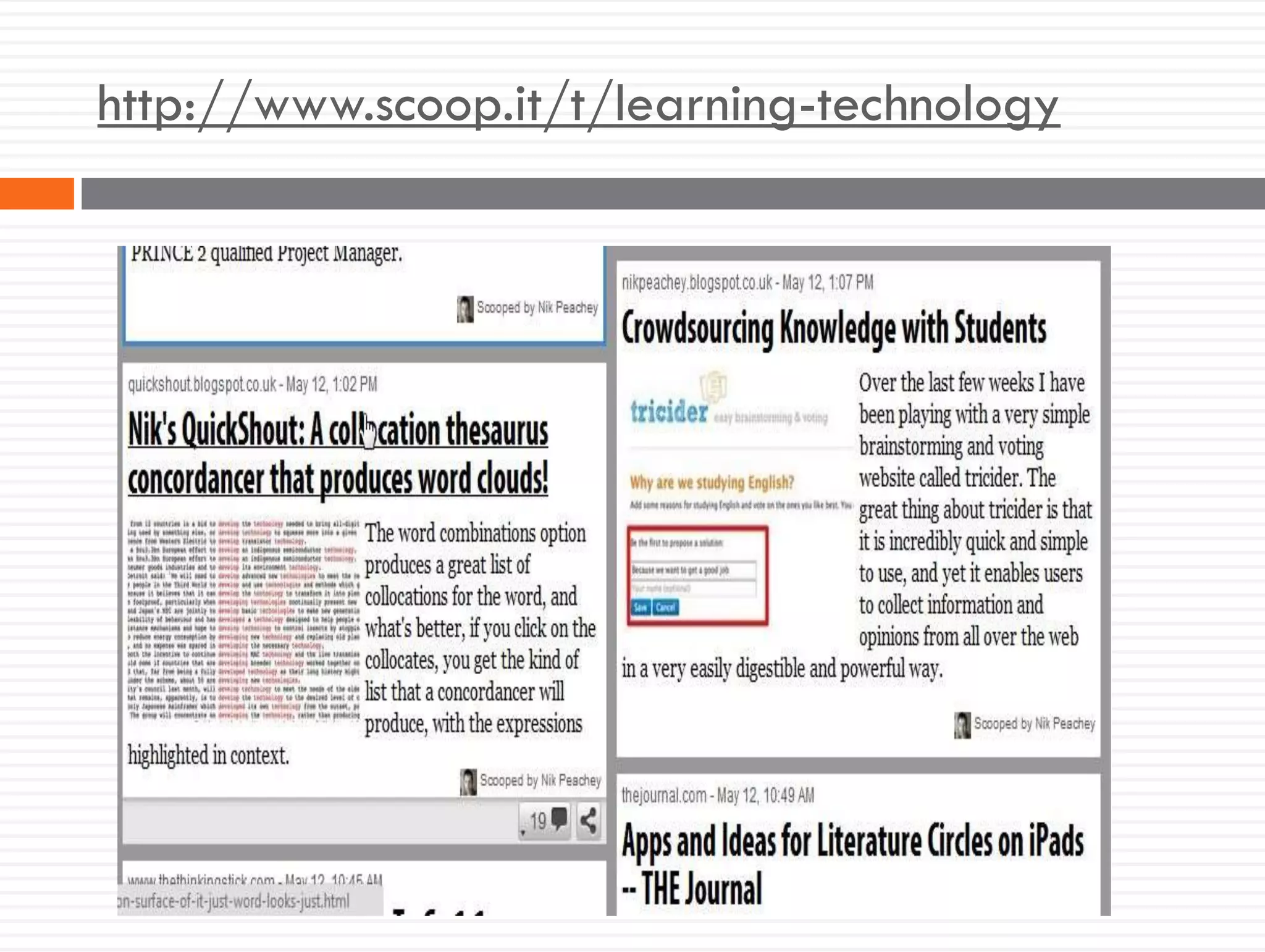
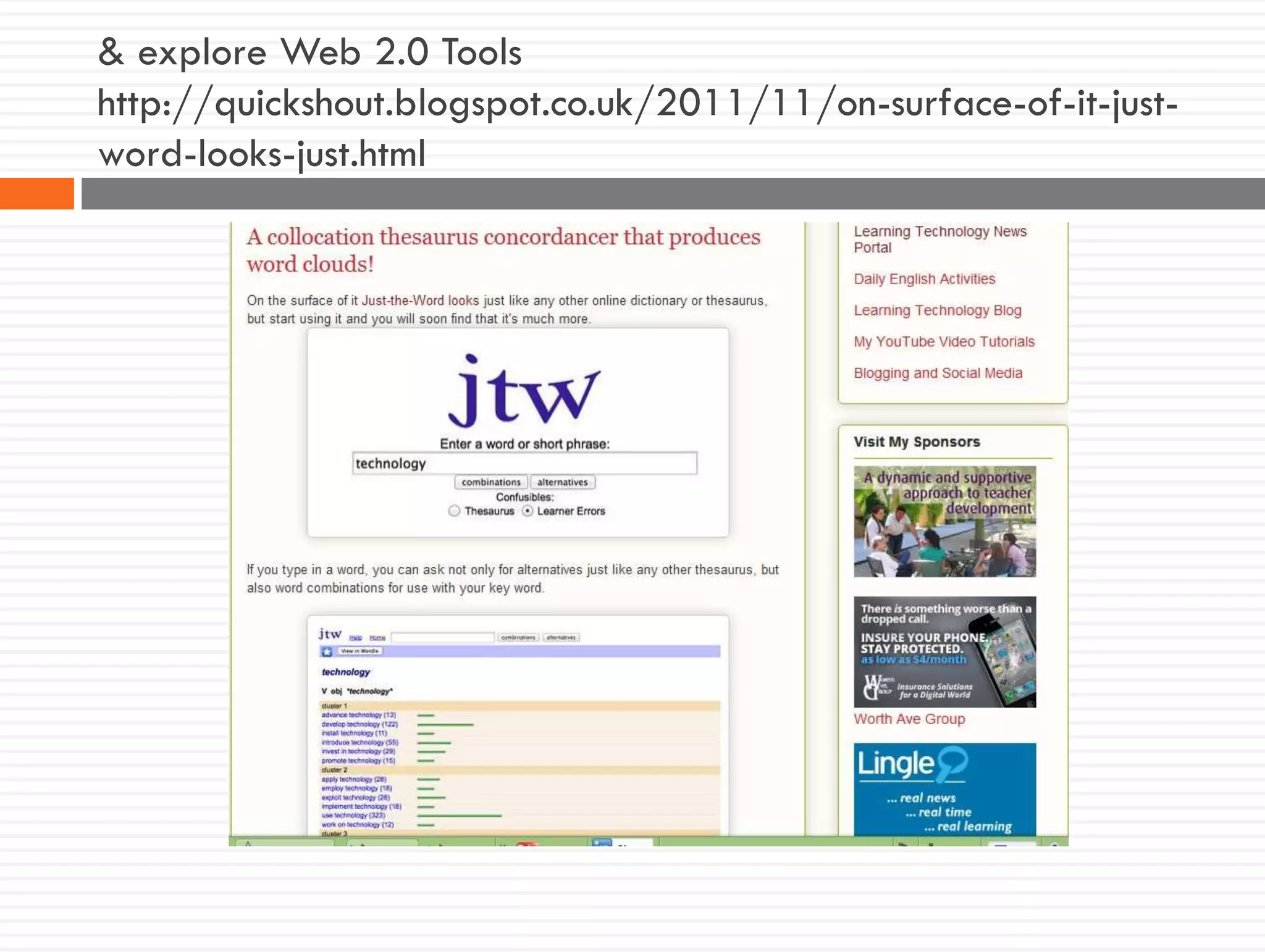
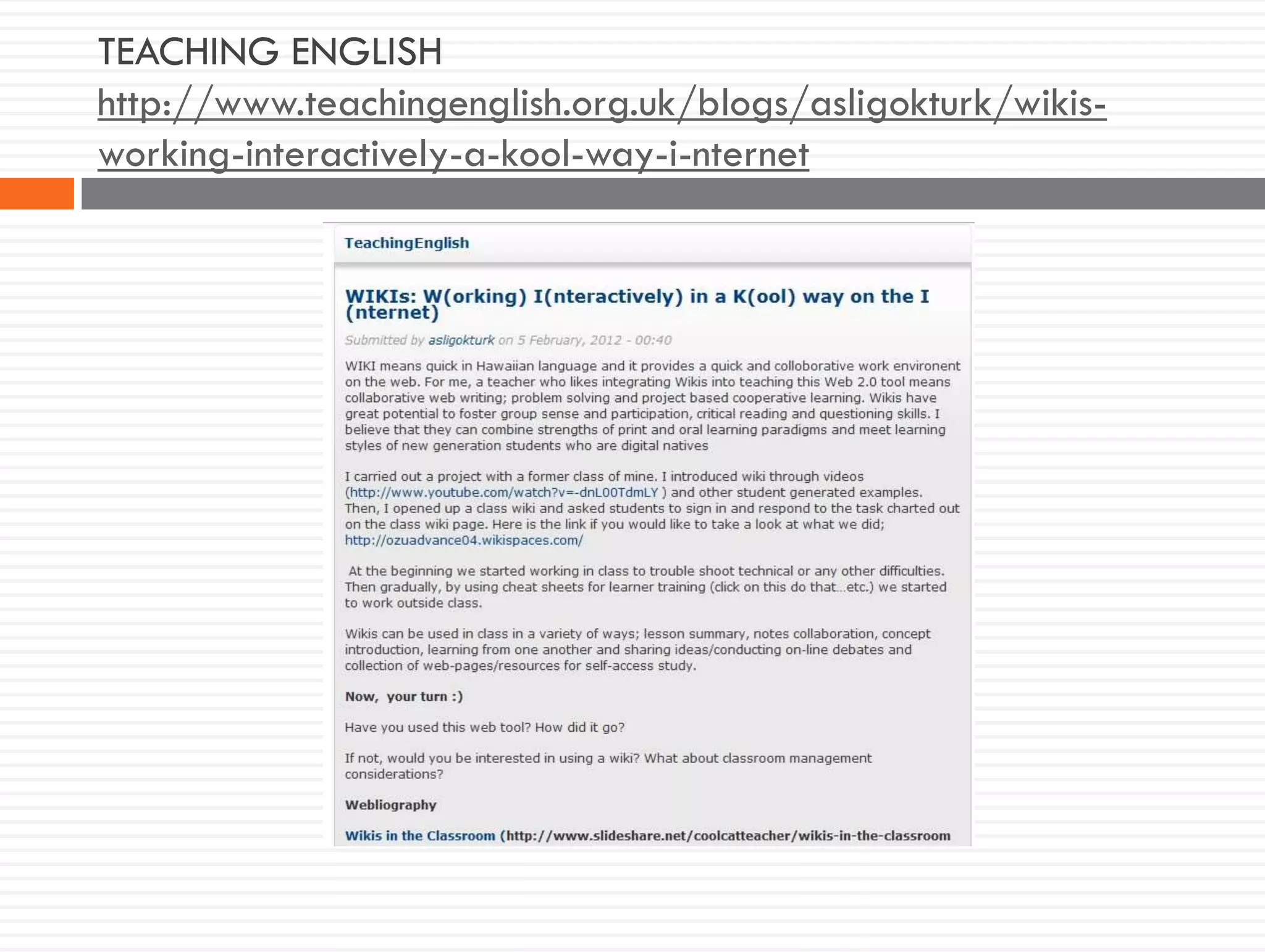
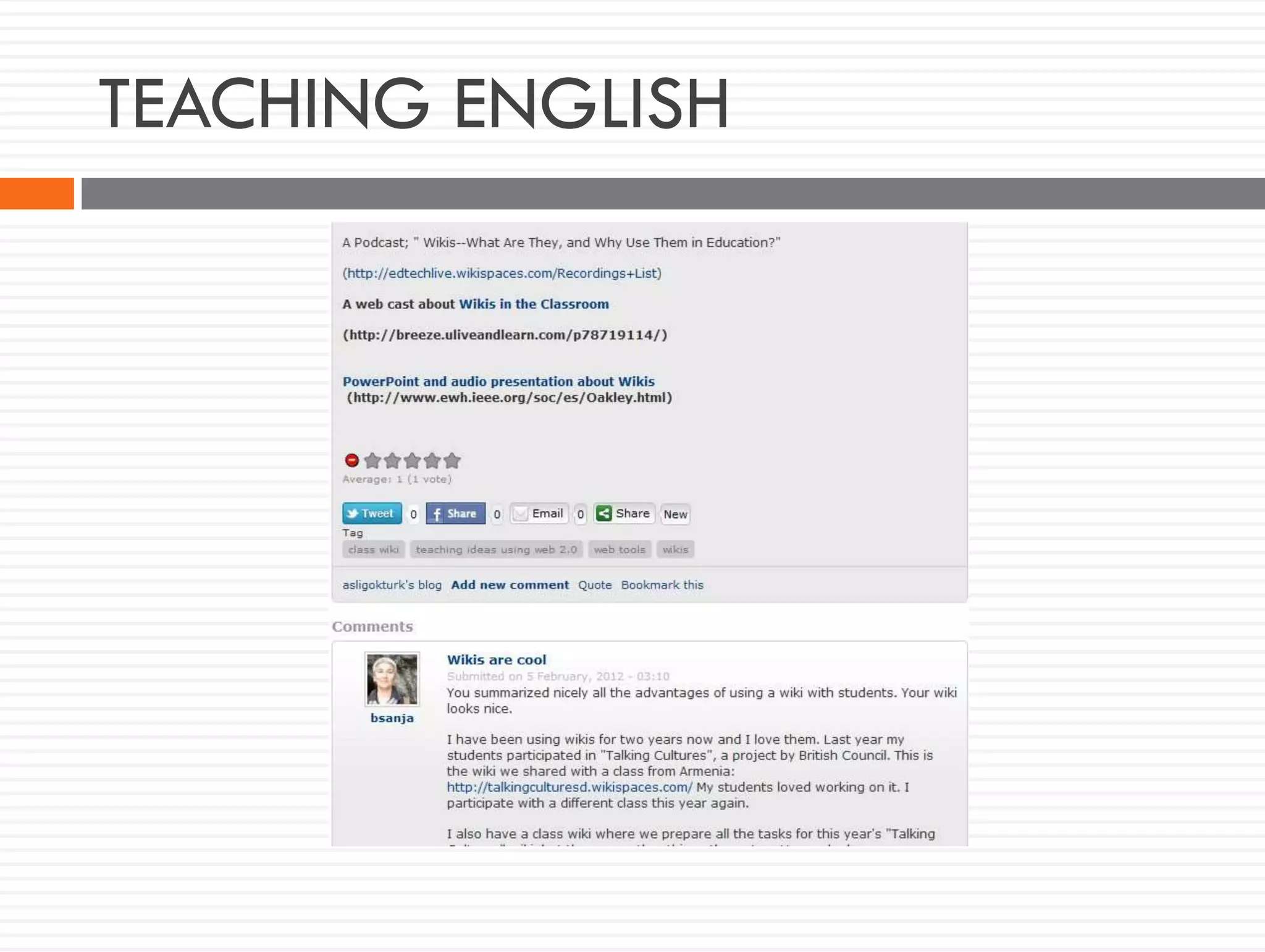
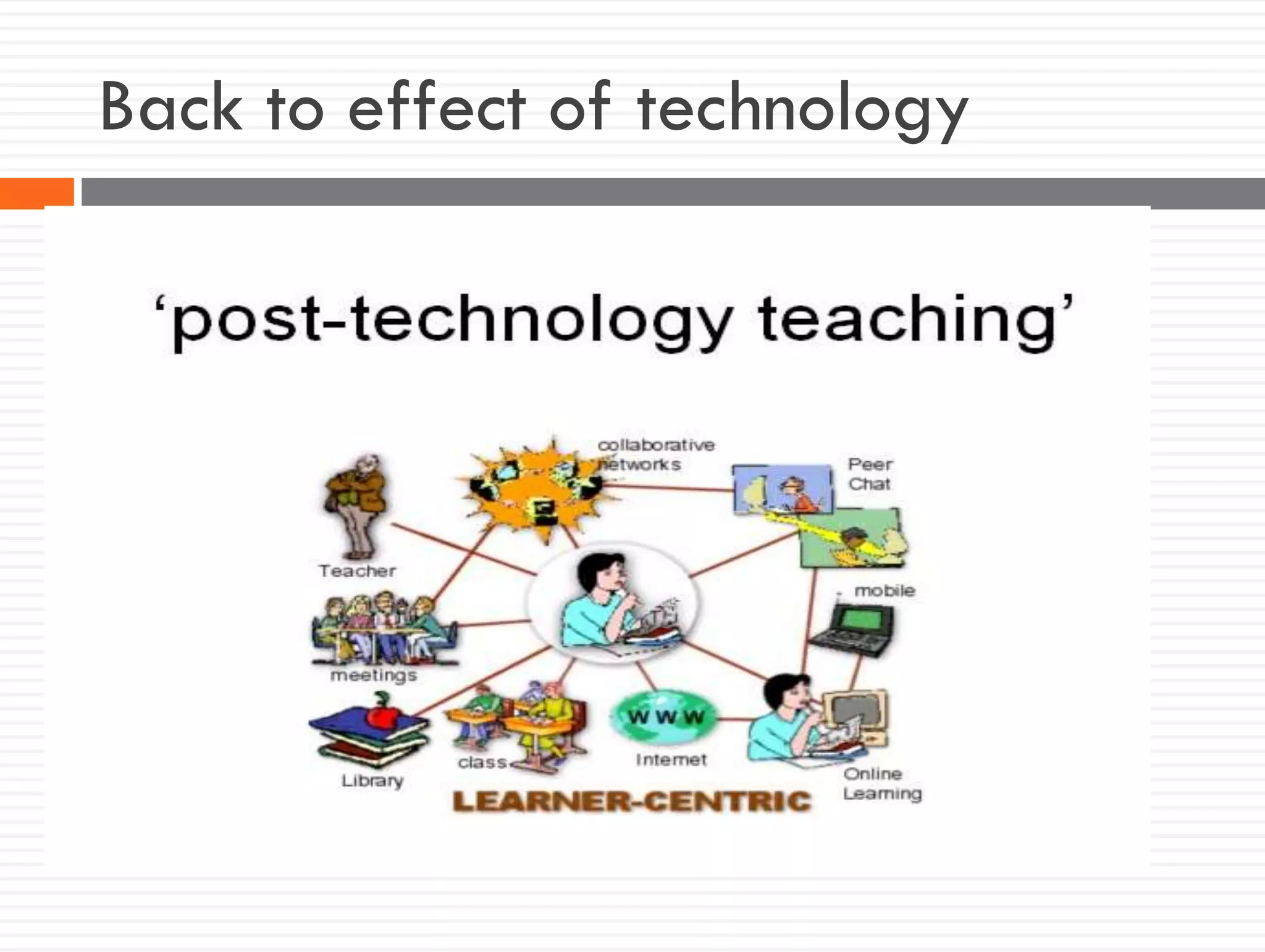
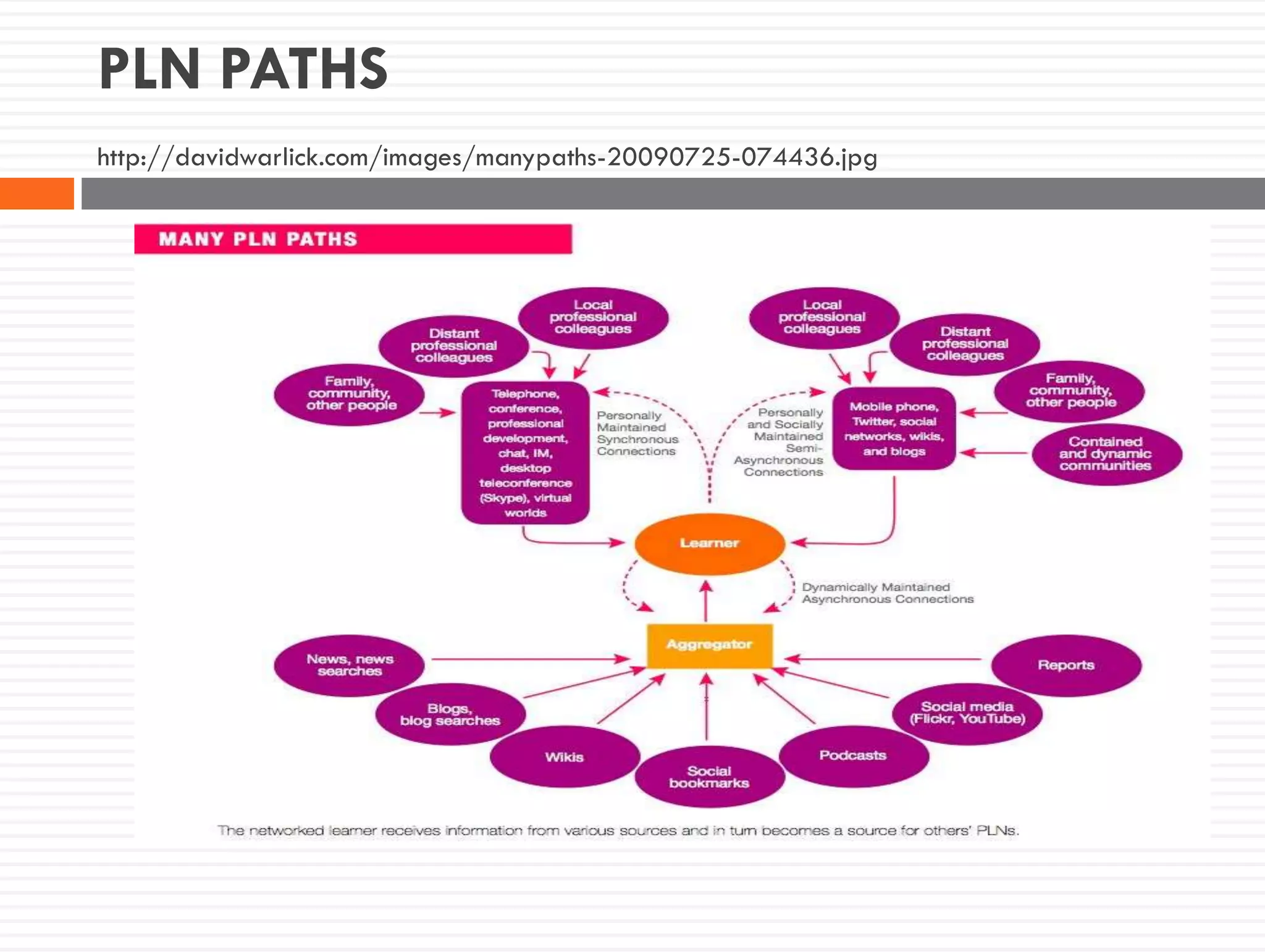
This document discusses teacher knowledge and the impact of technology on teacher professional development. It begins by outlining models of teacher knowledge, including Shulman's categorization of different types of knowledge teachers possess. It then examines how technology may affect teacher knowledge domains, referencing the TPACK framework which describes the interplay between technological, pedagogical and content knowledge. Examples are provided of online communities and tools that can support teacher learning and development, such as blogs, discussion boards and virtual conferences. The document concludes by reflecting on how digital technologies can enhance teachers' vision, motivation, understanding, reflection and community learning.