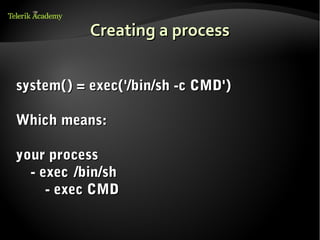
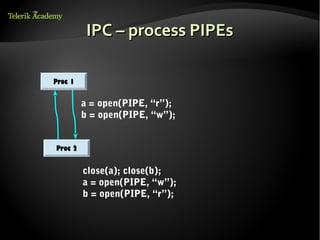
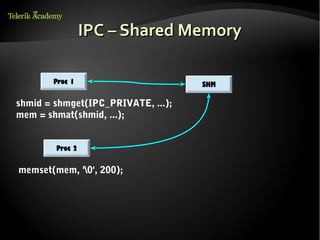
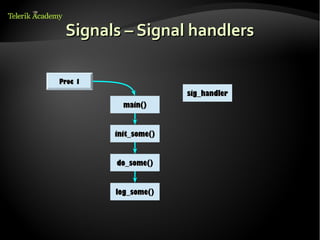
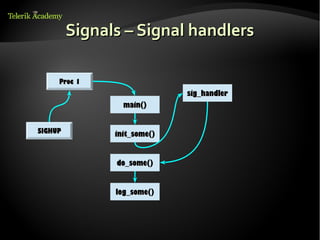
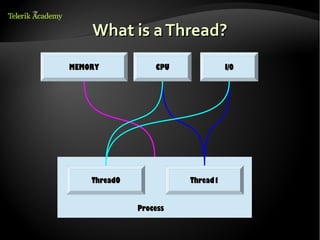
This document discusses processes and threads. It defines a process as a running program with a single flow of execution, while a thread is a flow of execution within a process. It describes how processes are created using fork and exec functions in Linux. It also discusses different types of processes like foreground, background, and daemon processes. Finally, it covers various inter-process communication (IPC) techniques like pipes, shared memory, message queues, semaphores, and signals that processes can use to communicate with each other.
![6 – Processes
and Threads
Borislav Varadinov
Marian Marinov
System
CEO of 1H Ltd.
Administrator
mm@1h.com
bobi [ at ] itp.bg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-processesandthreads-130418040541-phpapp02/85/6-processes-and-threads-1-320.jpg)






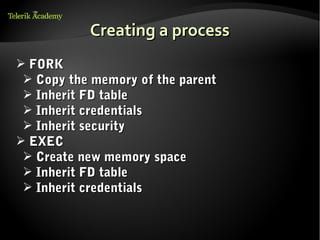





![Creating a process
EXEC functions
int execl(const char *path, const char *arg, ...);
int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg, ...);
int execle(const char *path, const char *arg,
..., char * const envp[]);
int execv(const char *path, char *const argv[]);
int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]);
int execvpe(const char *file, char *const argv[],
char *const envp[]);
Exec functions does not return](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-processesandthreads-130418040541-phpapp02/85/6-processes-and-threads-16-320.jpg)