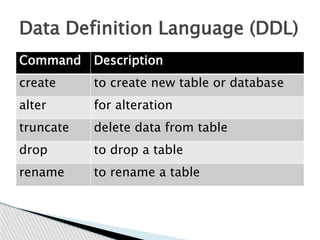
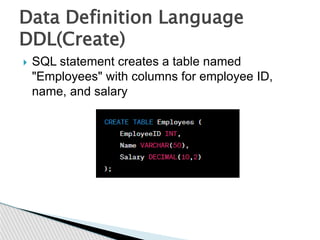
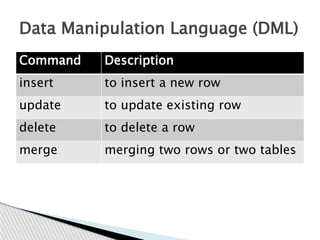
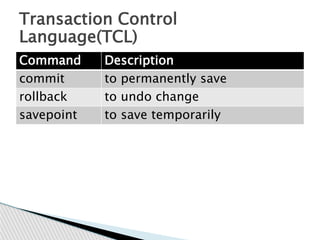
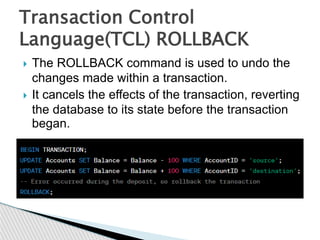
DBMS stands for database management system. It is a software system that allows users to define, create, maintain and control access to a database. Key functions of a DBMS include data storage, organization, modification, retrieval and user administration. Some examples of popular DBMS are MySQL, Oracle and PostgreSQL. DBMS provides advantages like data consistency, security, concurrency and scalability over traditional file-based data storage.