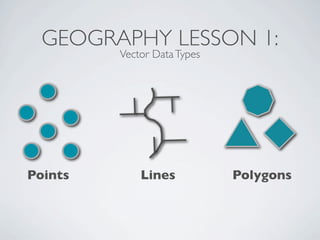
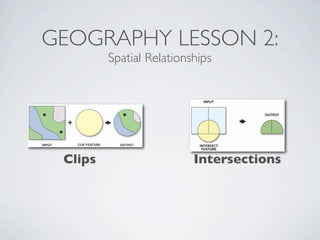
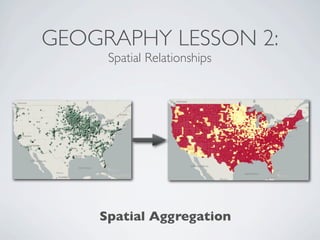
This document provides an introduction to geospatial Ruby libraries. It begins with three geography lessons: vector data types and OGC simple features, spatial relationships, and spatial reference systems. It then discusses several geospatial Ruby libraries including GEOS, GeoRuby, RGeo, and spatial database adapters. It also covers location-based APIs and services like Twitter, Instagram, Yelp, and Fusion Tables that can be used to generate geospatial data. Finally, it discusses the GeoCommons gem and platform for geospatial data storage, analysis, and visualization.



























![RUBY GEOCODER
http://www.rubygeocoder.com/
require ‘geocoder’
# look up coordinates of some location
Geocoder.coordinates("25 Main St, Cooperstown, NY")
=> [42.700149, -74.922767]
# distance between Eiffel Tower and Empire State Building
Geocoder::Calculations.distance_between([47.858205,2.294359],
[40.748433,-73.985655])
=> 3619.77359999382
# find the geographic coordinates for an IP address
Geocoder.coordinates("71.166.236.36")
=> [38.6485, -77.3108]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/osconjuly2011-110801095618-phpapp01/85/OSCON-july-2011-31-320.jpg)




![MONGODB
# Spatial indexes / queries
coll.create_index([["loc", Mongo::GEO2D]])
coll.find({"loc" => {"$near" => [50, 50]}}, {:limit => 20}).each
do |p|
puts p.inspect
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/osconjuly2011-110801095618-phpapp01/85/OSCON-july-2011-36-320.jpg)
![MONGODB
box = [[40.73083, -73.99756], [40.741404, -73.988135]]
coll.find({"loc" : {"$within" : {"$box" : box}}})
center = [50, 50]
radius = 10
coll.find({"loc" : {"$within" : {"$center" : [center, radius]}}})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/osconjuly2011-110801095618-phpapp01/85/OSCON-july-2011-37-320.jpg)







![YELP!
# a location-based search for ice cream or donut shops in SF
request = Yelp::Review::Request::Location.new(
:city => 'San Francisco',
:state => 'CA',
:category => [ 'donuts', 'icecream' ],
:yws_id => 'YOUR_YWSID_HERE')
response = client.search(request)
# a neighborhood name lookup for a geo-location point
request = Yelp::Neighborhood::Request::GeoPoint.new(
:latitude => 37.782093,
:longitude => -122.483230,
:yws_id => 'YOUR_YWSID_HERE')
response = client.search(request)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/osconjuly2011-110801095618-phpapp01/85/OSCON-july-2011-47-320.jpg)









![GEOCOMMONS GEM
getting data...
# get dataset and features
dataset = geoiq.dataset.find(1348)
features = dataset.features
# get features with a custom filter
filtered_features = @dataset.features({"filter[PERIMETER][][max]"
=> 0.3})
bbox_filtered_features = @dataset.features({:bbox =>
'-87.2,33.4,-75.9,38.4'})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/osconjuly2011-110801095618-phpapp01/85/OSCON-july-2011-58-320.jpg)

![GEOCOMMONS
create new datasets...
# Create a new overlay
data = {‘title’ => ‘My Overlay’, ‘attributes’ => {‘attr1’ => ...}}
overlay = @geoiq.dataset.create(data)
# add features to the overlay
features = {features => [{‘type’ => ‘Point’, ‘coordinates’ =>
[0,0]},{...}]}
@geoiq.dataset.update(id, features)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/osconjuly2011-110801095618-phpapp01/85/OSCON-july-2011-60-320.jpg)
![GEOCOMMONS
create new visualizations...
# Create a new map
map = @geoiq.map(:title => "my empty map")
@geoiq_map = map.create
# get a map and it's layers
@map = @geoiq.map.find(239)
layer_titles = @map.layers.map{ |l| l['title']}
# add a dataset to a map as a new layer
@map.add_layer(1466)
#deleting map or dataset
@map.delete
@dataset.delete](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/osconjuly2011-110801095618-phpapp01/85/OSCON-july-2011-61-320.jpg)


