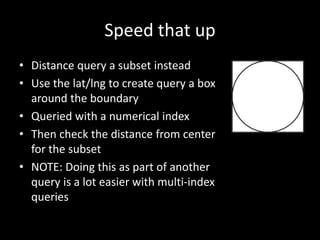
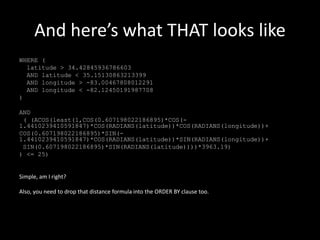
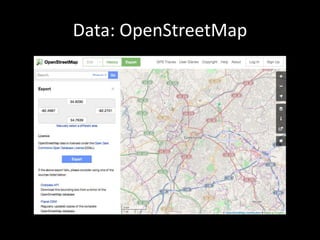
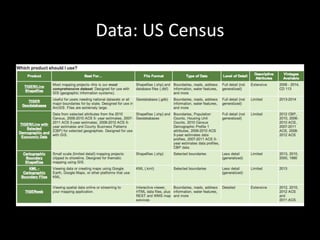
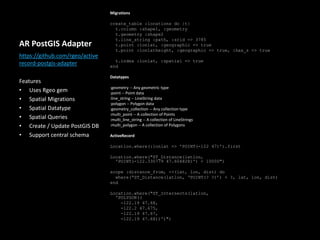
This document introduces PostGIS, an extension to PostgreSQL that adds support for geographic objects allowing location queries to be run in SQL. It discusses geospatial data types and functions in PostGIS for working with spatial features like points, lines, polygons, and rasters. PostGIS allows importing and exporting geospatial data, integration with GIS software, and access to open mapping data sources. It also covers spatial queries and analysis in PostGIS using functions for distance, containment, intersections and more. Additional topics mentioned include pgRouting for routing/navigation, generating maps/images from PostGIS data, and real-world use cases.