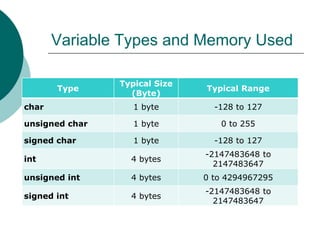
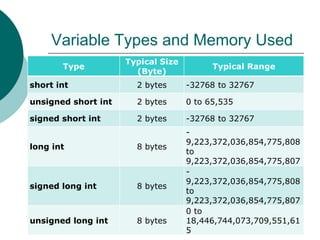
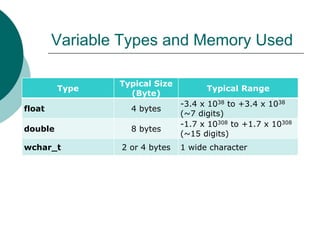
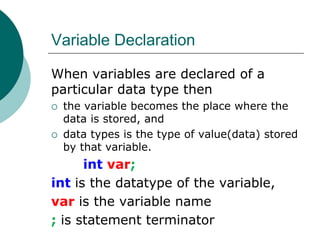
The document provides an introduction to data types in C++ programming language. It discusses the different levels of programming languages, common uses of C/C++, its character set, whitespace characters, and defines what a data type is. It then lists the primitive/built-in data types in C++ like integer, float, boolean, etc. and describes variables types and memory used. It also covers rules for constructing identifiers, variable declaration, and the four types of C/C++ instructions.



![C/C++ Character Set
C/C++ character set comprises of
following characters
A,B,C,….Z
a,b,c,…...z
0,1,2,……9
, . ; : ? ! “ / ‘ | ~
( ) [ ] { } < >
+ - # % _ ^ = & *
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-lec-datatypes-240119115525-cf6f32b0/85/5-Lec-Datatypes-ppt-4-320.jpg)