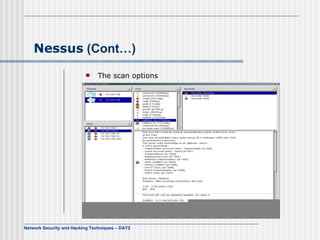
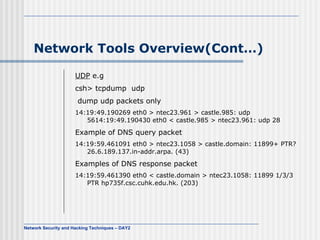
The document discusses various network security tools including TCP/IP headers, tcpdump, ethereal, ntop, MRTG, network scanners like Nmap and Nessus. It provides examples of using these tools to analyze network traffic, scan for open ports, detect operating systems, and monitor network usage.












![Network Tools Overview(Cont…) Address Resolution by using arp ARP command root23:/tmp> /sbin/arp –a ntec93 (192.168.128.93) at on eth0 router.arm.secureindia.net (192.168.64.254) at 00:B0:D0:11:CB:4B [ether] on eth0 castle (192.168.64.230) at 00:B0:D0:22:0A:28 [ether] on eth0 athena (192.168.64.232) at 00:01:02:3A:93:25 [ether] on eth0 PING host root23:/tmp> ping -c 2 ntec21 PING ntec21 (192.168.64.21) from 192.168.64.23 : 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from ntec21 (192.168.64.21):icmp_seq=0 ttl=255 time=0.3 ms 64 bytes from ntec21 (192.168.64.21): icmp_seq=1 ttl=255 time=0.2 ms --- ntec21 ping statistics --- 2 packets transmitted, 2 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 0.2/0.2/0.3 ms](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day2-090721102652-phpapp01/85/Day2-13-320.jpg)
![Network Tools Overview(Cont…) root23:/tmp> arp –a ntec93 (192.168.128.93) at on eth0 rou.secureindia.net (192.168.64.254) at 00:B0:D0:11:CB:4B [ether] on eth0 castle (192.168.64.230) at 00:B0:D0:22:0A:28 [ether] on eth0 ntec21 (192.168.64.21) at 00:D0:09:4E:46:06 [ether] on eth0 athena (192.168.64.232) at 00:01:02:3A:93:25 [ether] on eth0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day2-090721102652-phpapp01/85/Day2-14-320.jpg)

![Network Tools Overview(Cont…) Example of traceroute root# traceroute jksresearch.net traceroute to vsnl.com (202.54.1.73), 30 hops max, 38 byte packet Tracing the route to jksresearch.net (202.71.128.194) 1 telehouse3-telehouse1-100.1anetworks.net (193.243.177.10) 0 msec 0 msec 0 msec 2 195.66.224.166 [AS 5459] 0 msec 4 msec 0 msec 3 i-3-3.hhtstcbr01.net.reach.com (202.84.143.130) [AS 4637] 244 msec 248 msec 244 msec 4 i-1-1-0.hhtstcar02.net.reach.com (207.176.96.178) [AS 4637] 244 msec 244 msec 248 msec 5 202.40.142.138 [AS 4637] 368 msec 384 msec 368 msec 6 202.41.239.19 [AS 4637] 368 msec 388 msec 372 msec 7 202.41.232.10 [AS 4637] 492 msec 528 msec 512 msec 8 jksresearch.net (202.71.128.194) [AS 17447] 388 msec 384 msec 376 msec](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day2-090721102652-phpapp01/85/Day2-16-320.jpg)
















![NMAP (Cont…) Stealth Scanning # nmap -sS 192.168.7.7 Starting nmap V. 2.12 by Fyodor ( [email_address] , www.insecure.org/nmap/)Interesting ports on saturnlink.nac.net (192.168.7.7): Port State Protocol Service 21 open tcp ftp 25 open tcp smtp 53 open tcp domain 80 open tcp http Nmap run completed -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 1 second OS Fingerprinting # nmap -sS -O 192.168.7.12 Starting nmap V. 2.12 by Fyodor ( [email_address] , www.insecure.org/nmap/)Interesting ports on comet (192.168.7.12): Port State Protocol Service 7 open tcp echo 9 open tcp discard 13 open tcp daytime 19 open tcp chargen 21 open tcp ftp ... Remote operating system guess: Solaris 2.6 - 2.7 Nmap run completed -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 5 seconds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day2-090721102652-phpapp01/85/Day2-34-320.jpg)