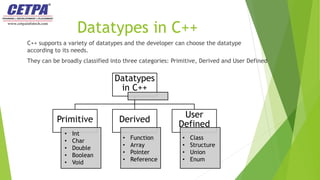
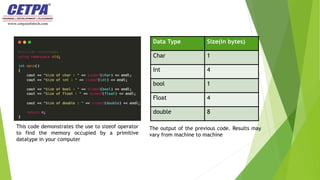
The document provides an overview of C++ and its data types, including primary, derived, and user-defined categories. It explains the definition and importance of data types and discusses various examples of each category, such as integers, arrays, and structures. The conclusion emphasizes the necessity for programmers to understand data types for effective programming and application development.